First Grade, Quarter 2, from Daniel Abeyta
advertisement
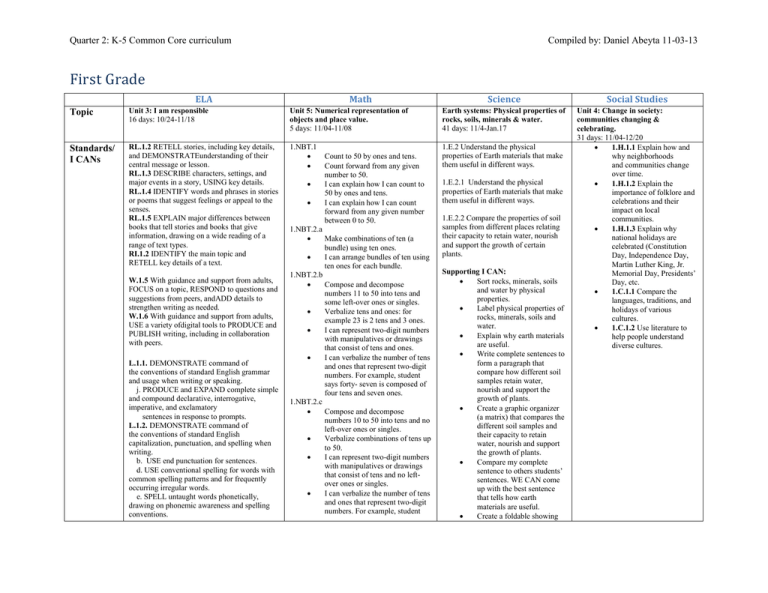
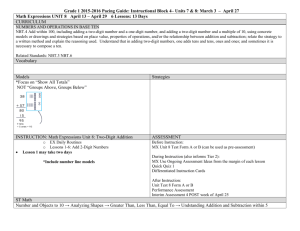
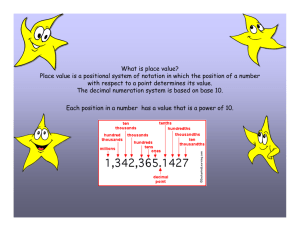
Quarter 2: K-5 Common Core curriculum Compiled by: Daniel Abeyta 11-03-13 First Grade Science Social Studies Topic Unit 3: I am responsible 16 days: 10/24-11/18 ELA Unit 5: Numerical representation of objects and place value. 5 days: 11/04-11/08 Earth systems: Physical properties of rocks, soils, minerals & water. 41 days: 11/4-Jan.17 Standards/ I CANs RL.1.2 RETELL stories, including key details, and DEMONSTRATEunderstanding of their central message or lesson. RL.1.3 DESCRIBE characters, settings, and major events in a story, USING key details. RL.1.4 IDENTIFY words and phrases in stories or poems that suggest feelings or appeal to the senses. RL.1.5 EXPLAIN major differences between books that tell stories and books that give information, drawing on a wide reading of a range of text types. RI.1.2 IDENTIFY the main topic and RETELL key details of a text. 1.NBT.1 Count to 50 by ones and tens. Count forward from any given number to 50. I can explain how I can count to 50 by ones and tens. I can explain how I can count forward from any given number between 0 to 50. 1.NBT.2.a Make combinations of ten (a bundle) using ten ones. I can arrange bundles of ten using ten ones for each bundle. 1.NBT.2.b Compose and decompose numbers 11 to 50 into tens and some left-over ones or singles. Verbalize tens and ones: for example 23 is 2 tens and 3 ones. I can represent two-digit numbers with manipulatives or drawings that consist of tens and ones. I can verbalize the number of tens and ones that represent two-digit numbers. For example, student says forty- seven is composed of four tens and seven ones. 1.NBT.2.c Compose and decompose numbers 10 to 50 into tens and no left-over ones or singles. Verbalize combinations of tens up to 50. I can represent two-digit numbers with manipulatives or drawings that consist of tens and no leftover ones or singles. I can verbalize the number of tens and ones that represent two-digit numbers. For example, student 1.E.2 Understand the physical properties of Earth materials that make them useful in different ways. Unit 4: Change in society: communities changing & celebrating. 31 days: 11/04-12/20 1.H.1.1 Explain how and why neighborhoods and communities change over time. 1.H.1.2 Explain the importance of folklore and celebrations and their impact on local communities. 1.H.1.3 Explain why national holidays are celebrated (Constitution Day, Independence Day, Martin Luther King, Jr. Memorial Day, Presidents’ Day, etc. 1.C.1.1 Compare the languages, traditions, and holidays of various cultures. 1.C.1.2 Use literature to help people understand diverse cultures. W.1.5 With guidance and support from adults, FOCUS on a topic, RESPOND to questions and suggestions from peers, andADD details to strengthen writing as needed. W.1.6 With guidance and support from adults, USE a variety ofdigital tools to PRODUCE and PUBLISH writing, including in collaboration with peers. L.1.1. DEMONSTRATE command of the conventions of standard English grammar and usage when writing or speaking. j. PRODUCE and EXPAND complete simple and compound declarative, interrogative, imperative, and exclamatory sentences in response to prompts. L.1.2. DEMONSTRATE command of the conventions of standard English capitalization, punctuation, and spelling when writing. b. USE end punctuation for sentences. d. USE conventional spelling for words with common spelling patterns and for frequently occurring