Test 1 Ch 4 - TeacherWeb
advertisement

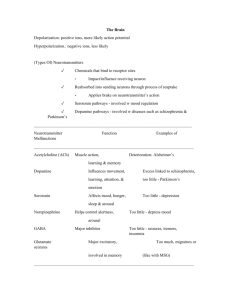
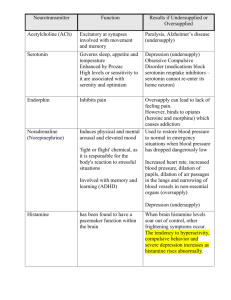
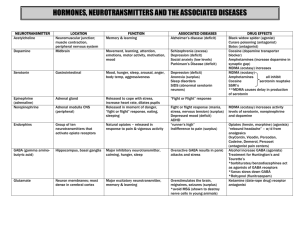
What is Dopamine responsible for? Involved in fine muscle movement; Involved in the integration of emotions and thoughts; Involved in decision making; Stimulates hypothalamus to release hormones (sex, thyroid, adrenal). What is Norepinephrine responsible for? Level in brain affects mood; Attention and arousal; Stimulates sympathetic branch of autonomic nervous system for "fight or flight" in response to stress What is Serotonin responsible for? Plays a role in sleep regulation, hunger, mood states, and pain perception; Hormonal activity; Plays a role in aggression and sexual behavior What is Histamine responsible for? Involved in alertness; Involved in inflammatory response; Stimulates gastric secretion What is a Decrease in Dopamine responsible for? Parkinson's disease and Depression What is an Increase in Dopamine responsible for? Schizophrenia and Mania What is a Decrease in Norepinephrine responsible for? Depression What is an Increase in Norepinephrine responsible for? Mania, Anxiety states, and Schizophrenia What is a Decrease in Serotonin responsible for? Depression What is an Increase in Serotonin responsible for? Anxiety states What is a Decrease in Histamine responsible for? Sedation and Weight gain What is GABA (an amino acid) responsible for? Plays a role in inhibition, reduces aggression, excitation, and anxiety; May play a role in pain perception; Has anticonvulsant and muscle-relaxing properties; May impair cognition and psychomotor functioning What is a Decrease in GABA (an amino acid) responsible for? Anxiety disorders, Schizophrenia, Mania, and Huntington's disease What is an Increase in GABA (an amino acid) responsible for? Reduction of anxiety What is Glutamate (an amino acid) responsible for? Is excitatory; Plays a role in learning and memory What is an Increase in Glutamate (an amino acid) responsible for? Prolonged increase state can be neurotoxic; Neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease; Improvement of cognitive performance in behavior tasks What is a Decrease in Glutamate (an amino acid) responsible for? Psychosis What is Acetylcholine (anticholinergic) responsible for? Plays a role in learning, memory; Regulates mood: mania, sexual aggression; Affects sexual and aggressive behavior; Stimulates parasympathetic nervous system What is a Decrease in Acetylcholine (anticholinergic) responsible for? Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, and Parkinson's disease What is an Increase in Acetylcholine (anticholinergic) responsible for? Depression What is Substance P (peptides) responsible for? Promotes and reinforces memory; Involved in regulation of mood and anxiety; Role in pain management What is Somatostatin (peptides) responsible for? Altered levels associated with cognitive disease What is a Decrease in Somatostatin (peptides) responsible for? Alzheimer's disease; some association with depression What is an Increase in Somatostatin (peptides) responsible for? Huntington's disease What is Neurotensin (peptides) responsible for? Endogenous antipsychotic-like properties What are the adverse effects of Lithium? Tremor, ataxia, confusion, convulsions, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, arrhythmias, polyuria, polydipsia, edema, goiter, and hypothyroidism What are Neurons? Nerve cells that respond to stimuli, conduct electrical impulses, and release chemicals called neurotransmitters. What are Circadian Rhythms? The fluctuation of various physiological and behavioral parameters over a 24 hr cycle. Include body temp and sleep/wake cycle. What is the Limbic System? Areas of the cerebrum that play a crucial role in emotional status and psychological function What is the Brainstem responsible for? Regulates the internal organs and is responsible for such vital functions as the regulation of blood gases and the maintenance of blood pressure. What is the Cerebellum responsible for? Regulation of skeletal muscle coordination and contraction and the maintenance of equilibrium. What is the Cerebrum responsible for? Mental activities and a conscious sense of being. Responsible for our conscious perception of the external world, our own body, emotional status, memory, control of skeletal muscles, language and the ability to communicate How are PET scans different from CT scans and MRIs? PET scans can detect functional abnormalities in the brain while CT scans and MRIs detect structural abnormalities in the brain. What is Pharmacokinetics? Refers to the actions of the person on the drug What is Pharmacogenetics? Explains how genetic variation leads to altered drug responses in different individuals and ethnic groups What do Benzodiazepines do? They potentiate, or promote the activity of GABA by binding to a specific receptor on the