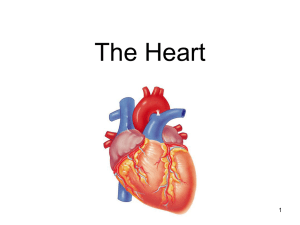
Physiology of the Cardiovascular System
advertisement
Physiology of the Cardiovascular System Conduction System SA Node Pacemaker Initiates the normal cardiac impulse Has intrinsic rhythm, initiates impulses at regular intervals even without stimulation by nerve impulses SA nodeinteratrial bundleleft atrium contraction of atria SA node3 internodal bundlesAV node AV node Impulse passes slowly thru AV node then speed up thru the AV bundle & Purkinje fibers causing ventricles to contract Ectopic pacemaker If SA node loses its ability to generate impulse, another portion of conduction system can generate impulse but will be at a slower rate Electrocardiogram (EKG) Graphic record of heart’s electrical activity P wave Depolarization of the atria, passage of electrical impulse from SA node thru the atria QRS complex Represents depolarization of ventricles Repolarization of atria also occuring T wave Repolarization of ventricles http://www.youtube.com/watch? v=qHjbEYUfzH8 Cardiac cycle Complete pumping cycle Systole (contraction) & diastole (relaxation) of atria & ventricles Atrial systole Contraction of atria Blood into ventricles AV valves are open Semilunar valves closed P wave of EKG Isovolumetric Ventricular Contraction Between start of ventricular systole & opening of semilunar valves Ventricular volume constant Ventricular systole coincides with R wave of ECG & 1st heart sound Ejection Semilunar valves open Initial rapid ejection: marked increase in aortic & ventricular pressure Longer reduced ejection: T wave appears Residual volume of blood remains in ventricles after ejection Isovolumetric Ventricular Relaxation Ventricular diastole Period between closure of semilunar valves & opening of AV valves Second heart sound is heard Passive ventricular filling Av valves forced open by increasing intra atrial pressure Heart sounds “lubb-dupp” First sound caused by contraction of ventricles & vibrations of the closing of AV valves Second sound caused by vibrations of the closing of semilunar valves Factors that affect heart rate Anxiety, fear, anger Exercise Increased body temperature Grief Decreased body temperature Venous Return to Heart Blood pumping action of respirations Skeletal muscle contraction Blood pressure Sphygmomanometer Systolic pressure: force with which the blood is pushing against the artery when ventricles are contracting Diastolic pressure: force of blood when ventricles are relaxed Pulse Alternate expansion & recoil of an artery Two factors are responsible Intermittent injections of blood from heart Elasticity of arterial walls Pulse sites Radial artery- wrist Temporal arterytemples Carotid artery- neck Brachial arteryelbow Popliteal arterybehind knee Dorsalis pedis- top of foot