AIM: SWBAT explain the overall reaction of photosynthesis and
advertisement

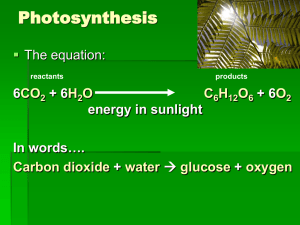
AIM: SWBAT explain the overall reaction of photosynthesis and describe the light reactions in detail Please Do Now: Explain specifically where in the cell chlorophyll is found Agenda Do Now Annotate article Begin notes on light reactions of photosynthesis Reminder Homeworks are due today Please put them in the bucket on your way out Annotating In this class, we will tackle the reading of some upper level texts To make this process more useful, I have a system of annotation I want you to follow while you read This should allow you to better understand the point of the article How should I be annotating text in this class? The main scientific claim(s) of the article should be boxed Any quantitative evidence to support the main scientific claim should be underlined and tagged with a pound sign (#) Any quantitative evidence to support the main scientific claim should be underlined and tagged with a star Vocabulary words that you are unfamiliar with should be circled You should write at least two questions that you have about the content in the margins of the page Abbreviated version Main point(s) # Quantitative evidence # Qualitative evidence Unknown vocabulary At least 2 questions should be going in the margins You try You will practice this annotation with a reading on the acidification of the Arctic Ocean Then, as a group, we will go over the article together to see how everybody did What is photosynthesis? The process of creating sugar using the energy in sunlight The sun’s energy is stored in the chemical bonds of the sugar Overall equation: sunlight + CO2 (carbon dioxide) + water (H2O) (oxygen) O2 + glucose (C6H12O6) How does sunlight turn into chemical bonds during photosynthesis? Photosynthesis takes place in two steps: Light Dependent Reactions A complex system of enzymes, membrane proteins, and pigments make ATP from sunlight Light Independent Reactions (Calvin Cylcle) The ATP generated in the LDR is used by enzymes in the Calvin Cycle to combine CO2 with a 5 carbon compound to make glucose H20 O2 CO2 Glucose Step 1: Oxygen Evolving Complex A complex sex of enzymes in the lumen splits water apart, freeing an electron Step 2: Light hits chlorophyll Chlorophyll, embedded in the thylakoid, catches sunlight Step 3: Electron Transport Chain the energy in the sunlight excites the electron to a higher energy state, and it flows through an “electron transport chain” ETC is actually a bunch of proteins in the thylakoid membrane that generates ATP and NADPH and a proton gradient inside the thylakoid Step 4: protons flow the protons flow through a membrane proton (ATP synthase) like a water wheel, generating more ATP Light Reactions EVEN MORE BRIEFLY Sunlight ATP out in Z scheme