E.1.9_content
advertisement

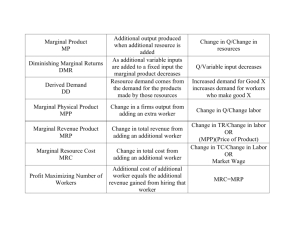
Standard 1 Understand the fundamental concepts relevant to the development of a market economy SS.912.E.1.9 Describe how the earnings of workers are determined Simple answer: supply and demand determine wages Firms demand labor services People supply labor services Also, don’t ignore opportunity costs Example: babysitter Why do firms hire people? The demand for resources is a derived demand- it is dependent on the demand for the product More specifically, why do firms hire people? If the firm already has 20 employees, why hire one more? Because that employee’s marginal production adds to total production Example: 20 employees produce 50 units, 21 employees produce 55 units, the marginal productivity of the 21st worker is 5 units Would you hire the 21st worker? From the previous example, what if those 5 new units sold for $10 each and the worker cost $40? Marginal revenue (MR) = $10 Marginal product (MP) = 5 Marginal revenue product (MRP) = $50 Marginal cost (MC) = $40 Decision rule for the firm: hire people as long as MRP > MC of worker If you were currently working for $25 an hour, would you be willing to work more for $30 an hour? The resource supply curve is upward sloping: higher wages increase quantity supplied An individual person would work more OR more people would be willing to work when wages increase S & D graph: Short answer question: Explain why it might make perfect economic sense to pay a professional athlete $20 million per year. Other considerations Union contracts Monopsony power- a single or limited number of sellers (i.e. workers) Compensating wage differentials Differences in productivity Compensating Wage Differential Video: Night at the Museum As an employer, you may have to offer higher (or lower) wages due to: Environment Risk Location Differences in productivity Video: Monsters, Inc.