Name: Date: ______ Period: ______ 8.1 Forming Chemical Bonds I
advertisement

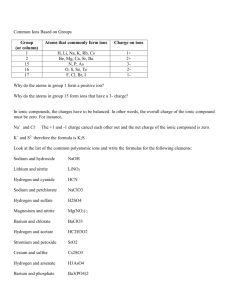
Name: ____________________________________________ Date: _____________ Period: _____________ 8.1 Forming Chemical Bonds I. A chemical bond is _______________________________________________________________________. A. Chemical bonds may form from two ways: ______________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ B. Only _________________ electrons are involved in the formation of chemical bonds between two atoms. C. Elements tend to react to acquire the _____________________________________________ of a noble gas. D. Positive ions form when _____________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 1. 2. 3. 4. Ex: If sodium loses its one valence electron, it takes on the electron configuration of ____________. A positive ion is called a ______________________. Ions retain their identities as elements because their number of ______________ doesn’t change. The reactivity of metals is based on ____________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Group 1A atoms form ions with a _________ charge; Group 2A atoms form ions with a __________ charge; Group 3A atoms form ions with a __________ charge. 6. It is difficult to predict the number of electrons lost by ____________________________________; they tend to form ions with a _____________ or _____________ charge (not always). 7. The relatively stable electron configurations formed by the gain or loss of electrons is referred to as _______________________________________________________________________. E. Negative ions form when ________________________________________________________________ 1. ______________________ tend to gain electrons to form a stable outer electron configuration. 2. Negative ions are called _________________________. 3. The names of negative ions are changed to end in ____________, so chlorine loses one electron to become a ______________________ ion. 4. Group 5A atoms form ions with a _____________ charge; Group 6A atoms form ions with a ________ charge; Group 7A atoms form ions with a ___________ charge. 5. Some nonmetals can lose or gain _________________________________________________________ to form an octet, such as phosphorus, which usually gains 3 electrons, but can also ____________ ____. 8.2 The Formation and Nature of Ionic Bonds I. Formation of an Ionic Bond A. An ionic bond is the _____________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 1. 2. 3. 4. Compounds that contain ionic bonds are _______________ compounds. If ionic bonds occur between metals and nonmetal oxygen, _______________ form. Most other ionic compounds are called _____________. When an ionic compound forms, the number of electrons lost must _______________ the number of electrons gained. a. EX: Calcium will lose ______ electron(s) to become a ________ ion; fluorine will gain _______ electron(s) to become a _________ ion. Therefore, for every _________ calcium atom(s), there will be _______ fluorine atom(s) so that the overall charge of the compound formed is _______. II. Properties of Ionic Compounds A. The chemical bonds that occur between the atoms in a compound determine many of the ___________________________ properties of the compound. B. When an ionic compound forms, the ions are packed into a regular repeating pattern that forms an _______________________________________________. C. The strong attraction of positive ions and negative ions in an ionic compound results in a _____________________________________________________, a three-dimensional geometric arrangement of particles where ____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________. D. _______________________________________, _______________________________________, and ______________________________ are physical properties that depend on how strongly the particles are attracted to each other. 1. In general, ionic compounds have ___________ melting points and boiling points. 2. ___________________ may also be related to the structure of ionic compounds. 3. Ionic crystals are also ___________, ______________, and ________________ solids due to the strong attractive forces that hold the ions in place. E. In the solid state, ionic compounds do not conduct electricity, but when in a liquid state or dissolved in water, they become ______________________________ able to conduct electricity because ions are free to move. F. During any chemical reaction, energy is either ______________________ or _______________________. 1. When energy is absorbed, the reaction is _____________________________; if energy is released, it is ________________________________. a. The formation of ionic bonds is always _____________________________. b. The energy required to separate one mole of the ions of an ionic compound is referred to as _______________________________________________________; the more __________________ the lattice energy, the ________________________ the force of attraction between the ions. i. Lattice energy is directly related to the _____________ of the ions bonded: smaller ions generally have a more __________________ value for lattice energy because the ____________________ is closer and has more attraction to the __________________________________________. ii. The value of lattice energy is also affected by the ___________________ of the ion: the ionic bond formed from the attraction of ions with larger positive or negative charges generally has a more _______________________ lattice energy. a) The lattice energy of MgO is almost ___________ times greater than that of NaF because the ___________________ of the ions is greater.