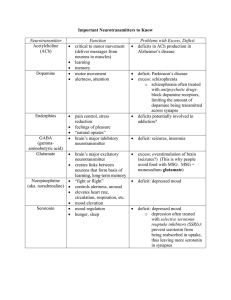
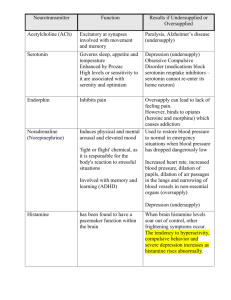
The Brain Depolarization: positive ions, more likely action potential
advertisement

The Brain Depolarization: positive ions, more likely action potential Hyperpolarization.: negative ions, less likely (Types Of) Neurotransmitters ✓ Chemicals that bind to receptor sites ⁃ ✓ Reabsorbed into sending neurons through process of reuptake ⁃ ✓ ✓ Parkinson’s Impact/influence receiving neuron Applies brake on neurotransmitter’s action Serotonin pathways - involved w mood regulation Dopamine pathways - involved w diseases such as schizophrenia & ____________________________________________________________________________ Neurotransmitter Malfunctions Function Examples of _____________________________________________________________________________ Acetylcholine (ACh) Muscle action, Deterioration: Alzheimer’s learning & memory Dopamine Influences movement, Excess linked to schizophrenia, learning, attention, & too little - Parkinson’s emotion Serotonin Affects mood, hunger, Too little - depression sleep & arousal Norepinephrine Helps control alertness, Too little - depress mood arousal GABA Glutamate seizures Major inhibitor Major excitatory, involved in memory Too little - seizures, tremors, insomnia Too much, migraines or (like with MSG) _____________________________________________________________________________ Glands Pituitary Ctrls all other glands Water, salt water balance Thyroid (& para-) Metabolism & calcium rate Adrenal freaking out (epinephrene, norepinephrine) salt & carbohydrate metabolism Gonads development and regulation of sex organs Endocrine System slow chemical communication system hormones synthesized by endocrine glands, are secreted into blood stream affect brain & other body tissues regulated by the hypothalamus