irregular words. e. SPELL untaught words phonetically, drawing on phonemic awareness and spelling conventions. Math 1.E.2.1 Understand the physical properties of Earth materials that make them useful in different ways. 1.E.2.2 Compare the properties of soil samples from different places relating their capacity to retain water, nourish and support the growth of certain plants. Supporting I CAN: Sort rocks, minerals, soils and water by physical properties. Label physical properties of rocks, minerals, soils and water. Explain why earth materials are useful. Write complete sentences to form a paragraph that compare how different soil samples retain water, nourish and support the growth of plants. Create a graphic organizer (a matrix) that compares the different soil samples and their capacity to retain water, nourish and support the growth of plants. Compare my complete sentence to others students’ sentences. WE CAN come up with the best sentence that tells how earth materials are useful. Create a foldable showing Quarter 2: K-5 Common Core curriculum Compiled by: Daniel Abeyta 11-03-13 says forty is composed of four tens and zero ones. Supporting standards Essential Questions SL.1.2 Ask and answer questions about key details in a text read aloud or information presented orally or through other media. SL.1.4 Describe people, places, things, and events with relevant details, expressing ideas and feelings clearly. SL.1.6 Produce complete sentences when appropriate to task and situation. 1.NBT.1/1.NBT.2abc I CAN write numbers of reversed digits and orally explain the difference. I CAN illustrate or create, label and identify in writing the tens and ones place value of a twodigit number. I CAN use comparative phrases to explain the place values (tens and ones) of given two-digit numbers. How do I use key details from the text to retell a story? Essential Questions What does counting help you understand about numbers? What are strategies to help you count quickly? What are the ways you can show how to make a number? How could you explain to a friend what you know about the number 10? How does the placement of a numeral in a number help you to understand the value of the number? Guiding Questions: How many counters do you have? Does that help you know how many? Are you sure? Are these numbers the same or different? (19 vs. 91) Is that true some of the time or all of the time? properties of rocks, minerals, soils, and water and explain (on each page) why the materials are useful. Pick 2 different soil samples and create a Venn diagram comparing them. Use the Venn Diagram to write a complete sentence. Information & Technology Standards 1.SI.1 Recall useful sources of information. 1.IN.1 Understand the difference between text read for enjoyment and text read for information. 1.TT.1 Use technology tools and skills to reinforce classroom concepts and activities. 1.SE.1 Understand safety and ethical issues related to the responsible use of information and technology resources. What are observable properties of rocks, minerals, soil and water? What are the properties of a solid? Of a liquid? How do we use Earth materials to support plant and animal life and to help solve problems? How do soils from different places compare? And how do the soils help support certain plants? What causes neighborhoods and communities to change? How do neighborhoods and communities change over time? How are neighborhoods and communities impacted by folklore and other types of cultural celebrations? Why are national holidays celebrated? Quarter 2: K-5 Common Core curriculum Vocabulary