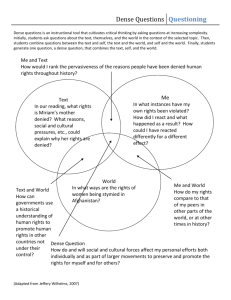
Population Close Reading
advertisement

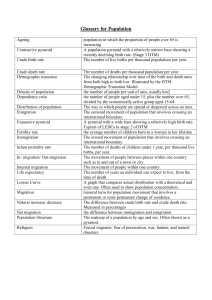
Chapter 2: Population Where in the world do people live and why? Demography is the study of __________ Population density is the number of people in a country relative to the country’s __________ Arithmetic population density is what this number is called No country has an __________ distributed population Physiologic Population Density Physiological population density is defined as the # of people per unit area of __________ land Arable means farmable Population distribution People are not distributed __________ across the world China and India are home to one third of the world’s population, but there are still places like the __________ where next to no one lives. Population distributions are __________ of locations of Earth where people live at varying scales Populations are often represented on __________ maps, one dot = however many people World population distribution and density Since the beginning of history, __________ have been spread out all over the world People gathered in areas where they could grow __________ Cities began in __________ areas Advances of __________ and __________ have changed this pattern East Asia This is the place with the largest dense population South Asia This is the place with the second largest dense population Europe This is the place with the third largest dense population North America __________ describes what the band from DC to Boston is – an agglomeration of people Chapter 2: Population Why do populations rise or fall in particular places? In the __________’s Paul Erlich published a book that frightened everyone His concepts were based off of Thomas __________’ theories from the 1800’s Malthus basically said that the world population was growing __________, while the world food production was only growing __________ Malthus was not entirely correct, he did not predict the use of __________, improved strains of __________, and __________ Population growth at World, Regional, National, and Local scales Demographers use different formulas and techniques depending on what scenario they are evaluating They use many formulas, but the most shocking is the doubling time, it really shows how fast things can add up! This also helps to show when population__________ occur Population growth at regional and national scales This basically shows how more developed countries have lower growth rates than less developed countries Population growth at the local scale This section shows how growth rates can differ within countries The demographic transition The high growth rates in __________ countries is not permanent These countries are just going through what more developed countries went through 300 years ago; they are a little behind due to the slowing effects of colonization Rate of natural __________ is the number of births – the number of deaths Crude birth rate is the number of __________ per 1000 people Crude death rate is the number of __________ per 1000 people The slowdown of the population growth in MDCs is called the Demographic __________ Chapter 2: Population This is how it works: Stage 1 is low growth, roughly 18th century Stage 2 is increasing growth, 19th century Stage 3 is population explosion, 20th century Stage 4 is decreasing growth, 21st century Stage 5 is declining population, in the future Why does population composition matter? Population composition is the percentages of an area that are men, women, and age Population __________ represent this data A Christmas tree-like shaped pyramid means __________ population growth A more rectangular shaped population pyramid represents a __________ growing population Declining total __________ rates are common in wealthier countries How does the geography of health influence population dynamics? Infant mortality Infant mortality rate is how many infants die per __________ Children and infants are very susceptible to diseases, so the country whose children get the least sick or die have the highest health standards How do governments affect population change? Communist governments used to lead __________ population policies Some govts lead __________ population policies The majority of today’s govts lead __________ population policies, an example being China’s __________ policy