GABA(a) receptor complex. Examples include Valium, Xanax, and Klonopin What is occasionally combined with Benzodiazepines that needs to be monitored for life threatening CNS depression? Other CNS depressants such as alcohol, opiates, or tricyclic antidepressants What is Buspirone (BuSpar)? A drug that reduces anxiety without having strong sedative-hypnotic properties. It is not a CNS depressant and therefore does not have as great a danger of interaction with other CNS depressants as Benzodiazepines do. What are Melatonin Receptor Agonists? These drugs mimic the hormone Melatonin (that is only excreted at night as part of the normal circadian rhythm) to help patient's fall asleep. What are Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs)? Antidepressant. Drugs that are thought to act primarily by blocking the reuptake of norepineprhine, therefore increasing the level of norepinephrine at the synapse. What are Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)? Antidepressant. Block the reuptake and the degradation of serotonin, but each specific SSRI has a different effect on neurotransmitters. What are Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors? Antidepressant. Drugs that increase Serotonin and Norepinephrine What are Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)? Antidepressant. Act by inhibiting the enzyme and interfering with the destruction of the monoamine neurotransmitters (norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine, serotonin, etc.), thereby leaving more of them available. What drugs are contraindicated with MAOIs? Antidepressants, sympathomimetic drugs, and oral decongestants What is Lithium used for? A mood stabilizer in patients with bipolar disorder. What is the Therapeutic Index? The ratio of the lethal dose to the effective dose, and is a measure of overall drug safety in regards to the possibility of overdose or toxicity. What how do Anticonvulsant Drugs work? They reduce the firing rate of very-high-frequency neurons in the brain; which possibly accounts for their ability to reduce the mood swings that occur in patients with bipolar disorders. What is carbamazepine (Tegretol) used for? Anticonvulsant. Useful in preventing mania during episodes of acute mania. Reduces the firing rate of overexcited neurons by reducing the activity of sodium channels. What is lamotrigine (Lamictal) used for? Anticonvulsant. Works well in treating the depression of bipolar disorder with less incidence of switching the patient to mania than antidepressants. Modulates the release of glutamate and aspartate. What are First-Generation Antipsychotics? Drugs that are strong antagonists (blocking the action) of Dopamine; Target mostly the positive symptoms of schizophrenia What are some side effects of First-Generation Antipsychotics? Extrapyramidal symptoms; Sedation and Weight gain What are Second-Generation Antipsychotics? Drugs that predominantly block Dopamine and Serotonin. Produce fewer extrapyramidal side effects; and target both the negative and positive symptoms of schizophrenia; Increased chances of developing Metabolic Syndrome * What is a major side effect to watch for in patients taking Clozapine (a 2nd-generation antipsychotic)? Agranulocytosis - requires constant measurement of WBC count What are some side effects of Risperidone (Risperdal) a 2nd-generation antipsychotic? Motor difficulties (ex. extrapyramidal symptoms); Sedation; Orthostatic hypotension; Weight gain What is aripiprazole (Abilify)? 3rd-generation antipsychotic. Known as a dopamine system stabilizer. Side effects include insomnia and akathisia What drug class is used for patients with ADHD? Psychostimulants Function of the brain Monitor changes in the external world, Monitor the composition of body fluids, Regulate the contractions of the skeletal muscles, Regulate the internal organs, Initiate and regulate the basic drives of hunger, thirst, sex, aggressive self-protection, Mediate conscious sensation, Store and retrieve memories, Regulate mood (affect) and emotions, Think and perform intellectual functions, Regulate the sleep cycle, Produce and interpret language, Process visual and auditory data. Cerebrum surface and deep areas of integrating gray matter (the cerebral cortex and basal ganglia; neuronal cell bodies, dendrites, and glial cells) as well as connecting tracts of white matter (link these areas with each other and the rest of the nervous system; myelinated nerve fibers (axons)). Progressive loss of both gray and white matter linked with schizophrenia as well as use of antipsychotic medication. Plasticity (change structurally and functionally as a result of input from the environment.) is evident throughout life as gray matter shrinks or thickens and synaptic connections are pruned or forged, especially in areas where learning and memory occur. Each hemisphere of the cerebral cortex is divided into four lobes: sensory