Sound and Light Test Study Guide

Sound and Light Test Study Guide
REFLECTION is the bouncing back of a wave after it hits an object. o LIGHT
Examples:
Seeing your image in a mirror
Moon appears to glow
We do not see objects; we see light reflecting off of an object.
White reflects all colors of spectrum
If an apple is red, it is reflecting red. o SOUND
Examples:
Echo
Echolocation (bats, dolphins, whales)
Sonar
Ultrasound
ABSORPTION is the disappearance of a wave into a medium. o LIGHT
Examples:
Wearing a black t-shirt makes you feel hotter.
Black absorbs all colors of the spectrum.
If an apple is red, it is absorbing all colors except red. o SOUND
Examples:
Acoustic ceiling tiles
Shouting into a pillow
Silencer on a gun
REFRACTION is the bending of a wave as it enters a medium. (The wave changes speed as it enters a new medium). o LIGHT
Examples:
Shining a flashlight into a prism.
Rainbow
Straw appears to be bent in a glass of water.
Makes objects appear closer than they are. (Magnifying glass or optical glasses) o SOUND
Examples:
Sound travels faster in a solid because it refracts when it hits molecules. A solid’s molecules are close together, so it travels much more quickly (think about a pinball machine).
Train whistle can be heard far way and seems louder as it bends around houses and objects.
DIFFRACTION is the spreading out of waves as they pass through a gap or opening. The size of the gap determines how much the wave will spread. o LIGHT
Examples:
Light from another room enters through crack under the doorway. o SOUND
Examples:
Hearing someone talking around a corner.
HOW DO MATERIALS TRANSMIT LIGHT?
o Transparent materials allow light to pass through easily...think of glass. o Translucent materials allow some light to pass, but scatter the light in all directions making it hard to make out objects on other side of material….think about wax paper or fabric.
What is scattering? o Spreading out of light rays in all directions, because particles reflect and absorb the light…..think about fog or a dirty window. o Scattering is also responsible for making the sky appear to be blue. o Opaque materials do not allow any light to pass through them…these are objects we cannot see through at all.
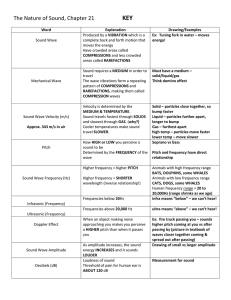
Sound
is a mechanical wave that is produced by vibrations.
o It cannot travel through a vacuum because it has to have a medium to vibrate.
Sound travels the fastest through a solid and the slowest through a gas because the molecules are closer together in a
solid.
The temperature can cause sound to slow down. A sound wave will travel faster as the temperature rises because particles move faster as the temperature rises.
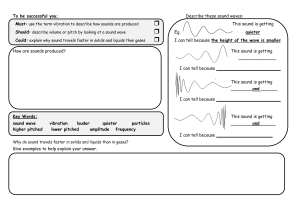
Pitch is the highness or lowness of a sound. It you increase the frequency of a wave; you will cause the pitch to increase. Think of an opera singer (higher frequency, higher pitch) versus a tube
(lower frequency, lower pitch).
Amplitude affects the volume of a sound. If you increase a wave’s amplitude, you increase its sound.
DOPPLER EFFECT o Is the change in perceived pitch that occurs when the source of the sound is moving. (The VVRRROOOMMM when a car passes you). o An ambulance’s siren has a higher pitch the closer it gets to you, the pitch deepens as it passes and moves away from you.