Neurotransmitter Function Results if Undersupplied or Oversupplied
advertisement
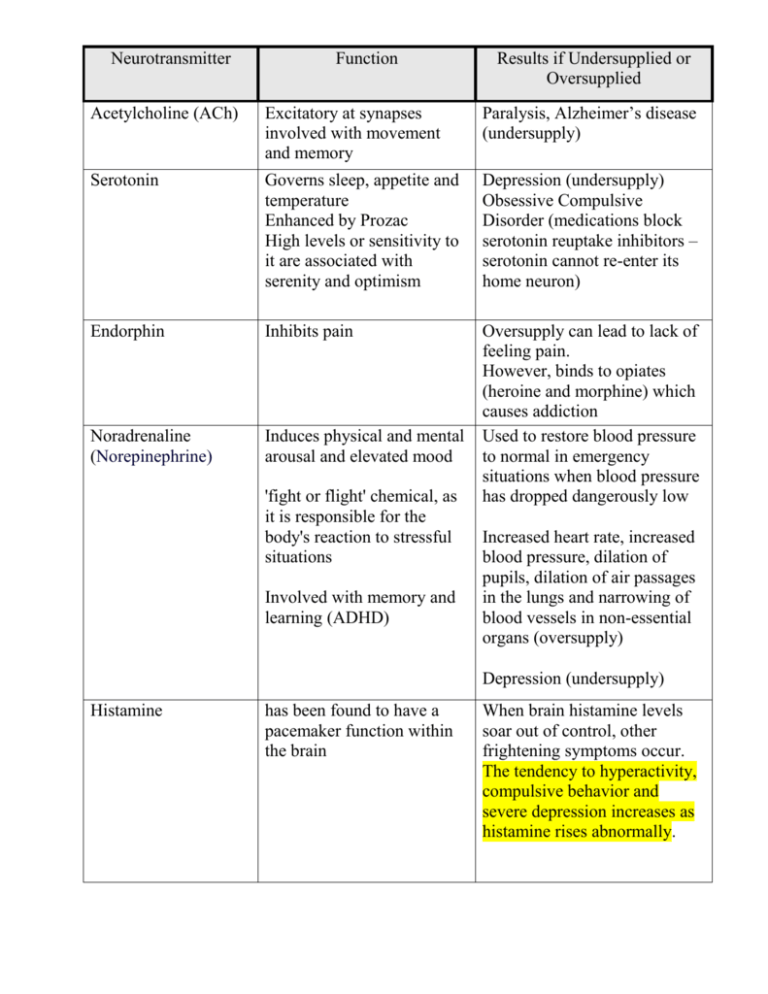
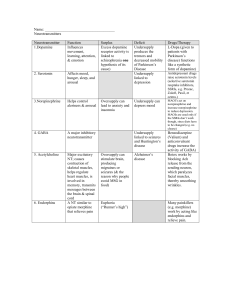
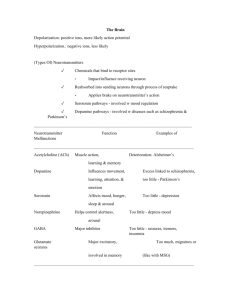
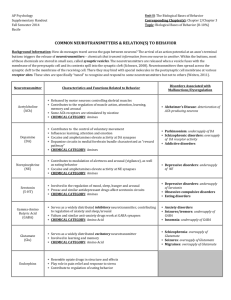
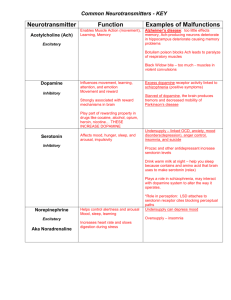
Neurotransmitter Function Results if Undersupplied or Oversupplied Acetylcholine (ACh) Excitatory at synapses involved with movement and memory Paralysis, Alzheimer’s disease (undersupply) Serotonin Governs sleep, appetite and temperature Enhanced by Prozac High levels or sensitivity to it are associated with serenity and optimism Depression (undersupply) Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (medications block serotonin reuptake inhibitors – serotonin cannot re-enter its home neuron) Endorphin Inhibits pain Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine) Induces physical and mental arousal and elevated mood Oversupply can lead to lack of feeling pain. However, binds to opiates (heroine and morphine) which causes addiction Used to restore blood pressure to normal in emergency situations when blood pressure has dropped dangerously low 'fight or flight' chemical, as it is responsible for the body's reaction to stressful situations Involved with memory and learning (ADHD) Increased heart rate, increased blood pressure, dilation of pupils, dilation of air passages in the lungs and narrowing of blood vessels in non-essential organs (oversupply) Depression (undersupply) Histamine has been found to have a pacemaker function within the brain When brain histamine levels soar out of control, other frightening symptoms occur. The tendency to hyperactivity, compulsive behavior and severe depression increases as histamine rises abnormally. Dopamine Involved with learning, emotional arousal and movement Schizophrenia (oversupply) and Parkinson’s disease (undersupply) ADHD drugs fall into a class of medications known as stimulants. ADHD stimulants boost levels of two neurotransmitters, or chemical messengers in the brain, known as dopamine and norepinephrine. Dopamine is thought to play a role in memory formation and the onset of addictive behaviors, while norepinephrine has been linked with arousal and attentiveness.