and motor function as well as higher mental activities (e.g., language, decision making, problem solving, and a conscious sense of being). Sensory areas are responsible for specific sensations: the parietal for touch, temporal for sound, and occipital for vision. Frontal Lobe/Motor areas controls voluntary movement. Frontal lobe/ The prefrontal cortex (PFC) coordinates complex cognitive functions (thought process) and enables us to plan and execute goals, insight, motivation, social judgment, voluntary motor ability starts here. Frontal lobe/ When circuitry in the PFC is impaired by a mental disorder (e.g., schizophrenia, major depression, or alcohol intoxication), there is a decrease in: executive function, attention, impulse control, socialization, regulation of drives (such as libido), and emotions. In addition to the gray matter forming the cortex, there are pockets of integrating gray matter lying deep within the cerebrum: (3) the hippocampus, the amygdala, and the basal ganglia. Hippocampus interacts with the PFC for: making new memories. Amygdala plays a major role in: processing fear and anxiety. Parietal Lobe (sensory and motor) receives and id's sensory information; concept formation and abstraction; proprioception and body awareness; reading; mathematics, right and left orientation. occipital lobe vision; interprets visual images, visual associations, visual memories, involved with language formation. temporal lobe auditory; language comprehension, stores sounds into memory (language/speech), connects with limbic system (emotional brain) to allow expression of emotion (sexual, aggression, fear) limbic system (emotional brain) 4 parts; The hippocampus and amygdala, along with the hypothalamus and thalamus, are part of a circle of structures limic system links: Linking the: frontal cortex, basal ganglia, and upper brainstem, limbic system mediates: thought and feeling through complex, bidirectional connections. Antianxiety drugs (anxiolytics) slow the: limbic system. The four subcortical basal ganglia that lie deep within the cerebrum are the striatum, the pallidum, the substantia nigra, and the subthalamic nucleus. basal ganglia plays major role in: motor responses via the extrapyramidal motor system: regulates movement including the diaphragm and muscles of the throat, tongue and mouth. dopamine- a neurotransmitter (basal ganglia) maintain proper muscle tone and motor stability (extra pyramidal motor system of basal ganglia). Haloperidal (an antipsychotic agent) can: reduce striatal (one of four basal ganglia) volume within hours, temporarily changing brain structure and predicting abnormal involuntary motor symptoms (extrapyramidal symptoms [EPS]). In the basal ganglia, two types of movement disturbances may occur: (1) acute extrapyramidal symptoms, which develop early in treatment; and (2) tardive dyskinesia, which usually occurs much later. These types of antipschotics are most likely to cause extrapyramidal side effects: Conventional antipsychotics (the first generation of antipsychotic medications) and high doses of the atypical agent (second generation of antipsychotic medications) risperidone (Risperdal) Drugs that affect brain function can stimulate or depress: respiration or affect speech patterns (e.g., slurred speech). brainstem (composed of the midbrain, pons, and medulla) basic vital life functions Reticular activating system (RAS), in the brainstem: sets the level of consciousness and regulates the cycle of sleep and wakefulness. drugs used to treat psychiatric problems may interfere with the regulation of sleep and alertness, thus the warning to take sedating drugs at bedtime and to use caution while driving. Cerebellum coordinator of motor function; interacts with the cerebrum in higher cognitive functions(speech memory, facial recognition, visual attention, and awareness) Cerebellar hypoactivation affecting posture and equilibrium is well-documented as occurring in some people with schizophrenia. Thalamus (above brain stem) major relay station for sensory impulses on their way to the cerebral cortex; plays a role in complex reflex movements, body-alerting mechanisms, and even emotions by associating sensory impulses with various feelings. Dopamine (thalmus)- monoamine Reduces the thalamic sensory filter, allowing more sensory input to escape from the thalamus to the cortex: Fine muscle movement, Integration of emotions and thoughts, Decision making, Stimulates hypothalamus to release hormones (sex, thyroid, adrenal) Increase:Schizophrenia, Mania Decrease:Parkinson's disease, Depression Corticostriatal-thalamic pathways are disrupted in: schizophrenia, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), and attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). hypothalamus maintains homeostasis by regulating temperature, blood pressure, perspiration, libido, hunger, thirst, and circadian rhythms, such as sleep and