Cell Theory Basic Kinds of Cells
advertisement

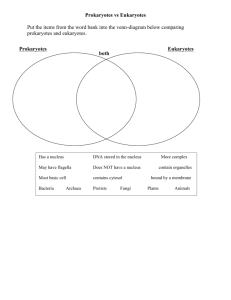
The Cell Theory and the Two Basic Kinds of Cells I. What are Cells? A. cell = the smallest unit of an organism that can perform all of the life functions (reproduction, growth and development, metabolism, response to stimuli, and movement). 1. Cells are often referred to as the “basic units of structure and function” in living things. II. Discovering and Naming Cells A. Robert Hooke was the first person to describe cells while observing a thin slice of cork under his microscope in 1665. 1. He observed that the cork was made up of little boxes that reminded him of the little rooms, or cells, that monks lived in at the abbey. 2. He named the little boxes “cells” which means “little rooms” in Latin. III. Developing the Cell Theory A. Many scientists studied plants and animals, but it took almost 200 years after Hooke’s discovery for them to conclude that all living things were made up of cells. 1. In 1838, Matthias Schleiden concluded that all plants were made of cells. 2. In 1839, Theodor Schwann concluded that all animal tissues were made of cells. 3. In 1858, Rudolf Virchow concluded that cells could only come from other cells. B. The work of these scientists lead to the creation of the Cell Theory. 1. The Cell Theory states: a. All organisms are made up of one or more cells. b. The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in all living things. All of the life functions are performed by individual cells or groups of cells. c. All cells come from cells that already exist. IV. The Two Basic Kinds of Cells A. Cells are classified into two groups based on whether or not the cell has a nucleus or parts that are surrounded by membranes (called “membrane-bound organelles”). B. Prokaryotes 1. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms that do not have a nucleus or any membranebound organelles. a. The DNA in prokaryotes is in a circular molecule that floats freely in the cytoplasm. 2. Bacteria and archaea are the only organisms that are prokaryotic. a. Bacteria are the smallest and simplest cells known and they live almost everywhere. b. Archaea are very similar to bacteria but live in extreme conditions (extremely hot or extremely salty places). C. Eukaryotes 1. Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells contain a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. a. The nucleus is made up of a membrane that surrounds and holds the cell’s DNA. b. Every organism other than bacteria or archaea is eukaryotic. 2. Eukaryotes can be single-celled or multicellular. a. Eukaryotic cells are the largest cells—about 10 times larger than bacteria cells.