File
advertisement

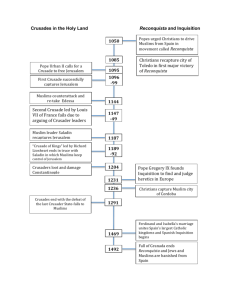
Warm-Up – 23.Sept.2014 You have 4 minutes after the tardy bell to complete the warmup. You have 2 minutes after that to check your. Questions based on Monday’s notes. Answers Questions (1) England & France; France (1) The Hundred Years (2) Civil War (b/w Houses of York War was between ___ & Lancaster) & ___. Who won? (3) - Killed over 1/3 of the (2) The War of Roses was population what type of war? - Anti-Semitism & ppl. start to (3) How did the Plague question the church effect Europe? (3 - Beginning of the end of the reasons) manorial system ROLE OF THE CHURCH System of Organization • Christianity had become the main religion of the Roman Empire – Spread to other parts of Europe – Christianity appealed to many during the medieval times since many people’s lives were filled with suffering and hardship and Christianity offered them the promise of a happy afterlife • The Church developed a system of organization – Priest was the head of a local community called a parish – Bishop – in charge of a group of parishes, area of authority called a bishopric or dioceses – Archbishop – watches over a group of bishoprics – The pope was the head of the entire Roman Catholic Church – formerly the Bishop of Rome – Monk – a man who separates himself from everyday life to dedicate himself entirely to God, lives in a monastery run by an abbot • Spent lots of time in prayer and physical labor, took a vow of poverty • Monks worked to spread Christianity throughout Europe –Called missionaries = people sent out to carry a religious message – Women who dedicated themselves to God were called nuns and lived in convents • Pope Innocent III strengthened papal power and believed that the pope was the supreme judge and ruler of European affairs – Used the interdict to exercise his powers • An interdict forbids priests to give the sacraments (Christian rites) to a particular group of people – A pope used an interdict against a country whose ruler has disobeyed him – People under interdiction lost the comforts and blessings of religion – They exerted pressure on their ruler to follow the pope’s wishes – Could also excommunicate people = to cast out of the Church Heresy and The Inquisition • Heresy = denial of basic Church doctrines, or beliefs that opposed the official teachings of the Church – People who committed heresy were called heretics and were usually burned at the stake • The Inquisition was a court created by the Catholic Church to find and try heretics – Used torture and heretics who converted to Catholicism were freed, while others were killed – The Spanish Inquisition was the most brutal and was still operating in the 1800s • The two groups it went after most were Jews & Muslims Decline of Church Power • Over time Popes became corrupt and used their position for wealth and power • The Great Schism divided Europe religiously and damaged the reputation of the Church – This was when there were two popes, both claiming power The Crusades • From the 11th to 13th centuries, European Christians went on the Crusades – The Crusades were a series of military campaigns to regain the Holy Land from the Muslims who were known as infidels (non-believers) – The goal of each Crusade was to take Jerusalem and the surrounding area away from the Muslims • Many Christians believed that Jesus would only come again once Christians held Jerusalem • The Muslims also considered Jerusalem holy • The First Crusade started when Muslim Turks attacked the Byzantine Empire – The Byzantine Emperor asked for help and Pope Urban II responded by urging Christians to take up arms in a holy war (1095) • Slogan: “God wills it!” – Two groups set out for the Crusade • Peasant Crusaders – slaughtered entire Jewish communities on the way to Jerusalem –Most died quickly when they did reach the Holy Land • Trained knights – even they were still unprepared for the hardship – Three years after heading out, the Crusaders finally reached Jerusalem • Captured Jerusalem & killed most of its inhabitants – Set up four Latin Crusader states that were surrounded by Muslims and were intended to be strongholds against future Muslim aggression • Second Crusade – A few years later the Muslims began to recapture lands – The Second Crusade is organized after one of the Latin Crusader states falls to the Muslims – It was a complete failure – took no lands from Muslims • Third Crusade – A new leader emerges among the Muslims – Salah adDin, whom the Europeans call Saladin • His goal was to recapture the Holy Land • In 1187 he captured Jerusalem – Due to this, the Third Crusade is launched and several monarchs set out for the Holy Land • Only Richard made it to and fought in the Holy Land – King Richard and Saladin fought fiercely against each other and although Richard won several battles, he was not able to take Jerusalem – Richard instead negotiates an agreement with Saladin for Christian pilgrims to be allowed to go into Jerusalem and he returns home • Children’s Crusade – Nicholas of Cologne brings thousands of children to the pope, saying that God has inspired him to lead the children to the Holy Land • The pope sends them home – At the same time, seven ships carrying 20,000 French children sails for the Holy Land • Two ships sink and the other five ships reach North Africa, where the rest of the children were sold into slavery • Effects of the Crusades – There were nine Crusades launched from 1096 to 1291 – the First Crusade was the only successful one – The Crusades increased trade and some Italian cities benefited economically – Lots of money and manpower spent on the Crusades – Led to the deaths of many knights and nobles • Kings gained power as they took over unoccupied lands – Brought knowledge of Muslim culture to Europe – Began to view all non-Christians as enemies • Undertaking holy wars against Muslims while the “murderers of Christ” ran free at home • Massacres of Jews became a feature of medieval European life, anti-Semitism increases • Anti-Semitism = hostility towards Jews – Breeds centuries of mistrust between Christians & Muslims Crusade First Second Third Fourth Children’s Reason For People Involved Result Revival and Growth of Trade • After the Crusades trade began to grow • Most of the early trading cities were found in Italy, with Venice being the most important – Other Italian cities, wanting to get wealthy, created their own trade routes • Trade in the north was dominated by the Hanseatic League – Group of northern German cities and towns that worked together to promote and protect trade • Trade encouraged people to use money again – Before, workers had been paid with goods – This led to some merchants allowing their customers to buy goods on credit • Credit = the promise of later payment – This also led to the creation of Europe’s first banks Medieval Trade • In the 12th century, craftspeople organized into business associations called guilds that played a leading role in urban economics – The primary functions of a guild was to restrict competition – Craft guilds set quality standards, specified methods of production, fixed the price of the finished product, and determined who could enter the guild • A person who wanted to learn a trade first became an apprentice to a master craftsperson around the age of 8 – They received room and board, but no pay – After 5 to 7 years, apprentices became a journeyman who worked for pay for other masters – To become a master, they had to produce a masterpiece which the guild would judge