Cardiovascular System p. 350-357
advertisement

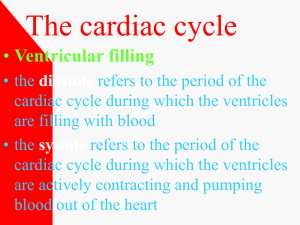
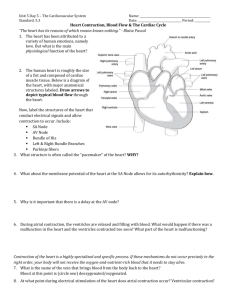
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM P. 347-352 Heart Actions CARDIAC CYCLE One complete heartbeat Pressure within heart Atrial contraction, ventricular relaxation Atrial relaxation, ventricular contraction Rises and falls as chambers fill and empty Atrial or Ventricular Contraction (Systole) Pressure Atrial or Ventricular Relaxation Diastole Pressure Pressure increases sharply Pressure goes back down AV Valves are opening and closing during pressure changes HEART SOUNDS Vibrations in heart tissue produce opening and closing of valves Heard as LubDup through stethoscope Lub Dup Heard during ventricular contraction (AV valves are closing) Heard during ventricular relaxation (pulmonary and aortic valves are shutting) MurMur Abnormal sound Usually occurs when heart valves don’t properly close causing blood to leak through CARDIAC MUSCLE FIBERS Act like skeletal muscles but connect to a network of sending impulses to contract all as a unit. Functional Syncytium Mass of merging cells that act as a unit CARDIAC CONDUCTION SYSTEM Coordinates events of cardiac cycle Sinoatrial Node (SA Node) Small mass of elongated specialized cardiac muscle tissue Cells reach threshold on own and membranes contract one another Initiate impulses that spread into the surrounding myocardium and stimulate cardiac muscle fiber to contract Rhythmic activity 70-80 impulses/min. (Pulse) Pacemaker (Rhythmic contracting) ATRIOVENTRICULAR NODE (AV NODE) Located in septum Receives slow impulse After received impulse AV node sends it on to AV Bundle Purkinje Fibers Allow transmission of impulse for contraction of the ventricles and pushes blood on out to aorta ECG/EKG…ELECTROCADIOGRAM Recording of the electrical changes in the myocardium during cardiac cycle Deflections = waves on paper Polarization and repolarization causes pen to move P QRS T WAVES P wave QRS Complex Time for complete excitation of ventricles Q-T Interval Wave travels through AV node, AV bundles, bundle branches and purkinje fibers S-T Segment Ventricles relax, pattern ends P-R Interval Waves correspond to depolarization of ventriular fibers that contract ventricles, atriums relax, ventricles contract T wave Depolarization, contraction of atriums Time required for complete excitation and recovery of ventricles T-P Interlude Time from completion of ventricular repolarization to next atrial excitation REGULATION OF CARDIAC CYCLE Read p. 356 Arrhythmia Abnormal heart rhythm http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xw4nDMgTOrw REVIEW Describe the pressure changes in the atria and ventricles during a cardiac cycle. What causes heart sounds? What is a functional syncytium? How is a cardiac impulse imitated? How is a cardiac impulse transmitted from the right atrium to the other heart chambers?