Ch. 7 Atoms and starlight
advertisement

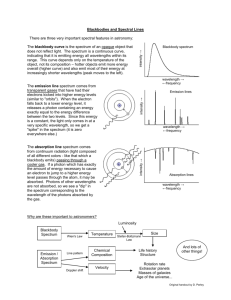
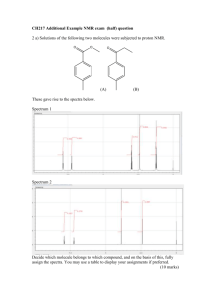
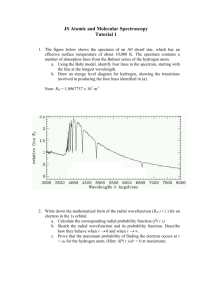
Chapter 7: Atoms and starlight Not all of these light sources emit the same kind of light Fluorescent light The Sun! Incandescent Bulb Halogen bulb Each part of the EM spectrum provides us with different information. If you pass white light through a prism, it separates into different colors. R O Y G B I V spectrum What can we learn by analyzing starlight? • A star’s temperature • Its composition An atom consists of a small, dense nucleus (containing protons and neutrons) surrounded by electrons - Model Proposed by Niels Bohr 1913 Atoms are mostly empty space So if a nucleus the size of an orange (10 cm) was located at the center of the football field, where would the electron be? End Zone? Grandstands? On Campus? In San Jose? Nucleus Photons (light-waves) are emitted from an atom when an electron moves from a higher energy level to a lower energy level Nucleus Photons (light-waves) can also be absorbed by an atom when an electron moves from a lower energy level to a higher energy level Nucleus Each chemical element produces its own unique set of spectral lines when it is excited Three types of spectra prism Hot/Dense Energy Source Continuous Spectrum prism Hot low density cloud of Gas Emission Line Spectrum prism Hot/Dense Energy Source Cooler low density cloud of Gas Absorption Line Spectrum Types of spectra: Some light sources emit all colors (appears as white light). Others emit just a few colors. Some are missing a few colors. Continuous spectrum is also called a “Blackbody Spectrum” What color is our 5800K Sun? The Sun emits all wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation (light); however, the wavelengths of light it emits most intensely are in the green/yellow part of the spectrum. Absorption spectrum: atmosphere of stars Emission Line Spectrum: Pictorial Graphical Absorption of light: electrons excited to higher energy levels. Photon is gone! Absorption Line Spectrum: Pictorial Graphical The Doppler Effect Astronomy Application V=0 An Atom’s Structure: The Bohr Atom Electron orbits in hydrogen and helium The pattern of energy levels is different for every element. When electron drops to lower energy level, it releases (emits) a photon. Photons released in random directions. The energy of the photon depends on the size of the jump between orbits. Emission spectra of hydrogen and helium Atomic Fingerprints H He Ne Kr Continuous spectrum is also called a “Blackbody Spectrum” Hot, low density gases generate emission line spectra. e.g. fluorescent lights Two stars orbiting one another. The diagram shows the orbital motion of one of the stars, and four different positions are marked (A, B, C, D). At which position is the light from the star redshifted? blueshifted? not shifted at all? D a) A, C, B/D b) C, A, B/D c) B, D, A/C A d) D, B, A/C B C The Earth’s atmosphere is opaque to the ________ part of the electromagnetic spectrum: a) b) c) d) e) f) Visible Infrared X-Ray All of the above A and C are correct B and C are correct Which of the following statements is true with regards to Blackbody radiation? a) A blackbody emits more energy at longer wavelengths as it heats up. b) A blackbody emits energy at all wavelengths c) The shape of the blackbody spectrum depends on what the source is made of. d) All of the above e) None of the above Which transitions were responsible for each of these absorption lines? a) A: 1-2 B: 2-4 C: 1-4 b) A: 1-4 B: 2-4 C: 1-2 c) A: 4-1 B: 4-2 C: 2-1