Powerpoint
advertisement

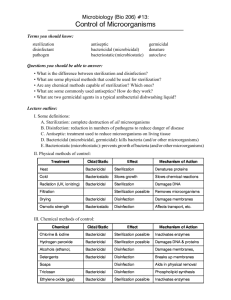
Using Disinfectants and practicing Sterilization in the Veterinary Clinic Next Generation Science / Common Core Standards Addressed! CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RH.11-12.9 INTEGRATE INFORMATION FROM DIVERSE SOURCES, BOTH PRIMARY AND SECONDARY, INTO A COHERENT UNDERSTANDING OF AN IDEA OR EVENT, NOTING DISCREPANCIES AMONG SOURCES. CCSS.ELA-LITERACY.RH.11-12.4 DETERMINE THE MEANING OF WORDS AND PHRASES AS THEY ARE USED IN A TEXT, INCLUDING ANALYZING HOW AN AUTHOR USES AND REFINES THE MEANING OF A KEY TERM OVER THE COURSE OF A TEXT . Agriculture, Food, and Natural Resource Standards Addressed • AS.07.01. Design programs to prevent animal diseases, parasites and other disorders and ensure animal welfare. • AS.07.01.05.b. Assess the safety and effectiveness of facilities and equipment used for surgical and nonsurgical veterinary treatments and procedures. Bell Work! • Why are multi-drug resistant bacteria a concern? • Why is it important to clean all surfaces prior to disinfection or sterilization? • How may surgical instruments be cleaned? • Where can an infectious organism live? • What are the various methods of sterilization? Terms: • Alkaline • Antiseptic • Aseptic • Chlorine • Disinfectant • Formaldehyde • Germicidal • Iodine • Pathogenic • Sterilization • Ultrasonic Disinfectants: • A chemical compound applied to an inanimate surface to reduce/eliminate pathogenic organisms is known as a disinfectant. • The act or process of destroying pathogenic organisms is known as “Disinfection”. • An inanimate surface such as a table may become contaminated with fungi, bacteria and viruses. • Feeding utensils, cages and floors are very easily contaminated. • A disinfectant is only effective when applied to a clean surface. Classes of Disinfectants • Alkalies are compounds having a high pH (basic). Examples would be lime, soda, potash, lye. • Lime is applied to the soil. • A lye solution would be used to disinfect rubber products such as boots, aprons reusable gloves. • Alkaline products are irritating to the skin and should not be in an area where animals will come into contact with the solution. Classes of Disinfectants: • Chlorine is an effective bleaching agent as well as one of the most effective disinfectants. • A solution of household bleach at a level of .05 - .2% is a very effective disinfectant. • Bleach has an offensive odor that may be irritating. Classes of Disinfectants: • Formaldehyde is very similar to chlorine. • A 5 % solution is very effective in disinfecting rubber boots, feeding supplies but it does have a very strong odor. Classes of Disinfectants: • Quaternary ammonium can be diluted to a level of 1:5000 and be effectively used on hard surfaces such as tables, cages, utensils and flooring. Handling Disinfectants Properly: • When handling disinfectants always wear rubber gloves. Follow the directions to properly dilute the product that you will be using. The following guidelines will help you in using disinfectants properly; • Mix the solution properly, too weak will fail to be effective, too strong is a waste of money. • Do not combine chemicals, the reaction could weaken the product or cause and adverse reaction. • Allow the solution to be in place for the proper amount of time. • Do not store the mixed solution as it will loose its effectiveness. • Organic material such a manure will reduce the solutions effectiveness, clean prior to disinfecting any area. Sterilization of tools and equipment: • Sterilization is the process of using either chemical or physical agents to kill all microorganisms whether they be viral, fungal or bacterial. • Disinfectants are applied to inanimate materials, antiseptics are applied the living body, both inhibit microorganism growth. • Skin can never be completely sterile, the absence of harmful microorganisms on the skin is known as “Asepsis”. • Contamination occurs when there is break in sterility or asepsis. • Sterilization helps to maintain “asepsis”. Microorganisms and Infection: • Maintaining a sterile operating area helps prevent wound infection which is common following surgery. • A would can not be completely sterile. • The goal is to minimize the number of bacteria present so that the body’s natural defense system will not be over whelmed. Methods of Sterilization: • Proper sterilization methods can prevent patient exposure to harmful microorganisms. • There are a variety or sterilization methods which the clinic may utilize; • Steam – Steam under pressure is the most commonly used method of sterilization. Steam temperature, exposure time and pressure are important. An Autoclave is a steam device most commonly used. Follow these guidelines; • Fifteen pounds of pressure at 250 degrees for fifteen minutes • Fifteen pounds of pressure at 275 degrees for ten minutes Methods of Sterilization: • Items that include plastic and rubber materials, such as power cables, endoscopes can not be subjected to the temperature and pressure of an autoclave. • A gas sterilizer using “Ethylene oxide” is used for these items. Ethylene Oxide is flammable and can cause health problems. It’s use is regulated and controlled. Methods of Sterilization: • A safe method of sterilizing heat sensitive materials is by plasma sterilization. • Reactive ions sterilize items in 45 minutes and 122 degrees. Methods of Sterilization: • Prepackaged sterile items such as suture packets and surgical gloves have been sterilized with ionizing radiation. • Cold chemical sterilization as another method of sterilizing items that cannot be exposed to steam. The most common method is immersion in a glutaraldehyde solution. • Following sterilization it is important to store surgical tools, instruments in areas that will maintain an aseptic environment until needed again. Antiseptics: • Antiseptics used for patient treatment prevent the growth of microorganisms and should not harm the patient. • The ideal antiseptic would be: • Non-irritating • Cost effective • Have a long shelf life • Cleansing • Active against pathogen growth • Safe for the patient and surgical team Common Disinfectants • The most common disinfectants used in the veterinary clinic would include; • Alcohol is an effective disinfectant for spot cleaning and small areas. • Chlorine compounds as mentioned previously are effective but may also be corrosive. • Iodine is effective but will stain clothing, surfaces and the skin. Preparing Surgical Instruments! • Surgical instrument must be free of all foreign materials before sterilization. Blood, feces, oil and any other residue must be removed. • Contaminated tools should bed soaked in a detergent solution prior to sterilization. • Avoid leaving tools in the pre-soak solution for more than an hour as non coated area will corrode/rust. • Effective methods of cleaning include hand scrubbing and ultrasonic cleaning • The ultrasonic cleaner will heat a solution during the process. The End!