Motivation and Leadership
advertisement

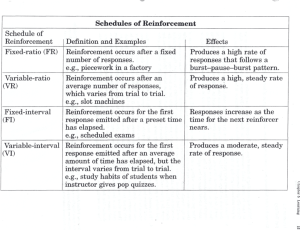
Motivation and Leadership Chapter 16 Section 16.1: Motivation • • • What is Motivation? What Motivates People? Integrating the Approaches to Motivation What You’ll Learn The meaning of motivation. The various theories of motivation. How expectations affect motivation. How managers use positive and negative reinforcement to motivate employees. How managers use the theories of motivation. Why It’s Important To be able to motivate the people who work for them, managers need to recognize what drives individuals’ behavior. Bell Ringer Write a brief response to the question, “What motivates you to do your homework?” Will not accept if not handed in in 15 minutes today. Please Include Name-Date-Period-Title of Assignment- Question Written out. Key Terms Motivation Positive Reinforcement Negative Reinforcement What is Motivation? Lori Ayeung, the manager of a four person product team, gets to work at 7:30 every morning. When her team is up against a deadline, she stays late. She also has been known to spend weekends at the office. Carlos Lomaz, a manager at the same company, often shows up late for work. He takes little pride in his work and does not seem to understand the importance of completing tasks on time. Carlos’ teammates find it frustrating to work with him because of his obvious disinterest. What is Motivation? What explains the difference between the behavior of these two managers? It lies in motivation, or the factors that give people a reason to act. Motivation is concerned with three sets of issues: – What makes people act – Why people try to achieve particular goals – What makes individuals stick with their goals Bell Ringer Successful athletes understand the importance of motivation. What do you think motivates this baseball team? What Motivates People? Researchers have studied how people perceive their needs, set their goals or accept those set for them and take action. They have come up with various theories about what motivates people. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs One theory of motivation is Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. As you learned in Chapter 2, according to Maslow, most people seek to meet lower-level needs. A person will fulfill the need for shelter before that of personal satisfaction, for example. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Managers apply Maslow’s principles by recognizing that employees seek to meet some needs before others. They should ensure that the physical working conditions are adequate before concerning themselves with creating interesting and satisfying jobs. Bell Ringer # 3 What basic needs does a construction worker need to fulfill before he will want to meet higher level needs? Essential Question? What is Motivation? Georgia Performance Standards Business Essentials Leadership and teamwork BCS-BE-4: The student participates in a variety of activities that demonstrate the importance of leadership within a business endeavor. Key Terms Defined Motivation-the factors that give people a reason to act. Positive Reinforcement-involves rewarding people who engage in behavior that the manager wishes to encourage. Negative Reinforcement-involves punishing or reprimanding people who engage in behavior that the manager hopes to discourage. All About Attitude Don’t Just Do Your Job! In today’s workplace, simply showing up isn’t good enough. Floating by and doing the minimum amount of work expected is a thing of the past. Challenge yourself to improve constantly upon your abilities. Your boss, co-workers and customers will all appreciate your effort! McClelland’s Achievement PowerAffiliation Approach David C. McClelland developed a third approach to motivation. According to McClelland, people are motivated by three needs: The need for achievement, or the desire to accomplish something or to do something new The need for power, or the desire to influence people and events The need for affiliation, or the desire to have close relations with other people. McClelland’s Achievement PowerAffiliation Approach Everyone aspires to fulfill all these needs to some degree. However, some people have stronger needs than others. To be effective, according to McClelland, managers must identify a person’s strongest need and seek to meet that need. Carmen Sanchez is the manager of the marketing department a large pharmaceutical company. Carmen works hard to identify what motivates each of her employees. She has noticed that one employee, Winston Brown, has a very strong need for affiliation. Last week, Carmen was asked to assign a member of her staff to a company-wide committee. Carmen chose Winston for the job because she recognized his appreciation for working with others. She believes that Winston’s need to work with people will motivate him to work hard on the committee. McClelland’s Achievement PowerAffiliation Approach Sheila Fagan, who also works on Carmen’s staff, is not as people-oriented as Winston is. She has a much stronger need to achieve, however. Recognizing Sheila’s need, Carmen assigns her tasks that will give her a strong sense of accomplishment. Last week, for example, Carmen asked Sheila to take charge of the annual report the marketing department prepares for senior management. She knows that Sheila’s need to achieve will motivate her to prepare a well-written report. Expectancy Theory A fourth theory of motivation is the expectancy approach. According to this theory, motivation depends on employees’ beliefs about how effort and performance affect outcomes. If employees believe that extra effort will result in better performance, they are likely to be motivated to work. If they believe that regardless of hard work they are unlikely to succeed, they are not likely to be highly motivated. Expectancy Theory Remy was accidentally placed into French IV, even though the language he has studied for two years is Spanish. He is not motivated to stud very hard for this class because he assumes his studying would make no difference. If instead he were placed in French I, he would probably study very hard, He would recognize that this class is not beyond his level and that his hard work would help him achieve a high grade. Expectancy Theory Managers try to assume that employees see a relationship between effort and performance by placing people in jobs they are able to perform. They avoid hiring people who are not up to the job, and they assign tasks that people will be able to