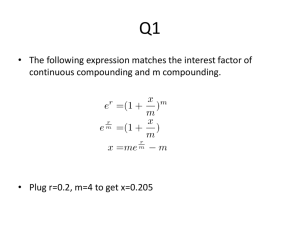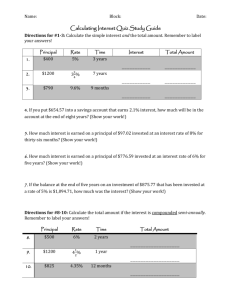
COMPOUND INTEREST AND
PRESENT VALUE
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Chapter
Nineteen
Copyright © 2014 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
LEARNING UNIT OBJECTIVES
LU 19-1: Compound Interest (Future Value) – The Big Picture
1.
Compare simple interest with compound interest.
2.
Calculate the compound amount and interest manually, using
algebraic formulas and with a financial calculator.
3.
Explain and compute the effective rate (APY).
LU 19-2: Present Value -- The Big Picture
1.
Compare present value (PV) with compound interest (FV).
2.
Compute present value using algebraic formulas and with a
financial calculator.
3.
Check the present value answer by compounding.
19-2
COMPOUND INTEREST
(FUTURE VALUE)
Compounding –
Compound Interest –
Involves the calculation of interest
periodically over the life of the loan or
investment
The interest on the principal plus the
interest of prior periods
Future Value (compound amount) –
Present Value –
The final amount of the loan or
investment at the end of the last
period
The value of a
loan or investment today
19-3
COMPOUNDING TERMS
Compounding Periods
Interest Calculated
Compounding Annually
Once a year
Compounding Semiannually
Every 6 months
Compounding Quarterly
Every 3 months
Compounding Monthly
Every month
Compounding Daily
Every day
19-4
FUTURE VALUE OF $1 AT 8% FOR FOUR
PERIODS (FIGURE 19.1)
Compounding goes from present value to future value
$5.00
$4.50
$4.00
$3.50
$3.00
$2.50
$2.00
$1.50
$1.00
$0.50
$0.00
Future
Value
Present
value
$1.00
0
After 1
period,
$1 is
worth
$1.08
After 2
periods,
$1 is
worth
$1.17
$1.08
$1.1664
1
2
Number of periods
After 3
periods,
$1 is
worth
$1.26
After 4
periods,
$1 is
worth
$1.36
$1.2597
$1.3605
3
4
19-5
TOOLS FOR CALCULATING
COMPOUND INTEREST
Number of periods (N)
Number of years multiplied by
the number of times the
interest is compounded per
year
Rate for each period (I)
Annual interest rate divided by
the number of times the
interest is compounded per year
If you compounded $1 for 4 years at 8% annually,
semiannually, or quarterly, what is N and I?
Periods
Rate
Annually:
4x1=4
Annually:
8% ÷ 1 = 8%
Semiannually:
4x2=8
Semiannually:
8% ÷ 2 = 4%
Quarterly:
4 x 4 = 16
Quarterly:
8% ÷ 4 = 2%
19-6
SIMPLE VERSUS COMPOUND
INTEREST
Simple
Compounded
Bill Smith deposited $80 in a savings
account for 4 years at an annual
interest rate of 8%. What is Bill’s
simple interest and maturity value?
I=PxRxT
I = $80 x .08 x 4
I = $25.60
MV = $80 + $25.60
MV = $105.60
Bill Smith deposited $80 in a savings
account for 4 years at an annual
interest rate of 8%. What is Bill’s
interest and compounded amount?
Year 1
Year 2
Year 3
Year 4
$
80.00 $ 86.40 $ 93.31 $ 100.77
x .08
x .08
x .08
x .08
Interest
$
6.40 $
6.91 $
7.46 $
8.06
Beg. bal
80.00
86.40
93.31
100.77
End of year $
86.40 $ 93.31 $ 100.77 $ 108.83
Interest: $108.83 -- $80.00 = $28.83
19-7
CALCULATING COMPOUND AMOUNT
USING FORMULA
Step 1. Find the periods n: Years multiplied by number of times
interest is compounded in 1 year.
Step 2. Find the rate i: Annual rate divided by number of times
interest is compounded in 1 year.
Step 3. Plug the PV amount, n, and i into the following formula: FV = PV(1 + i)n
Step 4. Solve. This gives the compound amount.
19-8
CALCULATING COMPOUND AMOUNT
USING THE COMPOUND INTEREST FORMULA
Bill wants to know the value of $80 in 4 years at 8%. He begins by identifying
the PV, n, and i:
PV = $80
n = 4 (4 years x 1 compounding period per year)
i = 8% (8% divided by 1 compounding period)
Calculator keystrokes for this problem are:
(1 + .08) yx 4 x 80 = $108.84
19-9
CALCULATING COMPOUND AMOUNT
USING YOUR TI BA II PLUS CALCULATOR
Remember to clear the TVM
each time you work with new
data: 2ND CLR TVM
To solve the future value of $80 at 8% compounded annually
for 4 years, using your calculator, follow these steps:
Step 1: Input 4 and then press N.
Step 2: Input 8 and then press I/Y.
