Does it eat seeds?

NOTE:
This presentation was not made for public use. Please do not use this presentation without my permission and the permission of each of the authors of the photographs, quotes, and other materials that they contain.
Thank you,
Vicki Hughes
Labs, Activities, and special WS for this presentation:
Dichotomous Key WS
Classification Video WS
Biological Evolution
Remember…
TIME
Evolution is change over time.
Recipe for Evolution 2:32 http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/selection/recipe/
What changes over time?
Animals
Telephones
Plants
What DOES NOT change over time ?
Conservation of Mass
weblo.com
• Many creatures that lived in the past don’t exist today.
dalje.com
www.geekologie.com
Many creatures that exist today look different from those in the fossil records.
painofpoetry.wordpress.com/2008/06/
57poets.files.wordpress.com
wildlifephototour.com
CHARLES DARWIN
Proposed a way to explain HOW evolution works
How did creatures change over time?
natural selection
Collected a lot of evidence to support his ideas
1809-1882
British naturalist biblauragraphy.files.wordpress.com
VOYAGE OF THE HMS BEAGLE
Invited to travel around the world
1831-1836 makes many observations of nature
main mission of the Beagle was to chart South American coastline
Robert Fitzroy
HMS Beagle mun.ca
VOYAGE OF THE HMS BEAGLE
Stopped in Galapagos Islands
500 miles off coast of Ecuador www.frontierdiving.com
DE Jeff Corwin Experience (Galapagos)
FIELD RESEARCH IN GALAPAGOS
Galapagos Research
Video www.frontierdiving.com
Darwin developes an idea.
• Adaptations
– traits that help individuals survive
• survive predators
• survive disease
• compete for food
• compete for territory
– traits that help individuals reproduce
• attracting a mate
• compete for nesting sites
• successfully raise young www.standardbredcanada.ca
farm3.static.flickr.com
mesh.biology.washington.edu
sagribow.sulekha.com
Adaptations
3.bp.blogspot.com
www.alaskanadventuretours.com
Survival & Reproduction of the fittest msnbcmedia.msn.com
firemice.wordpress.com
www.arktimes.com
pixdaus.com
Adaptations the traits that help an organism FIT the environment better to survive & reproduce www.uwyo.edu
Artificial vs. Natural Selection 6:10 http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/variation/recipe/
A little fun with camouflage…
conservationreport.com
bisbeemedia.com
www.dpughphoto.com
EOG L30 designboom.com
Natural Selection
Main Points of Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection
1. Over production .
Most organisms produce more offspring than can survive.
Main Points of Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection
2. Competition .
Organisms compete for food and resources.
Main Points of Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection
3. Variation .
There is genetic variation among individuals of a species.
Gene Pool = all genes found in a population
Mutations = changes in DNA
Main Points of Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection
4. Adaptation .
Individuals with traits best suited to the environment will survive and those without those traits will not.
Classic Example of Natural Selection’s effects on a population:
No lichen.
English Peppered Moth
Lichen cover.
ACT 35
Fossils and Speciation
Extinction = loss of all members of a species
99.9% of all species that have ever lived have gone extinct.
Mass extinction = large numbers of species go extinct.
Speciation = formation of a new species
Behavioral Isolation = isolation due to differences in
BEHAVIORS .
http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2007/02/070221-riflebird-video.html
astadnik.wordpress.com
Geographic Isolation = isolation due to differences in
LOCATIONS.
http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/content/chp24/2402002.html
Speciation = formation of a new species
Temporal Isolation = isolation due to differences in
SCHEDULES.
muleabides.wordpress.com
Liger
Parapatric Speciation = isolation due to differences in
ENVIRONMENTS.
evolution.berkeley.edu
http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/pages/bcsmain.asp?s=00020&n=01000&i=01020.01&v=category&o=%7C00510%7C00570%7C00520%7C00530%7C00540%7C00550%7C00580%7C00130%7C00PRS
%7C00560%7C00590%7C00010%7C00020%7C00030%7C00040%7C00050%7C00060%7C00070%7C00120%7C00080%7C00090%7C00100%7C00110%7C01
000%7C02000%7C03000%7C040&ns=0&t=&uid=0&rau=0
Darwin’s Finches = beaks had adapted to food resources
Species evolve in stages, usually with many new species developing along the way.
Hominid primates
Homo habilis
Homo erectus
Homo Homo sapiens neanderthalensis
Whale Evolution https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8cn0kf8mhS4
Pakicetus
Rhodocetus
Dorudon
Modern whale
Gradualism = gradual changes
Punctuated Equilibrium = points of change followed by periods of no change
ACT L36
Evidence of Evolution
HOMOLOGOUS Structures = same shape but different functions.
ANALOGOUS Structures = different shape but same functions.
Vestigial organs = organs that are still present but are no longer useful.
Comparative Embryology
Development of embryo tells an evolutionary story
Fish
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
• Development of embryo tells an evolutionary
Calf story
Salamander
Hog
– similar structures during development
Tortoise
Rabbit chicken
EOG L31
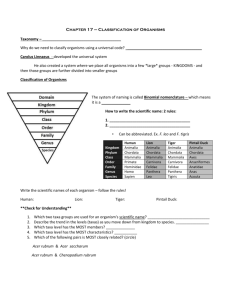
Classification
Classification = systematic grouping of organisms based on common characteristics
Taxonomist = scientists who study how to classify organisms.
Kingdoms
Linnaeus
…
Developed the binomial nomenclature
(named for Genus species ) system:
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus species
(Did King Phillip Come Over
For Good spaghetti?)
Know your human classification:
Domain: Eukarya
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Primates
Family: Hominidae
Genus: Homo
Species: sapiens
Classification Level Keys = compare organisms according to their levels of classification.
Family Tree = shows relationships of one group
Cladogram = shows relationships of several groups
SciShow Human Evolution https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ROwKq3kxPEA
Spider Keys = identify organisms using a system of questions that have only two answers...
drawn as a diagram .
Does it have wings?
Does it live in water?
Does it eat seeds?
Great Plains
Bison
Rainbow
Trout
Eagle Is it red?
Yellow Warbler Cardinal
Dichotomous Keys = identify organisms using a system of questions that have only two answers.
Great
Plains
Bison
Does it live in water?
Does it have wings?
Rainbow
Trout
Eagle
EOG L32 & ACT L37
Does it eat seeds?
Yellow
Warbler
Is it red?
Cardinal
Q1. Does it have wings?
No…Go to Question 2a.
Yes…Go to Question 2b.
Q2a. Does it live in water?
No…Great Plains Bison
Yes…Rainbow Trout
Q2b. Does it eat seeds?
No…Eagle
Yes…Go to Q3.
Q3. Is it red?
No…Yellow Warbler
Yes…Cardinal
Animal Phyla
Sponges simplest animals
Cnidarians hydra jellyfish sea anemones corals
Flatworms
Roundworms
Segmented worms
Mollusks
Arthropods
Echinoderms
Chordates
Vertebrates
ACT L38
Any
Questions?
10:00 Evolution Irreducible Complexity http://topdocumentaryfilms.com/evoluti on-irreducible-complexity/