wakefulness. Hypothalamic neurohormones, often called releasing hormones, direct the secretion of hormones from the anterior pituitary gland. For example, corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) is involved in the stress response. It stimulates the pituitary to release corticotropin, which in turn stimulates the cortex of each adrenal gland to secrete cortisol. hypothamlamic neurohormones is disrupted in mood disorders, posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and Alzheimer's dementia. The hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis is involved in the regulation of nearly every organ system because all major hormones and catecholamines (e.g., cortisol, gonadal hormones, insulin) depend on thyroid status. Release of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) results in pituitary secretion of thyrotropin (thyroid-stimulating hormone or TSH), which in turn stimulates the thyroid gland to release the thyroid hormones—thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). Thyroid hormones are used to treat people with depression or rapid-cycling bipolar I disorder. Also used as replacement therapy (lithium). hypothyroid state is a result of Lithium treatment and need thyroid hormone replacement therapy. hypothalamic neurohormone dopamine inhibits... the release of prolactin. dopamine blocked by conventional antipsychotic drugs blood prolactin levels increase (hyperprolactinemia) with subsequent amenorrhea, galactorrhea (milk flow), gynecomastia (development of breast tissue), or sexual dysfunction(conventional agents and the atypical drug risperidone ) hypothalamus sends instructions to the autonomic nervous system, autonomic nervous system divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems sympathetic system usually increases heart rate, respirations, and blood pressure to prepare for fight or flight, The sympathetic system is highly activated by sympathomimetic drugs, such as amphetamine and cocaine, as well as by withdrawal from sedating drugs, such as alcohol, benzodiazepines, and opioids parasympathetic system slows the heart rate and begins the process of digestion. Neuroimaging visualizes a brain that is structurally and functionally interconnected. Structural imaging techniques are computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). CT scans use a series of x-rays to view brain structure. MRI scans use a strong magnetic field and radio waves, distinguishing gray and white matter better than CT scans. Functional neuroimaging with positron emission tomography (PET) and single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) use use ionizing radiation to localize brain regions associated with perceptual, cognitive, emotional, and behavioral functions. Based on the increase in blood flow to the local vasculature that accompanies neural activity, PET scans have provided evidence of decreased metabolism in unmedicated individuals with depression or schizophrenia and increased metabolism in obsessive-compulsive disorder. PET and SPECT have also shown Can detect oxygen utilization, glucose metabolism, blood flow, neurotransmitter receptor interaction; dopamine system dysregulation in schizophrenia and loss of monoamines in depression (Blockade of serotonin transporter receptors with antidepressant medications); Alzheimer's disease: reduction in nicotinic receptor subtype Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) demonstrates : cognitive function without contrast injections or invasive tests: It is the major method used by cognitive neuroscientists to observe changes that occur in f the brain while subjects perform tasks involving higher intellectual processes (memory/attention). fMRI maps the modulatory effects of psychotropic medication, illustrating how a therapeutic response can be achieved at minimal doses. Antipsychotic medications are now prescribed at a fraction of the dosages that were once considered standard, in large part because of imaging studies. neurotransmission is: ability of neurons to initiate signals and conduct an electrical impulse from one end of the cell to the other synapses convert Electrical signals within neurons into chemical signals through the release of molecules called neurotransmitters, then elicit electrical signals on other side of the synapse. Together, action potentials and synaptic signals enable information processing in the brain. schizophrenia causes... excessive transmission may be due to excessive release of a transmitter or to increased receptor responsiveness. dopamine: neurotransmitter is a chemical messenger between neurons by which one neuron triggers another. Four major groups of neurotransmitters in the brain are monoamines (biogenic amines), amino acids, peptides, and cholinergics (e.g., acetylcholine). Monoamine neurotransmitters (dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin) and acetylcholine