Evolution - Gander biology
advertisement
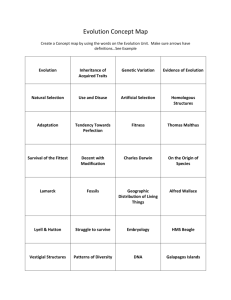
Evolution Theory • Well supported testable explanation of phenomena that have occurred in the natural world Biosphere • Part of earth in which life exists – EX: Land, water, air Evolution • A change over time • Most often used to refer to a change in a species over time • EX: Dinosaurs change into birds Charles Darwin • One of the first scientist to publish his ideas about evolution in The Origin of Species • He developed his theory of evolution from observations he had made during his world travels Charles Darwin (cont.) • Darwin traveled around the world on a ship called the HMS Beagle • He observed a wide variety of organisms, and noted characteristics that occur in similar species of plants and animals Galapagos Island • In five years of traveling on the HMS Beagle, the Galapagos Islands proved to be the most influential on Darwin’s ideas about evolution Galapagos Finches • Although the islands were close together, each island had its own distinct animal and plant populations – EX: Galapagos Finches – They had different beaks suited to the different foods they consumed Natural Selection • States that organisms with favorable traits are more likely to survive, reproduce, and pass those traits onto their offspring Survival of the Fittest • Also known as Natural Selection Fitness • An organism’s reproductive success • Organisms with greater fitness reproduce and pass on their traits to their offspring Adaptation • The process by which a population becomes better suited to its environment which increases chances of survival – EX: Peppered moth AND giraffes with long necks Mutation • A change in DNA. This is the only way of introducing a new trait to a species Recombination • Genes are rearranged during meiosis to create unique offspring and the species is more likely to survive a catastrophe, such as a disease – EX: Crossing over Evidence of Evolution Fossil Record • Older remains or fossils always lie beneath the newer remains or fossils • This allows us to determine the age of a fossil in relation to the other fossils Homologous Structure • Similar structure BUT different function • Evolve from a common ancestor – EX: Whale fins and human arms Analogous Structure • Different structures BUT same function • Share a similar environment – EX: Butterfly wing and bird wing Vestigial Structure • Structures in species that serve no function – EX: Leg and hip bones in whales AND appendix in humans Embryology • Study of similarities between organisms during early stages of development – EX: Humans and fish both have gills in early development Artificial Selection • Selection by humans for breeding of useful traits – EX: Pure breed dogs AND artificial crops