Ch. 19 PowerPoint Notes
advertisement

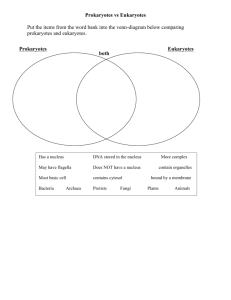
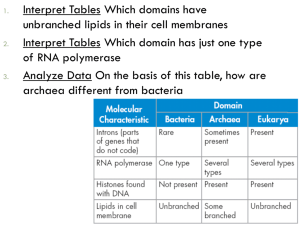
Domains and Kingdoms The 3 Domains of Life • Bacteria thought to be the oldest domain – Prokaryote • Archaea is next oldest – Prokaryote • Eukarya contains the 4 eukaryotic kingdoms – Animals – Fungi – Plants – Protists • Very diverse group (p. 413 – fig. 2) The Domain Bacteria • Contains a single kingdom called eubacteria • Most abundant organisms on earth • Prokaryotes • Bacteria found in practically every environment on Earth Characteristics of Bacteria • Cell Wall – Strong, exterior cell walls made of peptidoglycan • Gene Translation Apparatus – Amino acid sequences and RNA polymerases found in bacteria differ from those found in eukaryotes and archaeabacteria – This information can be used to determine evolutionary relationships of groups of bacteria Kinds of Bacteria • Wide range of bacteria exists – Disease-causing – Food-processing – Control agricultural pests – Perform genetic engineering – Producers – Consumers The Domain Archaea • Contains only 1 kingdom – Archaeabacteria • Prokaryotes • Diverged from bacteria • Can maintain life in a variety of environments Characteristics of Archaeabacteria • Cell Wall and Membrane – Differ from bacteria (no peptidoglycan) – Contain lipids, very different from bacteria and eukaryotes • Gene Structure and Translation – Genes of archaea interrupted by introns – Ribosomal proteins similar to eukaryotes and different from bacteria Kinds of Archaeabacteria • Methanogens – Obtain energy by combining hydrogen gas and carbon dioxide to form methane gas – Live in deep mud of swamps and poisoned by oxygen • Extremophiles – Thermophiles • Live in extreme heat (up to 106 degrees C) – Halophiles • Live in extremely salty environments – Some also live in extremely acidic conditions • Non-extreme Archaeabacteria – Grow in all the same environments as bacteria The Domain Eukarya • Made up of 4 kingdoms – Protista – Fungi – Plantae – Animalia • Eukaryotes • Early eukaryotes led to multicellular life Characteristics of Eukarya • Highly Organized Cell Interior – Have nucleus and other internal compartments – Allows cell to perform a variety of functions • Multicellularity – Activities of individual cells are coordinated with other cells • Sexual Reproduction – Life cycle involves sexual reproduction – Mitosis – Meiosis Kinds of Eukaryotes • Protista – Contain multi and unicellular organisms – Aquatic • Fungi – Heterotrophs – Mostly multicellular – Live on and decompose dead organisms • Plants – Multicellular – Autotrophs – Cell wall of cellulose • Animals – Heterotrophs – No cell walls – Tissue and organs • p. 417 – Table 1