complete. Another important aspect of expectancy theory if the belief that improving performance will lead to rewards, such as a raise or extra vacation days. Employees who believe their work will be rewarded are more likely to work harder than employees who do not see this connection. Many Wall Street companies, for example, pay large end-of-the-year bonuses to employees who perform well. The knowledge that working hard will result in a large bonus motivates many people on Wall Street to work very hard. Bell Ringer What can a manager do to make his staff more motivated? Bell Ringers Dog Trainers use both positive and negative reinforcement of behavior to train dogs. Which type of reinforcement do many managers consider more effective? Reinforcement Theory Reinforcement theory, or operant conditioning, is the idea that punishing or rewarding people will affect their future behavior. Parents apply this theory when they reward children for being good or discipline them for misbehavior. Reinforcement Theory Reinforcement theory uses two kinds of reinforcement-positive and negative. Positive reinforcement involves rewarding people who engage in behavior that the manager wishes to encourage. Negative reinforcement involves punishing or reprimanding people who engage in behavior that the manager hopes to discourage. Reinforcement Theory Managers use positive reinforcement when they praise their employees for work well done, give them a raise, or offer extra vacation days. Employees who receive this kind of reinforcement are likely to be motivated to behave in the same way again. Managers use negative reinforcement by reprimanding their employees or not giving them raises. Employees who receive this kind of reinforcement may be motivated not to engage in the behavior again. Storytellers Leaders often use different tactics to motivate others. The use of stories to communicate ideas is one of them. A parable or symbolism can help bring a difficult situation into a clearer picture of what needs to be accomplished. Shed new light on a subject by telling a story that your audience can relate to. Tips from Robert Half Money is not all a company can offer. Some companies offer benefits such as advancement opportunities, stocks options, tuition reimbursement, training, telecommuting, flex-time and child care. Employees who feel valued work harder. Bell Ringer Expectancy Theory Bond Traders are motivated to work hard because they receive hefty year-end bonuses if they do well. According to expectancy theory, what other factor affects motivation? Quiz Facts and Idea Review 1. 2. 3. 4. Name three theories of motivation and briefly describe each. According to Herzberg, what kinds of factors account for job satisfaction? According to McClelland, what are the three main forces that motivate people? Give one example of positive reinforcement and one example of negative reinforcement. Chapter 16.2 Power, Authority, and Leadership What You’ll Learn The difference between power, authority, and leadership Three types of leadership style Leadership skills managers need to master. Why It’s Important Good managers need to be effective leaders to help employees meet organizational objectives. Key Terms Power Leadership Universal Approach Contingent Approach Bell Ringer List five characteristics you think make a good leader. Distinguishing Between Power and Authority The production supervisor John Quiggin rushes onto the factory floor, barking out orders to his employees. Malcolm Jefferson, the warehouse supervisor, quietly gives instructions to the people he manages. Both men are using their power, or the ability they have to make other people act in certain ways. However, each has a different style of using power. Distinguishing Between Power and Authority Managers derive power from various sources. An important source of power is that managers determine their subordinates’ incomes. This kind of power is known as reward power. There are other important sources of power. Bill Gates, chairman and co-founder of Microsoft, is powerful not only because he has the power to fire his employees, but also because he is a well respected computer software expert. This kind of power is known as expert power. If Bill Gates was not respected as an expert in his field, his power would be much more limited. Authority Authority is the right to issue directives and expend resources. Power and authority often are related. Sometimes, however, people with power have no actual authority. An Advisor to the President of the United States, for example, may have no authority to make decisions. If the person has influence over the President, however, he or she may have significant power. What is Leadership? Leadership is the ability to influence people. Some people seem to be born natural leaders. Others are happy following their lead. However, leadership skills can be learned. Understanding what makes a good leader can make any manager stronger. What is Leadership? Leaders use their power to guide other people’s behavior. To be effective, leaders must have a vision for the future, develop strategies for achieving that vision, and motivate employees to implement them. They also must develop a leadership style. Bell Ringer What are some styles of leadership? Framework for Classifying Leadership Studies Leadership studies can be classified to by whether they take a universal or contingent approach. The universal approach assumes there is one way to lead, regardless of the circumstances. The contingent approach assumes that the best approach to leadership depends on the situation. These studies also can be classified by a focus on traits or behaviors. Traits are characteristics the leader possesses. Behaviors refer to what the leader does. The most important studies we will examine are classified further in this chapter. Trait Theory Early research focused on what a leader was like, rather than what a leader did. This stress on personal traits is called trait theory. Personality trait (originality, persistence, and enthusiasm), social traits (tact, patience, and sympathy), and even physical characteristics (height and weight) are examined to determine good leadership. Trait Theory Based on Trait Theory, those qualities most often associated with excellent leaders include: – – – – – – – – – – Loyalty Courage Stamina Empathy Decisiveness Timing Competiveness Self-confidence Accountability Charisma Styles of Leadership Researchers have identified three basic styles of leadership. They include