Ch. 19 Note Outline
advertisement

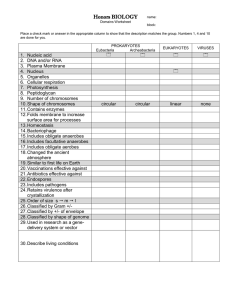
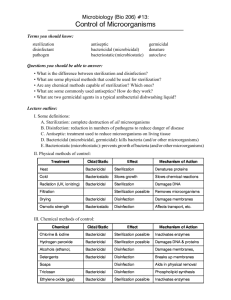
Chapter 19 Note Outline Bacteria What is the ultimate outcome of metabolic activity for bacteria? What does growth refer to? Nutrients are _______________ and used for _______________. How do Bacteria Get Energy? Autotrophs = Heterotrophs = Chemotrophs Phototrophs = What is the most common element in cells and never a limiting nutrient? Bacterial Environments Organotrophs = Lithotrophs = Obligate Aerobes = Obligate Anaerobes = Facultative anaerobes = Aerotolerant = Microaerophiles = Peroxide = Nitrogen What element is often growth-limiting? These six elements make up 95% of the dry weight of cells. Definitions Trace elements = Growth factors = Minimum growth temperature = Maximum growth temperature = Optimum growth temperature = Loving Environments Psychrophiles = Ex. Mesophiles = Ex. Thermophiles = Ex. Hyperthermophiles = Ex. Neutrophiles = Acidophiles = Features of hyperthermophiles that enable them to remain intact: 1. 2. 3. Two regions of body that acidity reduces microbes and malfunctions: 1. 2. How can microbes survive in dry conditions? 1. 2. Hypertonic = Hypotonic = Plasmolysis = Obligate halophiles = Barophiles = Relationships Antagonistic relationship = Synergistic relationship = Symbiotic relationship = Biofilms - Shapes and Arrangement Coccus = Bacillus = Spirillum = Vibrio = Diplo- = Staphylo- = Strepto- = Reproduction Binary fission: 1. 2. 3. 4. Spores = Budding = Endospore formation: 1. 2. 3. 4. Exponential Growth When does this occur? Carrying capacity = Phases of Growth: (draw a curve to the side and label each phase) 1. 2. 3. 4. Archae What don’t they have? Extremophiles = Thermophiles = Halophiles = Methanogens = Physical Methods for Control 1. Heat is used for sterilization, canned goods Thermal Death Point = Thermal Death Time = Decimal Reduction Time = 2. Moist Heat 1. Boiling 2. Autoclaving How do you know when something has been sterilized? 1. 2. Pasteurization = Flash Pasteurization = Ultrahigh-Temperature Sterilization = 3. Dry Heat Other Methods 1. Refridgeration = 2. Dessication = 3. Lyphilization = 4. Filtration = 5. Osmotic Pressure = 6. Radiation = 1. Ionizing Radiation = 2. Nonionizing Radiation = 7. Sterilization = 8. Aseptic = 9. Disinfection = 10. Antiseptic = 11. Degerming = 12. Sanitization = Microbial Death =