The cardiac cycle
advertisement

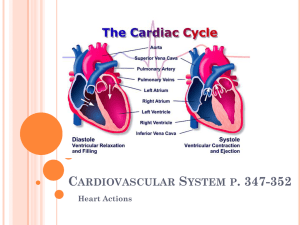
The cardiac cycle • Ventricular filling • the diastole refers to the period of the cardiac cycle during which the ventricles are filling with blood • the systole refers to the period of the cardiac cycle during which the ventricles are actively contracting and pumping blood out of the heart The cardiac cycle • Ventricular filling • end-diastolic volume refers to the volume of blood in the ventricle at the end of ventricular filling • Atrial contraction The cardiac cycle The cardiac cycle • Ventricular contraction isovolumetric ventricular contraction ventricular ejection • Ventricular relaxation isovolumetric relaxation The cardiac cycle Cardiac output • Cardiac output (CO) is the volume of blood pumped by each ventricle per minute • Cardiac output depends on the heart rate and the stroke volume • CO = HR x SV Stoke volume • Stroke volume is the difference between the volume of the ventricle just before contraction (end-diastolic volume) and the volume of the ventricle at the end of a contraction (end-systolic volume). Four factors affecting the enddiastolic volume • 1. Venous filling pressure • 2. Pressures generated during atrial contraction • 3. Distensibility of the ventricular wall • 4. The time available for filling the ventricla Regulation of Cardiac output • Regulation of heart rate • regulation of the stroke volume