Biomes - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
advertisement

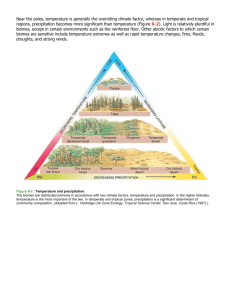
Biomes Standard 5e & 6a Standard 5e & 6a 5e: Students know rain forests and deserts on Earth are distributed in bands at specific latitudes. 6a: Students know weather (in the short run) and climate (in the long run) involve the transfer of energy into and out of the atmosphere. Energy Transfer We learned from last unit that the sun heats the earth unequally, causing differences in temperature. We also learned that evaporation and precipitation of water occurs because of the unequal heating. Because of these two main things, solar energy and precipitation, energy is transferred throughout the globe. Weather vs. Climate Energy transfer causes the weather; the state of the atmosphere at a given time or place (temperature, precipitation, humidity, air pressure) • Wind & Rain • Clouds, lightning, & thunder • Disasters: hurricanes, tornadoes Weather is different from climate; the long term average of weather. What affects climate? Climate in an area is affected by two main things • Direct sunlight (heat) • Precipitation Climate directly affects the type of biome • Biome is an environment with specific vegetation and organisms • If it is cold, you have organisms that are suitable to the ____ Sunlight Sunlight gives off different wavelengths When it strikes the earth, different wavelengths get reflected while others are absorbed, heating the Earth. Some of it escapes into space, some reflects back to earth due to greenhouse gases Greenhouse Effect Sunlight Some heat escapes into space Greenhouse gases trap some heat` Atmosphere Earth’s surface Latitude 90°N North Pole Low Sunlight Arctic circle Sunlight Most direct sunlight 66.5°N Tropic of Cancer Equator 23.5°N 0° Tropic of Capricorn 23.5°S Sunlight Arctic circle Low Sunlight 66.5°S 90°S South Pole The amount of direct light can affect the temperature. Remember that the equator gets the most sunlight, and polar regions gets the least. Precipitation The amount of water falling in the given area can greatly affect the type of climate Remember that precipitation falls at 0° and 60° Biomes Because of these two factors combined, we get specific biomes at specific areas. For example, at the equator, there is a lot of sunlight, and a lot of precipitation, so there is a tropical rainforest. At 30°, there is a lot of sunlight, but little or no precipitation, so there is a desert. Overview Sunlight and precipitation affect the climate Climate over an environment produces a biome A biome has organisms suited to the climate Biomes generally occur on the same latitudes Biomes There are two main types of biomes • Land • Aquatic (water) We will cover both today Land Biomes Most land biomes are named after their climax community. Some of the land biomes • Tundra • Taiga (TIGH-guh) • Temperate deciduous forest • Grassland • Tropical rain forest • Desert Tropical rain forest Temperate grassland Temperate forest Tundra Tropical dry forest Desert Northwestern coniferous forest Mountains and ice caps Tropical savanna Temperate woodland and shrubland Boreal forest (Taiga) Aquatic biomes There are 3 main types of aquatic biomes. The amount of salt determines the type of biome. The 3 main types of aquatic biomes • Freshwater • Marine (saltwater) • Estuaries Tundra Tundra • Located near the poles • Treeless biome covered by moss, lichens, and grasses • Permafrost – a layer of permanently frozen subsoil Taiga Taiga • Covered by coniferous (cone bearing) trees. • Bears, wolves, moose, elk are some of the typical animals Temperate Deciduous Forest Temperate deciduous forest • Plants change during the seasons (leaves change color) Grasslands Grasslands • Most of the rainfall occurs in one part of the season • Hot summers, cold winters Tropical Rain Forest Tropical rain forest • Located at equator • Receive 200-400 centimeters of rain a year • Constant temperature. • Home of the most types of animals than any other biome. Many colorful Deserts Deserts • Located at 30° latitude • Less than 25 cm of rain falls a year • Both plants and animals must be able to retain moisture. • Birds, lizards, snakes, insects are typical • Cactus and sagebrush sparsely cover the area Freshwater biomes Rivers, streams, and lakes Marine Biomes Includes all of the ocean Marine biomes are divided into 4 subcategories • Intertidal zone • Neritic zone • Open-sea zone • Deep-sea zone Estuaries Estuaries are the boundaries between freshwater and saltwater. Since it is a mix of the two, a variety of organisms can be supported. Examples of estuaries • Delta, swamp, lagoon Biome Project In groups of 4-5, create a biome presentation Give information about the biome, including: • Temperature range (graph) • Precipitation (graph) • Location (latitudes/areas) • Plants (vegetation) • Animals • Brief Description (Examples) • Koppen climate classifications Posterboard or Powerpoint acceptable More visuals, the better 500000000 points To help you out… A Biology Textbook http://mbgnet.mobot.org/ http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/La boratory/Biome/ Preplan… What kind of presentation will you do? Powerpoint? Posterboard? Who is doing what? Research? Picture finding? Who’s good with computers? Who’s bringing materials? When do you want to meet up? Contact info? Anything else you can think of…