Main idea Retell Details Character Setting Event Literary Expository Punctuation Informative explanatory Narrator Details Describe Context clue Meaning Fiction Nonfiction Materials The Injured Mason by Francisco de Goya Photos showing people that are responsible or irresponsible Sell School Home Environment Learn 360 resources: Franklin Wants a Pet Responsibility For Choices IRC Resources I am Responsible by Sarah Schuette Read Aloud: Mañana, Iguana by Ann Whitford Paul Teacher Directed Reading: I Am Responsible big book Responsibility by Lucia Raatma What Does It Mean to be Responsibleby Kathleen Holleneck Arthur’s Pet Business by Marc Brown Pigsty by Mark Teague Talking about our Environment by Malcolm Penny When I Get Up in the Morning by Clive Webster Additional Text Examples: Being Responsible by Robin Nelson Compiled by: Daniel Abeyta 11-03-13 count number numerals sequence number words 0-50 digit tens ones compose bundle left-overs singles groups greater/less than equal to digit two-digit decompose Carle, Eric. The Very Hungry Caterpillar. New York: Putnam, 1969. Christelow, Eileen. Five Little Monkeys Sitting in a Tree.New York: Scholastic, 1991. Crews, Donald. Ten Black Dots. New York: Greenwillow, 1986. Ehlert, Lois. Fish Eyes: A Book You Can Count On. New York: Harcourt Brace, 1990 Friedman, Aileen, The King’s Commissioners. New York: Heinemann, 1994 Gerth, Melanie. Ten Little Ladybugs. Santa Monica, Calif.: Piggy Toes Press, 2000. Giganti, Paul, Jr. How Many Snails? New York: Greenwillow, 1988. Grossman, Virginia. Ten Little Rabbits. New York: Scholastic, 1991 Peek, Merle. Roll Over. New York: Clarion, 1981. Rees, Mary. There Were Ten in the Bed. Boston: Little, Brown and Company, 1988. Schlein, Miriam, More Than One. New York: Greenwillow Books, 1996. Color Retain Shape Enhance Texture Create Sink Occupy Liquid Sustain Mineral Classify Physical Capacity properties Development Growth Structural Size Weight Flexibility Float Solid Nourish Rock Magnet properties Let's Go Rock Collecting by Roma Gans Rocks and Minerals by R.F. Symes, Natural History of London Sylvestor and the Magic Pebble by William Steig Stone Soup by Marsha Brown On My Beach There Are Many Pebbles by Leo Lionni The Best Book of Fossils, Rocks, and Minerals by Chris Pellant The Magic School Bus: Inside the Earth by Joanna Cole Planet Earth/Inside Out by Gail Gibbons Neighborhood Community Folklore Celebration Traditions Patriotic Quarter 2: K-5 Common Core curriculum Each Living Thing by Joanne Ryder Teamwork by Lisa Trumbauer Being a Good Citizen: A Book About Citizenship by Mary Small Respect and Take Care of Things by Cheri Meiners Jason Takes Responsibility by Virginia Kroll Jamaica’s Find by Juanita Havill Officer Buckle and Gloria by Peggy Rathmann Compiled by: Daniel Abeyta 11-03-13 Swinburne, Stephen, What’s a Pair? What’s a Dozen? Honesdale, PA: Boyds Mills Press, 2000. Wise, William. Ten Sly Piranhas. New York: Dial, 1993 Wood, Audrey, The Napping House. San Diego: Harcourt Brace, 1984. Morozumi, Atsuko. One Gorilla. New York: Trumpet Club, 1990. Pallotta, Jerry. The Hershey’s Kisses Addition Book. New York: Scholastic, 2001 Hong, Lily Toy. Two of Everything. Morton Grove, IL: Albert Whitman and Company, 1993 Irons, Rosemary and Calvin Irons. The Mean Machine.Crystal Lake, IL.: Rigby, 1987. Keats, Ezra Jack. Over in the Meadow. New York: Scholastic, 1971 Long, Lynette. Domino Addition. New York: Scholastic, 1996 McGrath, Barbara B. The M & M’s Counting Book. Cambridge: Charlesbridge, 1994 Merriam, Eve, 12 Ways to Get to 11.New York: Simon and Schutester, 1993.