Cardiac & Respiratory Dynamics - CHOW
advertisement

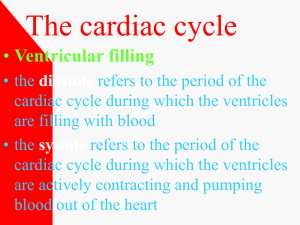
Cardiac & Respiratory Dynamics Vascular System Carry blood away from heart Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Carry blood to heart Capillaries Venules Veins Large Veins Venous Return • One-way valves – Ensure blood goes back to the heart and not backwards • Skeletal muscle pump – Low pressure in veins skeletal contracts to increase pressure • Thoracic pump – Difference in pressure between 2 cavities – Each breath taken, pressure in chest cavity low, abdominal pressure increases – Blood from abdominal to thoracic cavity • Venoconstiction – Nervous system sends signal to veins to slightly constrict Cardiac Cycle • Diastole – phase of relaxation • Systole – phase of contraction Systolic blood pressure – measure in arteries during contraction (120 mm Hg) Diastolic blood pressure – measure in arteries during contraction (80mm Hg) Normal person: 120/80 mmHg Hypertension: >140/90 mmHg – Elevated blood pressure Blood • Erythrocytes (red blood cells) – Transport O2 and CO2 – Contain hemoglobin bind O2 and CO2 • Leukocytes (white blood cells) – Protect body from diseases – Contain platelets blood clotting Cardiovascular Dynamics Cardiac Output • Volume of blood pumped out of the left ventricle in 1 minute (L/min) • Factors: stroke volume & heart rate Cardiac Output (L/min) Q = SV x HR Stroke Volume (mL) Heart Rate (beats/min) • Stroke Volume (SV) – Amount of blood ejected from left ventricle in single beat Stroke Volume (mL) SV = LVEDV – LVESV Left Ventricular End-Systolic Volume (mL) Left Ventricular Diastolic Volume (mL) • Heart Rate (HR) – Number of times hear beats in one minute Maximum Heart Rate = 220 – age (years) How do you increase Q? ↑ Heart Rate ↑ Stroke Volume Increase SV or HR? • Preferred way: ↑ stroke volume • Heart pushes more blood volume with each pump in left ventricle • Heart can beat fewer times • Less stress on heart • Athlete has lower heart rate and beats less than a sedentary person Cardiovascular Training • Cardiac output increase linearly with exercise intensity • Body needs more oxygen = more blood is needed to be pumped to body • Aerobic training • Increase in ventricular volume & thickness of ventricular wall • ↑ ventricular volume = ↑stroke volume Respiratory Dynamics Pulmonary Ventilation • Rate and/or intensity of work being done = air in and out of the body Ventilation (VE) • Inspiration + expiration • Volume of air moved by lungs in 1 minute Ventilation (L/min) VE = VT x ƒ Tidal Volume (L) – volume of air in each breath Respiratory Frequency (breaths/min) – # of breaths taken per minute Oxygen Uptake • Amount of oxygen consumed by body during cellular respiration • Measure as volume of oxygen consumed in given time (VO2) • Increases with activity • VO2max – maximal volume of oxygen that can be supplied to and consumed by body