Cardiovascular
advertisement

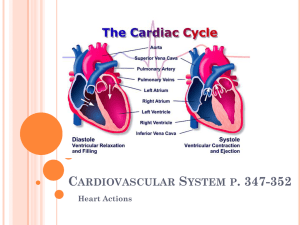
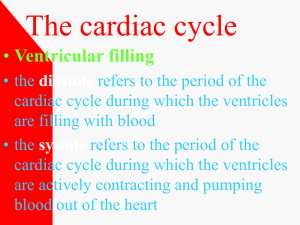
BIOL 2030 Human Anatomy & Physiology II What is the function of the heart? the heart’s function is to… Pump characteristics: Essentially ______________, hence 2 routes! -____________ -____________ Where should the tin man look for a heart? Location -________________ -________________ Size -___________ Orientation -_________ What is the external anatomy of the heart? Heart held in position via attachments: -on top: ______________ -below: What is the external anatomy of the heart? Heart surrounded by a double-layered protective sac the _______________ Fibrous pericardium Parietal pericardium Visceral pericardium Consists of three layers: _______________ _______________ _______________ Pericardial cavity _______________ He died of a broken heart... ___________________ What is the external anatomy of the heart? _____________ right = ________ left = _________ “_________” ______________ _______ _________________ (divides atria and ventricles) _________________ (divides ventricles) What is the external anatomy of the heart? The cardiac sulci are marked by ___________, which are associated with ____________________. What is the external anatomy of the heart? Vessels associated with sulci… __________________ (Right and Left) __________________ (anterior and posterior) What happens if a thrombus/embolus ends up in these vessels? What is the external anatomy of the heart? Vessels associated with sulci… __________________ _______________ return blood to heart via… ________________ To what chamber? ? What is the internal anatomy of the heart? _____________ -3 entrances *__________ *__________ ______________ _______________ …to pulmonary trunk 1 3 2 What is the internal anatomy of the heart? ______________ 4 entrances (_____________) ____________ (Mitral valve) _____________: Exit semilunar valves… to __________________ _____________________ separates the R&L ventricles _____________ separates R&L atria ____________ or ______________? 3 1 4 2 What is the anatomy of the heart wall? The 3 “cardiums” or layers of the heart wall: _________: smooth serous membrane and loose connective tissue _________: thick muscular layer _________: simple squamous epithelium and fibrous connective tissue What is the histology of the heart wall? Cardiac histology Characteristics: branch Intercalated discs nucleus Slower onset and longer duration of contraction myofibril sarcomere Why? mitochondria Take 5!!! Under resting conditions most ATP produced in cardiac muscle is derived from the metabolism of fatty acids. During periods of heavy exercise, however, cardiac muscle cells use Discuss with your lactic acid as an energy neighbor and predict an source. Why is this an answer advantage? What controls the timing and sequence of a heart beat? _________ “fires” Impulse reaches ___ ______, 0.1 sec delay Impulse travels to __ _______ (Bundle of His) Impulse travels down _________ _______________ Finally back up ______________ What happens when your pacemaker loses time? ____________: when tissue other than SA node initiates action potential If not SA node what other possibilities? How can we represent this electrical activity? Electrodes used to measure change electric potential = ____________________ Each wave represents an electric potential P wave = ________________ QRS complex = __________ _______________________ T wave = ____________ __________________ Where is atrial repolarization? What is the cardiac cycle? Terms can refer to atrial or ventricular condition… Two terms used to describe status of myocardium: ______ = contraction ______ = relaxation However, if not specified it is always ventricular What is the cardiac cycle? Distinct periods occurring include: Ventricular Systole 1) period of _______ _________ 2) period of _________ What is the cardiac cycle? Ventricular Diastole 3) period of ________ ________ 4) period of _______ _______ _______ (70%) 5) period of _______ ________ ____ Take 5!!! Fibrillation is abnormal, rapid contractions of different parts of the heart that prevent the heart muscle from contracting as a single unit. Why does atrial fibrillation not cause Discuss with your immediate death, but neighbor and predict an ventricular fibrillation answer does? What makes the rhythm of this drum in my chest? Heart sounds are caused by… Consists of: “Lubb” = “Dup” = Sometimes a third sound = Normal heart sounds Mitral valve stenosis How is the heart’s activity regulated? The heart is regulated in two fashions… 1) ______________ depends on characteristics of the heart itself (in or out of the body!) •____________ •______________ (preload relates to stroke volume) How is the heart’s activity regulated? 2) ____________ depends on neural and hormonal control •_______________ via vagus nerves < heart rate “vagal stimulation” •_______________ via cardiac nerves > heart rate & > force of contraction •_______________ > rate & > force...via which ones? How is homeostasis of the heart achieved? __________monitor conditions including: 1) Changes in pressure (______________) in major arteries work with medulla oblongata 2) Changes in chemistry (_____________) in medulla oblongata (CO2) and major arteries (O2) Effects of ions 1) ________+ can decrease heart contraction to heart block 2) _________++ can increase rate (death due to skeletal muscle tetany) Effects of temperature = ? What are some of the diseases/disorders of the heart? •Endocarditis •Congenital heart defects: •Myocarditis Septal defects •Rheumatic fever (endocarditis) Patent ductus arteriosus •Coronary heart disease •Angina pectoris •Myocardial infarction Stenosis Incompetent (prolapsed) valve •Cyanosis •CHF •Hypertension