Unit One: Technological and Environmental
Transformations (c. 8000 BCE to c. 600 BCE)
Chapters 1-6
Key Concepts:
1.1 Big Geography and the Peopling of the Earth
1.2 Neolithic Revolution and Early Agricultural Societies
1.3 Development and Interactions of Early Agricultural, Pastoral, and
Urban Societies
Key Concept 1.1
Big Geography and the Peopling of the Earth
Key Concept 1.2
Neolithic Revolution and Early Agricultural Societies
Key Concept 1.3
Development and Interactions of Early Agricultural, Pastoral, and Urban Societies
Carl Sagan’s Cosmic Calendar
Imagine that the entire
history of the universe is
compressed into one year with the Big Bang
corresponding to the first
second of the New Year's
Day, and the present time
to the last second of
December 31st (midnight).
Using this scale of time,
each month would equal a
little over a billion years.
Here's a closer look at
when important events
would occur when we
imagine the universe in
one year.
http://www.maniacworld.com/history-of-the-universein-single-year.html
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WPBkYgvzavo
The Theory of Evolution
The theory of evolution, formalized
by Charles Darwin in the 1800’s, is as
much a theory as is the theory of
gravity, or the theory of relativity.
However, unlike theories of physics,
biological theories (especially
evolution) have been argued long
and passionately in socio-political
arenas. Even today, evolution is not
often taught in primary schools.
However, evolution is the binding
force of all biological research - the
unifying theme - and is supported by
the scientific community.
As evolution became
widely accepted in
the 1870s,
caricatures of
Charles Darwin with
an ape or monkey
body symbolized
evolution for some.
http://www.phy.syr.e
du/courses/modules
/ORIGINS/origins.ht
ml
Evolution Timeline
http://archaeologyinfo.com/human-evolution-timeline/
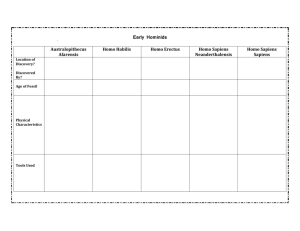
Basic Evolutionary Sequence:
Ardipithecus ramidus – (ardi = ground or floor, pithecus = ape)
Australopithecus – (southern ape)
Homo habilis – (with the ability to make tools)
Homo erectus – (upright-walking)
Homo sapiens – (thinking humans)
Homo sapiens sapiens – (modern thinking humans)
__________________________________________________________
Not So Basic Evolutionary Sequence:
Sahelanthropus tchadensis
Orrorin tugenensis
Ardipithecus ramidus
Australopithecus anamensis
Australopithecus afarensis
Kenyanthropus platyops
Australopithecus africanus
Australopithecus garhi
Australopithecus sediba
Australopithecus aethiopicus
Australopithecus robustus
Australopithecus boisei
Homo habilis
Homo georgicus
Homo erectus
Homo ergaster
Homo antecessor
Homo heidelbergensis (aka Homo sapiens
archaic)
Homo neanderthalensis
Homo floresiensis
Homo sapiens sapiens
http://www.berkeley.edu/news/media/releases/2009/10/01_ardiskeleton.shtml
Australopithecus:
“Southern Ape”
(This is Lucy!)
http://www.becominghuman.org/
The Fossil Record
Homo Habilis –
evidence of the first
use of tools
Homo Erectus
may have been first hominid species
to use fire, and first to migrate out
of Africa
Cro-magnon
(Homo sapiens sapiens)
Neanderthal
(Homo sapiens)
Flores man ... a model of a skull
from the newly found species of
hobbit-sized humans that lived
about 18,000 years ago in
Indonesia. (Reuters)
In 2003 Australian
scientists found a new
species of hobbit-sized
humans who lived about
18,000 years ago on an
Indonesian island. The
discovery adds another
piece to the complex puzzle
of human evolution. The
partial skeleton of Homo
floresiensis, found in a
cave on the island of
Flores, is of an adult
female that was a meter
tall, had a chimpanzeesized brain and was
substantially different from
modern humans.
Prehistory
•The time before written records were kept.
•Human beings and our ancestors (hominids) lived on earth for
millions of years before the start of history.
•Prehistory is divided into three main periods:
1. Paleolithic (Old Stone Age)
2. Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age)
3. Neolithic (New Stone Age)
The Peopling of the
Earth
During the Paleolithic Era, our
hominid ancestors began to migrate
out of Africa.
http://www.bradshawfoundation.com/journey/
The Development of Culture
**Prehistoric humans were
the first to begin developing
culture. The most basic
definition of culture is:
Learned patterns of
action
The existence of cave
paintings proves that culture
existed among early humans.
http://www.lascaux.culture.fr/?lng=en#/fr/00.xml
http://www.culture.gouv.fr/culture/arcnat/chauvet/en/
Prehistoric Cave Art
Another Definition
of Culture:
Culture: is a shared, learned, symbolic system of
values, beliefs and attitudes that shapes and
influences perception and behavior. An abstract
"mental blueprint" or "mental code."
