Reconstruction PowerPoint - Marion County Public Schools
advertisement
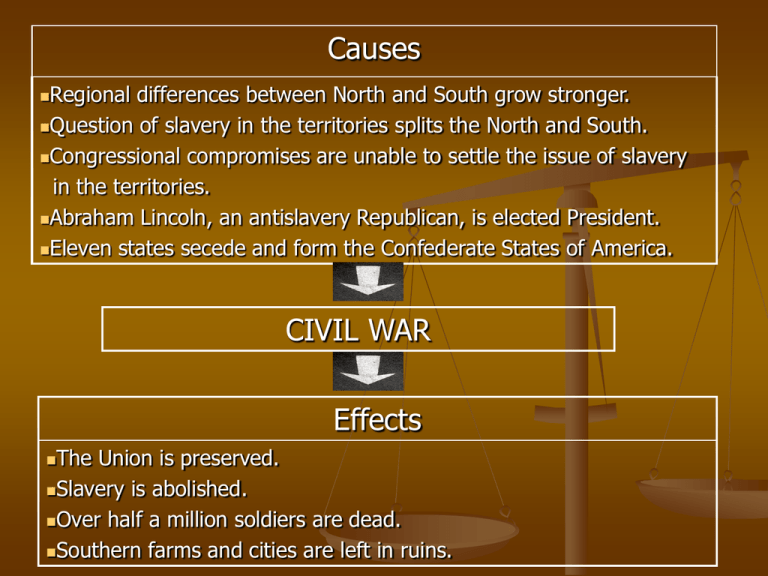
Causes Regional differences between North and South grow stronger. Question of slavery in the territories splits the North and South. Congressional compromises are unable to settle the issue of slavery in the territories. Abraham Lincoln, an antislavery Republican, is elected President. Eleven states secede and form the Confederate States of America. CIVIL WAR Effects The Union is preserved. Slavery is abolished. Over half a million soldiers are dead. Southern farms and cities are left in ruins. Plans for Reconstruction: 1865-1877 Problems of Reconstruction Punishment of the Confederate states and leaders. How to readmit those seceded states to the Union. Jobs, homes, etc. for the freed slaves. Lincoln’s Plan (before the end of the Civil War) Southern states did not secede because it is not constitutionally possible. Give amnesty to Confederates. Any state could send representatives back to Congress if 10% of 1860 voters pledged their oath to the Union. Establish the Freedman’s Bureau to assist former slaves and poor whites in the South Wade-Davis Bill (1864): A Proposal of the Radical Republicans Congress is responsible for Reconstruction because territories are seeking admission in the Union A state government would be accepted back into the Union if more than ½ of 1860 voters pledge that they never supported the Confederacy Andrew Johnson’s Plan States must declare their secession illegal. States must swear allegiance to the Union. States must promise not to pay back Confederate debts. States must ratify the 13th Amendment. By December 1865, all states but Texas had been readmitted. Reaction to Johnson’s Reconstruction Plan “Andrew Johnson’s Reconstruction and How it Works” --Thomas Nast, Cartoonist September 1, 1866, pages 552, 553 Harper’s Weekly Johnson’s Relationship with Congress worsens The South saw Johnson as a traitor; the North saw him as a Southerner. The Radical Republicans were infuriated by Johnson’s readmission of the Southern states. Johnson toured the country to campaign against the Radical Republicans in the Congressional Elections of 1866. The Turning Point in the Control of Reconstruction: The Congressional Elections of 1866 1866 Congressional Elections Despite Johnson’s campaigns against them, the Radical Republicans gained a 2/3 majority in Congress. Why is a 2/3 majority in Congress important? First Reconstruction Act Divided the seceded states into five military districts. Military tribunals replaced civilian courts. States required to give the AfricanAmericans the right to vote. States must ratify the 14th Amendment before rejoining the Union. Reaction to the First Reconstruction Acts Cartoon Caption: “We regard the Reconstruction Acts (so called) of Congress as usurpations, and unconstitutional, revolutionary, and void.”—Democratic Platform September 5, 1868, page 568, Harper’s Weekly Reaction to the First Reconstruction Act Johnson vetoed the bill, but Congress overrode the veto with their 2/3 majority. By the summer 1867, troops were sent to the South to maintain order. In 1868, the Radical Republicans find a way to impeach Andrew Johnson for not enforcing the First Reconstruction Act. Impeachment of Andrew Johnson Radical Republicans passed the Tenure of Office Act (said President couldn’t remove a cabinet member that he’d appointed without 2/3 approval of the Senate) Johnson fired Edwin Stanton, Secretary of War and radical sympathizer February 1868—found not guilty 35-19 (1 vote shy of 2/3 majority)—Stanton appointed by Lincoln, not Johnson Effects of Reconstruction on African-Americans Thomas Nast in Harper's Weekly, 1874. Radical Reconstruction in the South 1867-1877 Plantation work—whites have the land, but no workers, African-Americans want work, but have no land Sharecroppers and tenant farmers emerge More African-Americans participate in govt.—more blacks than whites registered to vote in the south Scalawags Carpetbaggers Southerners sought to minimize Reconstruction through: the Black Codes segregation the KKK poll taxes literacy tests Black Codes Could marry, own property, sue in court, go to school Could not serve on juries, marry whites, testify against whites, break curfew, travel without permit, start own business Ku Klux Klan in the 1870s Known to burn churches and commit murder Pres. Grant passed the Force Acts in 187071 Federal supervision of elections in the South Pres. could declare martial law where the Klan was active (Grant sent troops to 9 S.C. counties in 1871) Grant’s corrupt administration 1873-Grant’s Sec. of Treasury caught accepting kickbacks and resigns Whiskey Ring—238 IRS officials indicted for keeping revenue taxes collected on whiskey—Grant’s personal secretary also indicted Election of 1876 Republican Candidate—Rutherford B. Hayes Democratic Candidate—Samuel J. Tilden Tilden had more popular votes, but was one electoral vote shy of the majority to be elected President 1876 Election Scandal 20 votes in dispute (1 OR, 19 in FL, LA, SC) Democrats scared away black voters Radical Republicans threw out Dem. Ballots and made up their own returns Both sets of ballots sent to Congress The Decision Democrats made a deal—Hayes becomes President if 1) troops withdrawn from FL, LA, SC 2) federal $ for building railroads and improving waterways 3) a conservative Southern cabinet member added Hardships on Southern AfricanAmericans by 1900 Voting Restrictions (1896 voters-130,334; 1904 voters-1,342) Discrimination went around 14th & 15th Amendments Literacy tests Poll taxes Grandfather Clause Segregation Laws—Jim Crow Laws








