Urinary System
advertisement

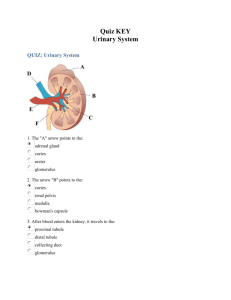
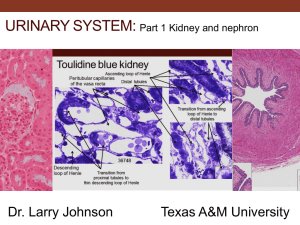
Urinary System Dr. Raeesa Mohammed Associate professor of Histology Urinary System Includes: 2 Kidneys. 2 Ureters. Single Urinary bladder. Single Urethera. Kidney Bean-shaped organ Covered by dense irregular collagenous connective tissue capsule Has a lateral convex border & a medial concave border with hilum, where the: Arteries enter Ureter & veins leave the kidney Kidney cont’d Each kidney is divided into: • • • • Outer Cortex Inner Medulla: which is composed of 10-12 renal pyramids The base of pyramid is toward the cortex, and the apex (renal papilla) toward the hilum Renal pyramids are separated by cortical tissue called renal columns of Bertin P Kidney cont’d The apex of each pyramid is perforated by 15-20 large collecting ducts (papillary ducts of Bellini) that open into the minor calyx The minor calyx, surrounds the apex of each pyramid 3 or 4 minor calyces join to form a major calyx The major calyces, 3-4 in number open into the renal pelvis. Nephron It is composed of : • • • • Renal corpuscle Proximal tubule Loop of Henle Distal tubule Renal Corpuscle Composed of: Glomerulus: Tuft of fenestrated capillaries. Afferent & efferent arterioles supply & drain the glomerulus at the vascular pole Bowman’s capsule: Encloses the glomerulus. It has two layers: • Parietal layer formed by simple squamous epithelium. • Visceral layer formed by podocytes Renal Corpuscle cont’d Bowman’s (urinary or glomerular) space: Space between the parietal and visceral layers, drains at the urinary pole into the proximal convoluted tubule Interstitial tissue is composed of mesengium (mesangial cells & the extracellular matrix manufactured by them) Podocytes Are modified cells with multiple processes and pedicles Form the visceral layer of Bowman’s capsule Their processes and pedicles surround the glomerular capillaries. The spaces between adjacent pedicles, called the filtration slits are covered by slit diaphragms. Form a thick basal lamina that is interposed between the podocytes and the endothelial cells Glomerular Filtration Barrier The barrier is formed by: • the podocyte layer of Bowman's capsule • the fenestrated endothelium of the glomerulus • a thick basement membrane shared between the two cellular components GFB Collecting Tubule Is composed of: Proximal convoluted tubule: Loop of Henle: It has 3 regions: • Descending thin limb. • Henle’s loop • Ascending thin limb Distal convoluted tubule: Proximal tubule: It is composed of simple cuboidal epithelium with: • Extensive striated or brush border Thin limb of Henle’s Loop: It is composed of simple squamous epithelium Distal Tubule It is composed of simple cuboidal epithelium. Juxtaglomerular Apparatus It has 3 components: • • • The macula densa of distal tubule. Juxtaglomerular cells of glomerular arterioles (modified smooth muscle of tunica media); they secrete renin, angiotensin-converting enzyme and angiotensin. The extraglomerular mesangial cells called lacis cells. Collecting Duct Several distal convoluted tubules join each collecting duct Are composed of simple cuboidal epithelium. Renal medulla contains: Collecting tubules (ducts) Henle’s loop Peritubular blood vessels (vasa recta) Renal interstitium Ureter Is composed of: Mucosa: formed of transitional epithelium & lamina propria. Muscularis (muscular coat): is formed of 2 layers of smooth muscle: • • Inner longitudinal Outer circular Adventitia: fibrous connective tissue covering Urinary bladder It has the same structure as the ureter, except: a. The muscularis has 3 layers of smooth muscle, inner longitudinal, middle circular and outer longitudinal. Serosa/adventitia is outer covering Practical Slides Kidney Cortex Kidney Medulla Urinary Bladder Urinary Bladder