Culture is examined by studying behavior,
customs, material culture (artifacts, tools,
technology), language, etc.
7 Characteristics of Culture
• Learned. Process of learning one's culture is called enculturation.
• Shared by the members of a society. No "culture of one."
• Patterned. People in a society live and think in ways that form definite
patterns.
• Mutually constructed through a constant process of social interaction.
• Symbolic. Culture, language and thought are based on symbols and
symbolic meanings.
• Arbitrary. Not based on "natural laws" external to humans, but created
by humans according to the "whims" of the society. Example: standards
of beauty.
• Internalized. Habitual. Taken-for-granted.
Perceived as "natural."
The Agricultural
Revolution(s)
•Archaeologists and historians
believe plant domestication began
about 10,000 years ago among
some human groups. This led to the
first permanent, or sedentary,
villages.
•Domestication of animals was also
an important part of the Neolithic
Revolution.
•Several agricultural revolutions
occurred at different times
throughout the world. Some
societies, because of geography,
climate, and resource availability, did
not develop agriculture.
•Calendars were developed to keep
track of planting/harvesting seasons.
Regions of world where agriculture first
developed:
•Southwest Asia
•East Asia
•Southeast Asia
•Mesoamerica
(Independently
developed
agriculture)
•Northeastern America
•East Africa (Nile Valley)
•West Africa
•Southeast Europe
•South America (Andes Region)
(Evidence indicates
agricultural knowledge and
technology may have been
borrowed from, or spread
from other regions.)
Agricultural Revolutions occurred
throughout the world between
9000 BCE – 2000 BCE.
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Yocja_N5s1I&list=PLBDA2E52FB1EF80C9
&index=1
Origins and Early Spread of
Agriculture
©2011, The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. All Rights
Reserved.
Agriculture and Population Growth
©2011, The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. All Rights
Reserved.
Early Agricultural Society
• Emergence of villages and towns
• Discoveries at Çatal Hüyük – a prominent
village located in Turkey, occupied 72505400 B.C.E.
– Pots, baskets, textiles, leather, stone, metal
tools, wood carvings, carpets, beads, and
jewelry
• Development of crafts – pottery,
metallurgy, and textile production
©2011, The McGraw-Hill
Companies, Inc. All Rights
Reserved.
Neolithic Revolution - domestication of plants and
animals begins
Villages form, population increases
Need for food surplus and irrigation arises
Job specialization becomes more complex
Political organization begins in order to organize labor for large
irrigation projects
Social classes form and social structures
become more complex
The Origins of Urban Life
•
•
•
•
•
Craft specialization
Social stratification
Governance
Cultural workers
Development of the city – a gradual
process
©2011, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
•The earliest complex societies, or civilizations (located
in Egypt and Mesopotamia) began to develop about
5000 years ago, around 3100 B.C.E. This is often
referred to as the “Urban Revolution.”
•Writing also began about 5000 years ago in some
societies, due to the need to keep economic and
administrative records.
•People began to acquire more possessions
•New technologies were developed (irrigation, etc.)
•Women lost status as a result of the development of
agriculture in most societies.
Q: Why do you think this occurred?
A:
Civilization - Official Definition: An organized social
structure.
Main Features of early civilizations, according to some
historians:
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
cities
central government
religion
job specialization (such as scribes, artisans, priests, etc.)
social classes
arts and architecture
public works
a form of writing
Another characteristic of many early civilizations was
polytheism. Also, the use of slave labor was common.
“The truest test of civilization is, not the census, nor
the size of the cities, nor the crops, but the kind of
man that the country turns out.”
-Ralph Waldo Emerson
“The true civilization is where every man gives to every
other every right that he claims for himself.”
-Robert Green Ingersoll
“You can’t say civilization isn’t advancing: in every war
they kill you in a new way.”
-Will Rodgers
Some Early Civilizations
of the Middle East
Sumeria
Babylonia
Assyria
Phoenicia
Canaan (Palestine)
Persia
Egypt
Nubia
•The Fertile Crescent,
(including
Mesopotamia) was
home to many of the
earliest and most
advanced civilizations.
•As society and
population grew, scarce
resources and a variety
of ideas and beliefs led
to conflict in the region.
The Four Early River Valley
Civilizations