autocratic leadership, laissez-faire leadership, and democratic leadership. Autocratic Leadership Autocratic leaders are leaders who do not listen to other people but make all decisions themselves. These leaders make most decisions alone because they have little trust in the people they work with. Few people enjoy working for an autocratic leader. There is little room for initiative. Autocratic leaders are unlikely to acknowledge their subordinates’ work or give them credit for their achievements. While autocratic leaders can be effective when they are present, performance and productivity are likely to decline when the leader is away from the work site. Autocratic Leadership A generation ago, most managers were autocratic leaders who simply told their subordinates what to do. Although some autocratic managers still exist today, the trend has been toward different leadership styles. Laissez-Faire Leadership Laissez-Faire means hands off. LaissezFaire leaders are leaders who choose not to lead. This situation can occur when someone is thrust unexpectedly, or unwillingly, into a leadership position. These leaders often lack confidence in their leadership abilities and allow other people in the group to make decisions. They fail to set goals for the group and provide no real leadership. Democratic Leadership Democratic leaders are often the best kind of leaders. This kind of leader listens to other people’s opinions and encourages the exchange of ideas. Democratic leadership helps develop a feeling of responsibility among group members. When democratic leaders make a decision, they will explain the reasoning behind their actions. This creates a group that feels empowered. Democratic leadership usually results in high productivity, strong morale, and good teamwork. Bell Ringer Imagine three different classrooms, one lead by an autocratic teacher, one a laissez-faire teacher, and the other a democratic teacher, and the other a democratic teacher. Which classroom would you prefer? Why? Fiedler’s Contingency Studies of Leadership Early leadership studies attempted to identify universal principles that could be applied to any situation. However, in performing these studies, researchers began realizing the difficulty of generalizing, for example between a military unit and a PTA committee. Even within he business environment alone, leadership practices appropriate to the production floor might not work in the executive suite. Contingency Approach Later studies looked at leadership styles specific to particular situations. This is called he contingency approach. Fred Fiedler conducted one of the first contingency studies. He studied the match between a leader’s personality and the situation. Fiedler defined two basic leadership traits: Task motivated leaders gain satisfaction from the performance of a task. Relationship-motivated leaders gain satisfaction from interpersonal relationships. Path Goal Theory of Leadership Path-goal theory addresses the relationship between a leader’s behavior and subordinates’ performance and job satisfaction. Leader behavior affects employees’ perception of their work environment. This model categories leaders into four basic types. One of these types is the autocratic style discussed earlier in this chapter. Path Goal Theory of Leadership Here are the four basic types of Path Goal Theory of Leadership: Role Classification-leaders let group members know what is expected of them, establish the methods o use, coordinate work within the group, and maintain standards of performance. Such clarification is helpful to employees engaged in unstructured tasks. Path Goal Theory of Leadership Supportive Leaders-create a pleasant work environment and are approachable. This is satisfying to those working on highly structured tasks, as friendliness can lighten an oppressive routine. Path Goal Theory of Leadership Participative Leaders-consult with subordinates in the decision-making process. These discussions improve the performance of employees working on ambiguous tasks. Path Goal Theory of Leadership Autocratic Leaders-issue orders that subordinates are not expected to question. This leadership style hurts job performance and satisfaction in most situations. Developing Good Leadership Skills With so many different theories on leadership, it may be difficult to find the one that works for you. Regardless of which theory you choose, here are many good leadership skills that are effective in most situations. To become effective leaders, managers need to master the following set of skills. Developing Good Leadership Skills 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Plan Become a Teacher Delegate Encourage independent thinking Build a Team Set an Example Share credit with subordinates. Developing Good leadership Skills With dynamic forces at work in the marketplace, managers and employees must continually adapt to new situations. The need to improve performance under conditions of constant change challenges managers continually to improve their motivation and leadership skills. Business Plan Outline Plan Outline 1.0 Executive Summary 2.0 Company Summary – Company Ownership – Start-up Summary – Company Locations and Facilities 3.0 Products and Services 4.0 Market Analysis Summary 5.0 Strategy and Implementation Summary 6.0 Management Summary 7.0 Financial Plan Appendix Chapter 16 Quiz Answers: 1. (1) Maslow's hierarchy of needs; (2) Herzberg's motivation-maintenance model; (3) McClelland's achievement-power-affiliation approach; (4) Expectancy theory; or (5) reinforcement theory. 2. Herzberg concluded that job content factors (the opportunity for promotion and the chance to grow) and hygiene factors (pay, benefits, and working conditions) account for job satisfaction. 3. McClelland said that the three motivating forces are the need for achievement, the need for power, and the need for affiliation. 4.Give example of positive reinforcement and an example of negative reinforcement. Your own words. Classroom Rules It’s a New Day….. No Cursing in Class There will be assigned seating No Talking in class Absolutely no cell phones visible in class No Ipods on or Earphones in ear during class No game playing in class No walking around classroom No leaving class without permission No arguing back at teacher –Automatic Write-up If you talk about the teacher you will be written up – All these rules are enforceable on 1 warning then a write-up. Vocabulary Quiz Define the Following Terms Power Leadership Universal Approach Contingent Approach