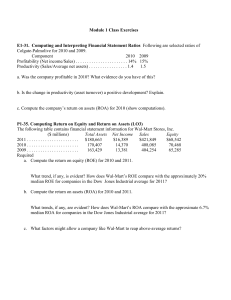
August 5

Intercorporate Entities, i.e., consolidations, equity investments, partnerships
Chapter 7
Acquisitions
• Purchase (old and new)
– Goodwill
– mark-to-market analogy
• Pooling
– Simply added BVs of assets and liabilities
– No reflection of MVs at purchase
– 12 criteria (p. 467)
– practice no longer allowed under GAAP
Equity Investments
• Majority => > 50%
– control
– consolidated (Vs. acquired)
• Minority Active => 20% to 50%
– create an asset and adjust for share in NI and dividends
– Equity method
• Minority Passive => < 20%
– mark to market
– Market value method
Comprehensive Income
• Stockholder Equity impact (SFAS 130)
– as compared with I/S impact
• Arises from
– hedging (foreign currency and other derivatives) (SFAS 133)
– pension reporting
– certain mark to market adjustments
Segment Reporting
(SFAS 131)
• Reportable operating segments
• Geographic coverage
• Major customers
• Be able to identify unique risk in each
Segments, continued
• What is reported?
• Operating segments:
– Sales
– Profit / Loss
– Assets
• Customers: (if
10%)
– Have to report sales
– Often named
• Geographic Segments:
– Sales and fixed assets
Chapter 8
Profitability
ROA and ROE expanded
ROA, as a function of:
• Operating Leverage
– i.e., fixed costs (committed and discretionary)
• Business Cycle
• Product Life Cycle
Leverage
• Earn a higher return than the cost of the investment
• Operating Leverage
– Reflects investment in fixed costs
– Measure as fixed costs (expense) as a percent of total expenses
Strategic Management
• Life cycle of a firm
–Introduction
–Growth
–Maturity
–Decline
Industry-Specific ROA
Problems
• High Tech
• Airlines / Travel and Transport
• Service firms
• Retailers
Expand to ROCE
• ROCE = ROA x CEL x CSL
• Reversion to the Mean