Cells and Their Environment
advertisement

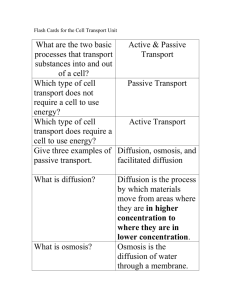
Cells and Their Environment Section 4-1 PASSIVE TRANSPORT Review • What is homeostasis? • Cells maintain homeostasis by controlling the movement of substances across the cell membrane Random Motion and Concentration • Passive transport is movement across the cell membrane that does not require energy • Substances travel from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration • The difference in the concentration of a substance across the space is the concentration gradient • An substance of high concentration will move into a lower concentration until it is in equilibrium or equal Movement of Substances • Particles of a substance will move randomly • If there is a concentration gradient (uneven concentration) then diffusion occurs • Diffusion is the movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to low caused by the random movement of particles Movement of substances cont… • Many molecules and ions dissolve in the cytoplasm and outside of the cell • The concentration of substances is different inside and outside of the cell • Molecules will diffuse, to equalize, and need to pass through the cell membrane • Selectively permeable Movement of substances cont… • The diffusion of molecules across the cell membrane is the simplest type of passive transport Water Diffuses In and Out • Water molecules are small and can diffuse through the cell membrane easily • Osmosis is the diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane Osmosis • Osmosis is a form of passive transport • 3 possibilities of water movement 1. Water moves out 2. Water moves in 3. No net movement Water Moves Out • When water diffuses out of the cell, the cell shrinks • A solution that causes a cell to shrink is hypertonic Water Moves In • When water moves into the cell, the cell swells • A solution that causes a cell to swell because of osmosis is hypotonic No Water Moves • If the outside and inside of the cell have the same concentration of water molecules, then water diffuses in and out at the same rate – No net movement • A solution that produces no change is isotonic Proteins Help Transport Substances • Transport proteins provide passageways for polar molecules and ions to pass through the cell membrane • Each channel only allows a certain substance through Diffusion Through Ion Channels • Sodium Na+, Potassium K+, Ca 2+ and chlorine Cl-, are important in cell functions • Ion channels are a doughnut shaped transport protein for ions like Na+ to pass through Diffusion Through Ion Channels • Some pores are always open, others are closed by gates • The rate of movement of a substance across the membrane is determined by the concentration gradient • An ions movement across the membrane is determined by its charge • The inside of a cell is usually negative Facilitated Diffusion • Carrier proteins carry specific substances across the membrane • They carry substances down their concentration gradient • Facilitated diffusion uses no energy Facilitated Diffusion • Step 1: molecule outside of cell binds to carrier protein • Step 2: carrier protein transports molecule across membrane • Step 3: molecule is released in the cell