KEY
advertisement

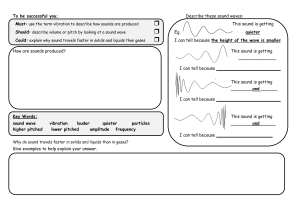
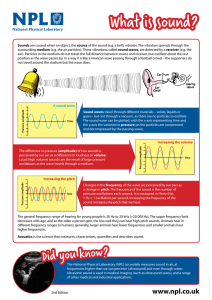
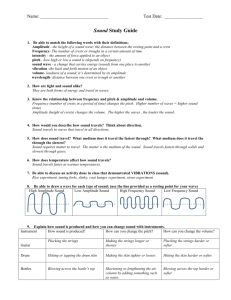
The Nature of Sound, Chapter 21 Word Sound Wave Mechanical Wave Sound Wave Velocity (m/s) Approx. 343 m/s in air Pitch KEY Explanation Produced by a VIBRATION which is a complete back and forth motion that moves the energy Have crowded areas called COMPRESSIONS and less crowded areas called RAREFACTIONS Drawing/Examples Ex: Tuning fork in water – moves energy! Sound requires a MEDIUM in order to travel The wave vibrations form a repeating pattern of COMPRESSIONS and RAREFACTIONS, making them called COMPRESSION waves Must have a medium – solid/liquid/gas Think domino effect Velocity is determined by the MEDIUM & TEMPERATURE. Sound travels fastest through SOLIDS and slowest through GAS. (why?) Cooler temperatures make sound travel SLOWER. Solid – particles close together, so bump faster Liquid – particles further apart, longer to bump Gas – furthest apart high temp – particles move faster lower temp – move slower Soprano vs bass How HIGH or LOW you perceive a sound to be Determined by the FREQUENCY of the wave Higher frequency = higher PITCH Sound Wave Frequency (Hz) Pitch and frequency have direct relationship Frequencies below 20Hz Animals with high frequency range BATS, DOLPHINS, some WHALES Animals with low frequency range CATS, DOGS, some WHALES Human frequency range = 20 to 20,000Hz (range shrinks as we age) infra means “below” – we can’t hear! Frequencies above 20,000 Hz ultra means “above” – we can’t hear! When an object making noise approaching you makes you perceive a HIGHER pitch than when it passes you Ex: fire truck passing you – sounds higher pitch coming at you vs after passing by (picture in textbook of waves closer together coming & spread out after passing) Drawing of small vs larger amplitude Higher frequency = SHORTER wavelength (inverse relationship!) Infrasonic (Frequency) Ultrasonic (Frequency) Doppler Effect Sound Wave Amplitude Decibels (dB) As amplitude increases, the sound energy INCREASES and it sounds LOUDER Loudness of sound Threshold of pain for human ear is ABOUT 120 dB Measurement for sound Word Sound Interaction – Reflection Sound Interference – Constructive Sound Interference – Destructive Sound Interference - Resonance Noise Sound Interaction - Diffraction Explanation Called an ECHO Drawing/Examples Bats/Whales/Dolphins use ECHOLOCATION Ships use SONAR Ultrasounds used for MEDICAL DIAGNOSIS Compressions overlapping result in sound being LOUDER Compressions overlapping rarefactions result in the sound being SOFTER / CANCELING Soloist vs choir (higher amplitude) Noise canceling headphones (lower amplitude) The tendency of an object to vibrate at maximum amplitude at certain frequencies…. One vibrating object causes the other object to VIBRATE at the same resonant frequency Instruments – Undesired sound due to mix of random FREQUENCIES of sound Sound can travel around BARRIERS or through OPENINGS in order for you to hear it Tacoma Narrows Bridge – Ex: glass breaking w/ high soprano note (high pitch) CAFETERIA OR AUDITORIUM Why you hear students in the locker area in our classroom