are implicated in a variety of neuropsychiatric disorders. Amino acid neurotransmitters, such as the inhibitory γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) and the excitatory glutamate, . balance brain activity Peptide neurotransmitters such as hypothalamic CRH can be thought of as modulating or adjusting general Computed tomography (CT) "slices," providing a 3D-like reconstruction of each segment and can detect lesions, abrasions, areas of infarct, aneurysm: Schizophrenia, Gray matter reduction, Ventricle abnormalities Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) Uses a magnetic field and radio waves to produce cross-sectional images; Used to exclude neurological disorders in those presenting with mental illness (schizophrenia) Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) Relies on magnetic properties to see images of blood flow in brain as it occurs; avoids exposure to radioactive isotypes; Can detect edema, ischemia, infection, neoplasm, trauma; psychotropic drugs produce effects through alteration of synaptic concentrations of dopamine, acetylcholine, norepinephrine, serotonin, histamine, GABA, or glutamate. (through receptor antagonists-blocking activity of a neurotransmitter) or agonists (promoting activity of a neurotransmitter), interference with neurotransmitter reuptake, enhancement of neurotransmitter release, or inhibition of enzymes. Dopamine (monoamine) -reuptake neurotransmitter involved in cognition, motivation, and movement. Controls emotional responses and the brain's reward and pleasure centers, stimulates the heart, and increases blood flow to vital organs. Cocaine (like drugs) interfere with... reuptake of dopamine, thereby allowing more of the neurotransmitter to stay active in the synapse for a longer time. dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia observation that drugs (e.g., amphetamines) that stimulate dopamine activity can induce psychotic symptoms whereas drugs that block dopamine receptors (e.g., haloperidol) have antipsychotic activity. acetylcholine (neurotransimtter) balances dopamine. Neurons that release acetylcholine are cholinergic: thought to be involved in cognitive functions, especially memory. Alzheimers Acetylcholine is deficient in Alzheimer's disease, attempts have been made to enhance the function of neurons that secrete acetylcholine by use of drugs that inhibit the enzyme that degrades acetylcholine (i.e., acetylcholinesterase). Therefore acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors are prescribed to delay cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease. norepinephrine (NE)- monoamine/reuptake called noradrenergic; NE and serotonin play a major role in regulating mood, attention/arousal, fight or flight (sympathetic system). A deficiency within the limbic system is thought to underlie depression, whereas an excess has been associated with mania, anxiety, schizophrenia. NE or serotonin BLOCK can cause (monoamine) vasodilation and a consequent drop in blood pressure, or orthostatic hypotension. The α1 receptors are also found on the vas deferens and are responsible for the propulsive contractions leading to ejaculation. Blockage of these receptors can lead to a failure to ejaculate. deficiency of one/both may underlie depression serotonin found in/helps (reuptake) brain and spinal cord, helps regulate mood, arousal, attention, behavior, and body temperature. Increase: Anxiety states Decrease:Depression serotonin syndrome serotonin increased (antidepressants mixed with St. Johns wort or dextromethorphan) Symptoms of high levels of serotonin range from mild (restlessness, shivering, and diarrhea) to severe (muscle rigidity, fever, and seizures). These symptoms can be alleviated by muscle relaxants and drugs that block serotonin production. Current research focuses on serotonin dysfunction in impulsive aggression and suicide (Cardish, 2007). Platelet Serotonin release plays an important role in hemostasis Histamine (H1, H2)- monoamine Increase: Alertness, Inflammatory response, ^ gastric secretion. Decrease: Sedation, Weight gain. γ-Aminobutyric acid (GABA); GABAA; GABAB-amino acid Inhibitory neurotransmitter: Reduces anxiety, excitation, aggression; May play a role in pain perception Anticonvulsant and muscle-relaxing properties May impair cognition and psychomotor functioning Increase: Reduction of anxiety Decrease: Mania, Anxiety, Schizophrenia Glutamate (NMDA, AMPA)- amino acid Excitatory neurotransmitter: AMPA plays a role in learning and memory Increase AMPA: Improvement of cognitive performance in behavioral tasks Increase NMDA: Prolonged increase can kill neurons (neurotoxicity) Neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease Decrease NMDA: Psychosis Acetylcholine (ACh): Nicotinic, muscarinic (M1, M2, M3) cholinergic Plays a role in learning, memory Regulates mood: mania, sexual aggression Affects sexual and aggressive