Unit 4a-Photosynthesis- Study Outline
advertisement

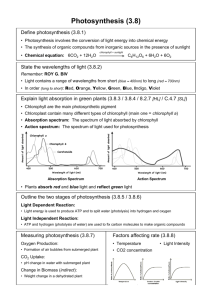
Name____________________________________________ Date_________________ Period________ Honors Living Environment 8th Grade Honors Living Environment Unit 4a (Photosynthesis) Study Outline This handout will serve as a resource to help guide you in studying for the Unit 4 Quest (Photosynthesis). We encourage that you find a study method that works best for you. Use this page as a reference as you review class notes, handouts, quizzes, Castle Learning assignments, etc. In addition, there are excellent resources on the internet that you can use for supplemental review and reinforcement. Visit our teacher webpages for some suggestions on internet sources. As always, come to extra help and to our review sessions if you have any questions. Best of luck! I. II. Nutrition a. Autotroph i. Make own food through process of photosynthesis 1. Takes place in the leaves of plants a. takes place in the chloroplasts (organelle) ii. Need water, carbon dioxide, and sunlight iii. Make glucose (food) and oxygen (waste product) b. Heterotroph i. Get food from environment ii. Ingestiondigestionegestion Absorption of light a. Visible light has many wavelengths i. Different wavelengths are recognized as different colors (ROYGBIV) b. Chloroplasts are green i. Absorbs red and blue light very well ii. Reflects green light 1. Our eyes detect wavelength of green light and our brain processes it as green c. Pigments- absorb certain wavelengths of light and reflect others i. Chlorophyll 1. Chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b ii. Accessory pigments- pigments other than chlorophylls (in much smaller amounts than chlorophyll) 1. Carotenoids 2. Xanthophylls 3. Anthocyanins iii. Chromatography-technique for separating pigments (must know technique) Name____________________________________________ Date_________________ Period________ Honors Living Environment III. Biochemistry of Photosynthesis a. Equation i. Chemical equation 1. Sunlight + 6 CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2 ii. Word equation 1. Sunlight + carbon dioxide + water glucose + oxygen b. Chloroplast i. Outer membrane ii. Inner membrane iii. Thylakoid iv. Grana v. Stroma vi. Lumen c. 2 main stages of photosynthesis i. Light Dependent reactions 1. AKA- light reactions 2. Location-Thylakoid membrane 3. Inputs- sunlight and water 4. Outputs- NADPH & ATP (used in light-independent reactions), O2 (waste product) 5. A more detailed look at light reactions… a. In thylakoid spaces of the grana in the chloroplast. b. Sunlight strikes the chlorophyll contained within the thylakoid spaces which causes electrons to become excited and infused with energy. c. Electrons are transferred down an electron transport chain. d. The energy in the electrons is used to set up a proton gradient across the membrane of the thylakoid spaces. e. Protons flowing back across the thylakoid membrane according to the concentration gradient are harnessed to produce ATP and NADPH (the reduced form of NADP). f. As a by-product of this process, molecules of water are split into molecular hydrogen and oxygen (photolysis). g. The plant needs the hydrogen to produce ATP. h. The oxygen you’re breathing right now is some of that waste product. i. The purpose of the light reaction is to make the usable energy necessary to run the lightindependent reaction. ii. Light-Independent Reactions 1. AKA- dark reactions, calvin cycle, carbon fixation 2. Location- stroma 3. Inputs- NADPH & ATP (from light reactions), CO2 4. Outputs- glucose Name____________________________________________ Date_________________ Period________ Honors Living Environment 5. A more detailed look at dark reactions… a. The reaction takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast b. In the dark reaction, the carbon from carbon dioxide is added to the five-carbon sugar ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) to produce a six-carbon compound. c. This unstable six-carbon sugar is immediately split into two three-carbon molecules, which in a chain reaction using the ATP and NADPH from the light reaction are modified to form glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P). d. The glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate can be synthesized into carbohydrates such as glucose. e. One of the glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate molecules is made into carbohydrates, while the other molecules remain in the Calvin cycle to serve as raw materials for the next round of production. d. Factors that affect photosynthesis (be familiar with relationships for each factor) i. Light intensity ii. Carbon dioxide iii. Temperature iv. Water v. Minerals IV. Plant Adaptations a. Parts of leaf i. Palisade mesophyll ii. Spongy mesophyll iii. Cuticle iv. Stomata v. Guard cells 1. Water regulation a. Stomates open- water leaves plant, CO2 and O2 enter leaf b. Stomates closed- water does not leave, CO2 and O2 cannot enter b. Transport i. Vascular Tissue 1. Xylem- transports water a. One direction (roots to leaves) b. Root hairs c. Root pressure d. Capillary action e. Transpiration f. Transpiration pull 2. Phloem- transports nutrients a. Both directions