Step 3: Input 80, press +/- and then press PV.
Step 4: Input 0, and then press PMT.
Step 5: Press CPT FV = 108.84
19-10
COMPOUNDING (FV)
FIGURE 19.2
19-11
CALCULATING THE COMPOUND
INTEREST
FV – PV = Compound interest
$108.84 - $80.00 = $28.84
19-12
NOMINAL VERSUS EFFECTIVE RATES
ANNUAL PERCENTAGE YIELD (APY)
Nominal Rate (stated rate) –
The rate on which the bank calculates interest
Effective rate (APY)4 = Interest for 1 year
Principal
19-13
CALCULATING EFFECTIVE RATE (APY)
19-14
NOMINAL AND EFFECTIVE RATES (APY)
OF INTEREST COMPARED (FIGURE 19.3)
19-15
PRESENT VALUE OF $1 AT
8% FOR FOUR PERIODS (FIGURE 19.4)
19-16
RELATIONSHIP OF COMPOUNDING (FV) TO
PRESENT VALUE (PV) – BILL SMITH EXAMPLE
19-17
CALCULATING PRESENT VALUE
USING FORMULA
Step 1. Find the periods n: Years multiplied by number of times
interest is compounded in 1 year.
Step 2. Find the rate i: Annual rate divided by number of times
interest is compounded in 1 year.
Step 3. Plug the FV amount, n, and i into the following formula:
PV = FV
(1 + i)n
Step 4. Solve. This gives the present value.
19-18
CALCULATING PRESENT VALUE
USING FORMULA
Since Bill knows the bike will cost $108.84 in the
future, he completes the following calculation:
PV = $108.84/(1 + .08)4 = $80.00
Calculator keystrokes for this problem are:
(1 + .08) yx 4 = STO 1 108.84 ÷ RCL 1 = $80.00
19-19
CALCULATING PRESENT VALUE
USING A FINANCIAL CALCULATOR
Remember to clear the TVM
each time you work with new
data: 2ND CLR TVM
Since Bill knows the bike will cost $108.84 in the
future, he completes the following calculation:
Step 1: Input 4 and then press N.
Step 2: Input 8 and then press I/Y.
Step 3: Input 108.84 and then press FV.
Step 4: Input 0 and then press PMT.
Step 5: Press CPT PV = -80.00
19-20
COMPARING COMPOUND INTEREST (FV)
WITH PRESENT VALUE (PV)
19-21
COMPARING COMPOUND INTEREST
(FV) WITH PRESENT VALUE (PV)
19-22
PROBLEM 19-11
Lynn Ally, owner of a local Subway shop, loaned $40,000 to Pete Hall to help
him open a Subway franchise. Pete plans to repay Lynn at the end of 8 years
with 6% interest compounded semiannually. How much will Lynn receive at
the end of 8 years? LU 19-1(2)
Solution:
8 years x 2 = 16 periods
6% = 3%
2
$40,000 x (1 = .03)16 = $64,188.26
Step 1: Input 16 and then press N.
Step 2: Input 6/2 = and then press I/Y.
Step 3: Input 40,000 +/- and then press PV.
Step 4: Input 0 and then press PMT.
Step 5: Press CPT FV = 64,188.26.
19-23
PROBLEM 19-13
Melvin Indecision has difficulty deciding whether to put his savings in Mystic Bank
or Four Rivers Bank. Mystic offers 10% interest compounded semiannually. Four
Rivers offers 8% interest compounded quarterly. Melvin has $10,000
to invest. He expects to withdraw the money at the end of 4 years. Which bank
gives Melvin the better deal? Check your answer. LU 19-1(2)
Solution:
Mystic
Four Rivers
4 years x 2 = 8 periods
4 years x 4 = 16 periods
10% = 5%
2
FV = $10,000(1 + .05)8 = $14,774.55
$14,774.55 - $10,000 = $4,774.55
8% = 2%
4
FV = $10,000(1 +.02)16 = $13,727.86
$13,727.86 - $10,000 = $3727.86
19-24
PROBLEM 19-14
Lee Holmes deposited $15,000 in a new savings account at 9% interest compounded
semiannually. At the beginning of year 4, Lee deposits an additional $40,000 at 9%
interest compounded semiannually. At the end of 6 years, what is the balance in Lee’s
account? LU 19-1(2)
Solution:
3 years x 2 = 6 periods
9%
2 = 4.5%
$15,000(1 + .045)6 = $19,533.90
+ 40,000.00
$ 59,533.90
$59,533.90(1 + .045)6 = $77,528.62
19-25
PROBLEM 19-23
Paul Havlik promised his grandson Jamie that he would give him $6,000 8 years
from today for graduating from high school. Assume money is worth 6% interest
compounded semiannually. What is the present value of this $6,000?
LU 19-2(2)
Solution:
8 years x 2 = 16 periods
6% = 3%
2
Step 1: Input 16 and then press N.
Step 2: Input 6/2 = and then press I/Y.
Step 3: Input 6000 and then press FV.
Step 4: Input 0 and then press PMT.
Step 5: Press CPT PV = -3739.00
$6,000(1 + .03)16 = $3,739.00
19-26