behavior Stimulates parasympathetic nervous system Decrease: Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's chorea, Parkinson's Increase: Depression Substance P (SP) cholinergic Centrally active SP antagonist has antidepressant and antianxiety effects in depression Promotes and reinforces memory Enhances sensitivity to pain receptors to activate Involved in regulation of mood and anxiety Role in pain management Somatostatin (SRIF) -cholinergiv Altered levels associated with cognitive disease Decrease:Alzheimer's disease Decreased levels of SRIF in spinal fluid of some depressed patients Increase: Huntington's chorea Neurotensin (NT) Endogenous antipsychotic-like properties Decreased levels in spinal fluid of schizophrenic patients combining selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and antipsychotics produces changes in GABAA receptors produce synergism significantly improves negative symptoms in patients unresponsive to antipsychotic treatment. Pharmacokinetic interactions are the effects of drugs on the plasma concentrations of each other. when a potent CYP450 enzyme inhibitor or inducer is added to drugs metabolized by one or more CYP450 enzymes, the patient experiences an adverse drug effect or therapeutic failure. Pharmacodynamic interactions are the combined effects of drugs. additive or synergistic effect ;alcohol is taken with psychotropic medications. Monoamines: a type of organic compound, including the neurotransmitters neurotransmitters that are further divided into subgroups called catecholamines (e.g., norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine) and indolamines (e.g., serotonin) and many different drugs and food substances Monoamine oxidase (MAO): an enzyme that destroys monoamines Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs): drugs that increase concentrations of monoamines by inhibiting the action of MAO MAOIs block the enzyme that metabolizes monoamines, they may occasionally be used to increase the levels of serotonin and norepinephrine in intractable depression. MAOIs combined with other sympathomimetics (amines that stimulate the sympathetic nervous system). vasopressor effects that occur (constriction of blood vessels). hypertensive crisis If a patient takes over-the-counter medications with pseudoephedrine or consumes the adrenergic monoamine tyramine, commonly found in aged foods and beverages. selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotoninnorepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) preferred over MAOI's MAOI'S nursing teaching do not take with thiamine containing foods to avoid hypertensive crisis. (including 2 wks after stopping MAOI's Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) act primarily by blocking the presynaptic transporter protein receptors for norepinephrine and, to a lesser degree, serotonin: blocking prevents norepinephrine from coming into contact with its degrading enzyme, MAO, and thus increases the level of norepinephrine at the synapse. (ex: such as amitriptyline (Elavil) and nortriptyline (Pamelor)) TCAs treat difficult cases of depression and chronic pain TCA side effects side effects: anticolinergic effects(dry up) block H1 receptors, causing sedation and weight gain. Strong binding at adrenergic receptors causes dizziness and hypotension, thereby increasing the risk for falls Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) preferentially block the reuptake and thus the destruction of serotonin. [fluoxetine (Prozac), sertraline (Zoloft), paroxetine (Paxil), citalopram (Celexa), and escitalopram (Lexapro)] Serotonin ^^^ while taking SSRI's can result in anxiety, insomnia, sexual dysfunction, and gastrointestinal disturbances. Serotonin toxicity occur with coadministration of other serotonergic drugs (e.g., MAOIs, SSRIs, SNRIs, lithium, triptan, buspirone, tramadol, over-the-counter cough and cold medications containing dextromethorphan) or antidopaminergic drugs. SSRI discontinuation= discontinuation syndrom when discontinuation is abrupt; most likely to occur with SSRIs or SNRIs having a short half-life. Thus it is more common with paroxetine (Paxil) than with fluoxetine (Prozac). Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRIs) increase the levels of both serotonin and norepinephrine. Venlafaxine (Effexor) is more of a serotonergic agent at lower doses, but norepinephrine reuptake blockade occurs at higher doses, leading to the dual SNRI action. Duloxetine (Cymbalta) is used for depression and pain associated with diabetic neuropathy. Serotonin-Norepinephrine Disinhibitors (SNDIs) mirtazapine (Remeron), increase norepinephrine and serotonin transmission by blocking presynaptic α2-noradrenergic receptors. Mirtazapine: antianxiety and antidepressant effects, with minimal sexual dysfunction secondary to serotonin blockade. This is an antiemetic via serotonin blockade. Norepinephrine-Dopamine Reuptake