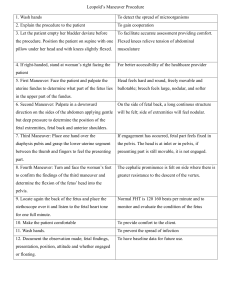
Human Development

Human Development
27.9 Relate the structure of sperm to its role in fertilization.
Describe the mechanisms that prevent more than one sperm from fertilizing an egg and that prevent hybridization between different species.
Describe this picture…
27.10
Describe the process and results of cleavage. Explain how identical and nonidentical twins form.
Describe this picture…
27.11 Describe the process of gastrulation and the resulting arrangement of the embryo.
Gastrulation
Establish 3 cell layers
ectoderm
outer body tissues
skin, nails, teeth
nerves, eyes, lining of mouth
mesoderm
middle tissues
blood & lymph, bone & notochord, muscle
excretory & reproductive systems
endoderm
inner lining
digestive system
lining of respiratory, excretory & reproductive systems gastrulation in primitive chordates ectoderm endoderm mesoderm protostome vs. deuterostome
27.12 Explain how organs form after the development of a gastrula.
Explain how changes in cell shape, induction, cell migration, and apoptosis contribute to development
Pattern formation during embryonic development is controlled by ancient genes
27.15 Describe the initial embryonic stages and the formation and functions of the extraembryonic membranes in humans.
Human fetal development
4 weeks 5 weeks
Human fetal development
10 weeks
Human fetal development
14 weeks 20 weeks
Human fetal development
The fetus just spends much of the 2 nd & 3 rd trimesters just growing
…and doing various flip-turns & kicks inside amniotic fluid
Week 20
Human fetal development
24 weeks (6 months; 2nd trimester) fetus is covered with fine, downy hair called lanugo . Its skin is protected by a waxy material called vernix
Human fetal development
30 weeks (7.5 months) umbilical cord
Getting crowded in there!!
32 weeks (8 months)
The fetus sleeps 90-95% of the day & sometimes experiences REM sleep, an indication of dreaming