ABNORMAL PSYCHOLOGY
advertisement

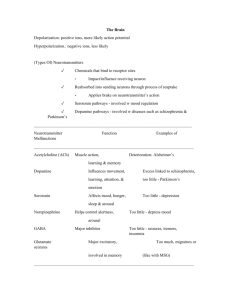
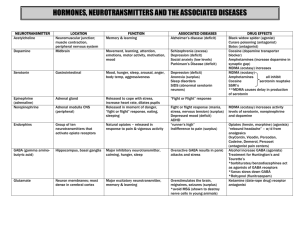
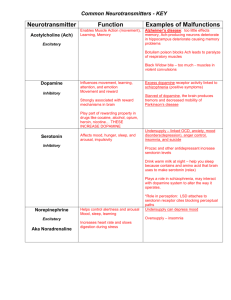
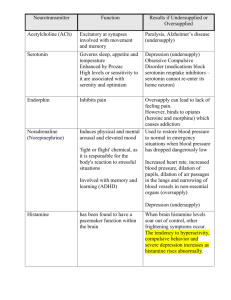
• Breuer and Freud: • Freudian Theory – – – Ego id • ID – – – • ID • EGO – Reality Principle – – • SUPEREGO – – • Ego’s Battles • Keep Id in Check via: – – – – • ORAL STAGE (Birth-18 Months) • ANAL STAGE (18 Months-3 Years) • PHALLIC STAGE (3-6 Years) – Odeipus and Electra Complexes • LATENCY PERIOD • GENITAL STAGE (Puberty) • EGO OR SELF-PSYCHOLOGY – Anna Freud • OBJECT RELATIONS – Klein and Kernberg • JUNG AND ADLER Contributions of Freud’s Theories • Focus on the individual’s inner workings. He tapped into our complexities by identifying our competing and conflicting thoughts and emotions created & popularized therapy • defense mechanisms prompted thought about how anxiety is controlled on a conscious level • made us think about how children develop: • posited the existence of the unconscious….evidence: – Subliminal perception – Implicit memory (vs explicit, consciously recalled material) – Dissociative phenomena – Automatic Processes Limitations of Freud’s Theories • • Concepts too subjective and unscientific, cannot be objectively measured and validated. • Skewed clinical sample, not representative of all HUMANITY, as his ideas were thought to be / relied heavily on early childhood reports but saw no children / personality dev’t theory is highly implausible and impossible to verify / guilty of forcing seduction scenarios onto his patients? Patients often didn’t accept his interpretations /Whatever pts. said, Freud interpreted to fit his current theory • Psychoanalytic theory and therapy ______________________________________________________________ • PERSON-CENTERD THERAPY – – – – • CLASSICAL CONDITIONING – Pavlov & Watson – Contemporary Views • OPERANT CONDITIONING – Skinner and Behavior Analysis Behavior Environment Emotion Cognition Biology • Rejection of Psychoanalysis • Wolpe and Behavior Therapy – Systematic Desensitization • Later Hybrids COGNITIVE EMOTIVE INSIGHTS "People are not upset by things but by their idea of things." Epictetus "Our life is what our thoughts make it." Marcus Aurelius "There is nothing good or bad but thinking makes it so." Shakespeare "The mind is its own place and in itself can make a heaven of hell, or hell of heaven." Milton "The ancestor of every action is a thought - a man is what he thinks about all day long." Emerson COGNITIVE EMOTIVE INSIGHTS “Man is the inventor of his own happiness.” Thoreau "Most folks are about as happy as they make up their minds to be." Lincoln "You are not what you think you are, but what you think, you are." Norman Vincent Peale "My life has been filled with terrible misfortunes, most of which never happened." Mark Twain “A person’s behavior springs from his/her ideas.” Alfred Adler • Lack of Social Support – Depression and Suicide – Illness and Suppressed Immune Function – Variety of Other Disorders • Increasing Social Support Helps - Social Influences Biological Influences Behavioral Influences Cognitive & Emotional Influences • Abnormal Behavior is a Disease • Treat the Disease, Cure the Problem – 1930s: _________________________ – 1950s: _________________________ – 1970s: _________________________ • Abnormal Behavior is a Disease • Problem is Biological (Brain), not Psychological • More Pharmacologic Remedies • Language of Medicine • No Single Gene • 50% Contribution We Inherit Predispositions, not Psychological Disorders • Diathesis-Stress Model • ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ________________________________ • Diathesis-Stress Model • Reciprocal Gene-Environment Model – Genes Lead us to Take Risks – – • Family Studies – Index Cases or “Probands” • Pedigree Studies ____________________ • Twin Studies – ___________________________ • Adoption Studies – More Compelling Approach Neuroscience Perspective • NERVOUS SYSTEM CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM – Brain – Spinal Cord Neuroscience Perspective • Central Nervous System • PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM – Autonomic System • _________________________ • _________________________ – Somatic System Agonists – Increase Activity of a Neurotransmitter Antagonists – Decrease or Block a Neurotransmitter Inverse Agonists – Produce Effects Opposite the Neurotransmitter Norepinephrine (noradrenaline) Serotonin Dopamine Gamma Aminobutyric Acid (GABA) • Major Neurotransmitters in Psychopathology Norepinephrine (noradrenaline) – Helps regulate emotion & arousal states – Alpha and Beta Andrenergic Receptors – Beta Blockers Serotonin – Regulates Thought, Emotion, and Behavior – Low levels: Impulsivity, Aggression, Suicide, Overeating – SSRI Drugs - Prozac – 15+ different receptors Norepinephrine (noradrenaline) Dopamine – – – – Exploratory, Pleasure-Seeking L-DOPA (Dopamine Agonist) Parkinson’s Disease (too little) Schizophrenia (too much) Serotonin Norepinephrine (noradrenaline) GABA – Reduces Overall Arousal and Emotion (inhibitory) – Valium, Librium, Xanax Make More GABA Available – Anxiety and Stress Dopamine Serotonin Norepinephrine (noradrenaline) Where Does a Psychological Approach to Abnormal Behavior Fit? Interaction of Psychosocial Factors and Brain Function • Rhesus monkeys, control, and GABA • Rats in complex environments vs. “couch potatoes”: ______________________________ • The battle of crayfish and serotonin levels • One-Dimensional Models ONE CAUSE Multidimensional DISORDER Models MANY CAUSES • Many Paths to a Given Problem – Principle of Equifinality Social Factors Age and Development Genes and Biology Cogniton, Emotion, and Behavior Perspective: The Blind Men and the Elephant Social Factors Age and Development Genes and Biology Cogniton, Emotion, and Behavior