Inhibitors (NDRIs) bupropion (Wellbutrin); inhibits dopamine-norepinephrine reuptake, also inhibits nicotinic acetylcholine receptors to reduce the addictive action of nicotine. (used for smoking cessation) Antidepressants also treat... anxiety disorders because of shared symptoms, neurotransmitters, and circuits. SSRIs are commonly used to treat panic disorder, generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), OCD, PTSD, and social phobia. GAD= generalized anxiety disorder. SNRIs venlafaxine (Effexor) and duloxetine (Cymbalta) are also used to treat GAD GABA IS... major inhibitory (calming) neurotransmitter in the CNS. benzodiazepines (diazepam (Valium), clonazepam) The most commonly used antianxiety agents, reduce neuronal excitement in seizures and alcohol withdrawal. Romote activity of GABA by binding to a specific receptor on the GABAA receptor complex. limited potential for toxicity; potential for tolerance and withdrawal. Non-Benzodiazepines (Buspirone) Reduces anxiety without having strong sedative-hypnotic properties. high affinity for serotonin receptors, acting as a serotonin Not a CNS depressant and thus not great danger of interaction with other CNS depressants, such as alcohol. The potential for addiction that exists with benzodiazepines does not exist for buspirone. Short-Acting Sedative-Hypnotic Sleep Agents: zolpidem (Ambien), zaleplon (Sonata), and eszopiclone (Lunesta), demonstrate selectivity for GABAA receptors containing α1 subunits. Have sedative effects without the antianxiety, anticonvulsant, or muscle relaxant effects of benzodiazepines. Mood Stabilizers: Lithium treatment for bipolar disorder is well established Long-term use of lithium increases the risk of both kidney and thyroid disease. Mood Stabilizers: Anticonvulsant-Valproate divalproex sodium (Depakote) and valproic acid (Depakene), is recommended in bipolar disorder for mixed episodes and rapid cycling and managing impulsive aggression. Baseline lab work includes liver function tests and complete blood count (CBC). Valproate levels are measured every 6 months and generally range from 50 to 100 mcg/mL. Mood Stabilizers: Anticonvulsant-Carbamazepine (Tegretol) Treats acute mania. A CBC must be done periodically because of rare but serious blood dyscrasias (e.g., aplastic anemia and agranulocytosis). Mood Stabilizers: Anticonvulsant-Lamotrigine (Lamictal) Maintenance treatment of bipolar disorder, effective in decreasing the time between episodes of bipolar depression. The most common adverse effects are usually mild,develop a rash during the first 4 months of treatment. possibly a toxic epidermal necrolysis called Stevens-Johnson syndrome Cross-cultural psychopharmacology explores different effects/responses that exist among ethnic groups and the reasons for these effects. predict patients' responses, scientists search for variants in genes that code for drug metabolizing enzymes in the liver. Pharmacogenetics studies how genes influence drug metabolism and response. KP-actions of the brain sensory, motor, intellectual—are carried out physiologically through the interactions of nerve cells. These interactions involve impulse conduction, transmitter release, and receptor response. KP-Alterations in Basic BRAIN processes can lead to mental disturbances and physical manifestations. KP-excess activity of dopamine is involved in the thought disturbances of schizophrenia, and deficiencies of norepinephrine, serotonin, or both underlie depression and anxiety. Insufficient activity of GABA also plays a role in anxiety. KP- Pharmacological treatment of mental disturbances is directed at the suspected transmitter-receptor problem. Antipsychotic drugs decrease dopamine levels, antidepressant drugs increase synaptic levels of norepinephrine and/or serotonin, and antianxiety drugs increase the effectiveness of GABA or increase 5-HT and/or norepinephrine levels. KP- immediate target activity of a drug can result in many downstream alterations in neuronal activity, drugs with a variety of chemical actions may show efficacy in treating the same clinical condition. newer drugs with novel mechanisms of action are being used in the treatment of schizophrenia, depression, and anxiety. KP-agents used to treat mental disease can cause various undesired effects. sedation/Excitement, motor disturbances, muscarinic blockage, αadrenergic antagonism, sexual dysfunction, and weight gain. Q1 All mental activity has its locus in the: BRAIN Q2 Standard anti-psychotic drugs: lower the seizure threshold; can cause extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS), AND may lead to neuroleptic malignant syndrome. Q3 The patients who should be most carefully assessed for untoward cardiac side effects are those receiving: LITHIUM Q4 Clozaril: is an atypical anti-psychotic drug AND may cause agranulocytosis. Q5 Pharmacological agents: may have undesired effects in some cultural groups.