File - JALC PSY 132
advertisement

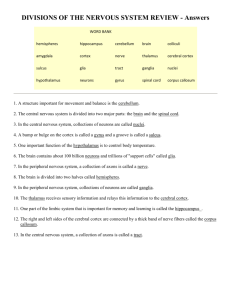
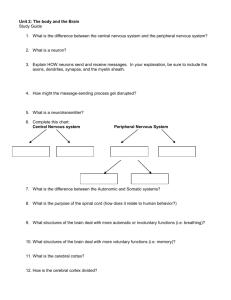
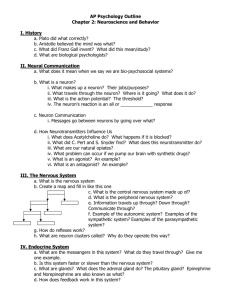
Chapter 2 Brain and Behavior Neurons -the brain consists of some 100 billion neurons (individual nerve cells) which carry and process information, activate muscles and glands -they form vast networks to produce intelligence and consciousness -linked to one another in tight clumps and long chains Parts of a Neuron 1. Dendrites -receive messages from other neurons 2. Soma – they are the main body of a neuron; also accepts incoming information, but sends messages of its own down a thin fiber called the axon 3. Axon – a thin fiber that carries information away from the cell body of a neuron. 4. Axon terminals – allows information to pass from neuron to neuron. The Nerve Impulse 1. Ions are electrically charged molecules found in and around nerve cells 2. Resting potential is the electrical charge of an inactive neuron at rest 3. Threshold is the point at which a nerve impulse is triggered 4. Action potential is the nerve impulse, which can travel up to 200 miles per hour. Once a neuron reaches a certain point on the threshold then it goes to the action potential. 5. The axon membrane is pierced by tiny molecular tunnels called ion channels. Salatory Conduction -gaps in myelin that help impulses move faster Myelin – fatty tissue coating axons Synapses and Neurontransmitters 1. nerve impulse is primarily electrical 2. communication between neurons is chemical 3. Synapse is the microscopic space between two neurons over which messages pass 4. When an action potential reaches the tips of the axon terminals, neurotransmitters are released into the synaptic gap 5. Neurotransmitter molecules cross the synaptic gap and attach to special receptor sites on the receiving neuron 6. Receptor sites are areas on the surface of neurons and other cells that are sensitive to neurotransmitters or hormones 7. Excite or inhibit the neurons Neural Regulators 1. Neuropeptides are brain chemicals that regulate the activity of neurons. 2.Enkephalins regulate reactions to pain and stress 3.Endorphins -pain killing effect Nervous System Neurons are tiny cells; Nerves are large bundles of axons and dendrites 1. Many nerves have a whitish color because they contain axons coated with a fatty layer of tissue called myelin 2. Neurilemma is a thin layer of cells that encases many axons outside the brain and spinal cord Neural Networks Central Nervous System and Peripheral Nervous System -the brain communicates with the rest of the body through the spinal cord Peripheral nervous system -consists of all parts of the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord -The peripheral nervous system can be divided into two parts: Somatic system which carries messages to and from the sense organs and skeletal muscles Autonomic system serves the internal organs and glands of the body 1. Sympathetic branch that arouses the body 2. Parasympathetic branch that quiets the body Research Methods Biopsychology - The study of how biological processes, especially activity in the brain and nervous system, relate to behavior. Clinical studies – examining how brain diseases or injuries affect personality, behavior or sensory capacities Ablation – surgical removal of parts of the brain – causes changes in behavior or sensations, which gives insight to the purpose of the missing part Cerebral Cortex Cerebrum is the two large hemispheres that cover the upper part of the brain. Cerebral cortex is the outer layer of the cerebrum Gray matter is the areas in the nervous system made up of mostly nerve cell bodies Cerbral Hemispheres Corpus callosum is the bundle of fibers connecting the cerebral hemispheres The left side of the brain mainly controls the right side of the body. The right side of the brain mainly controls the left body areas Damage to the right hem may cause Spatial neglect: ignoring one side of the vision or of the body after damage to a brain hemisphere. Left Brain Roughly 95% of all adults use the left brain for language (speaking, writing, and understanding). - superior at math, judging time and rhythm and coordinating the order of complex movements, such as those needed for speech. -mainly involved with analysis (breaking information into parts) -processes information sequentially Right hemisphere can produce only the simplest language and numbers - Right brain is especially good at perceptual skills, such as recognizing patterns, faces, and melodies, putting together a puzzle, or drawing a picture. - detecting and expressing emotion If the right brain is damaged people lose their ability to understand jokes, irony, sarcasm, implications, and other nuances of language. The right hemisphere appears to process information simultaneously and holistically -Is better at assembling pieces of the world into a coherent picture; it sees overall patterns and general connections Lobes of the Cerebral Cortex Occipital lobes – the portion of the cerebral cortex where vision registers in the brain Parietal lobes – the area of the brain where bodily sensations register Somatosensory area is the receiving area for bodily sensations within the Parietal lobe Temporal lobes – the areas that include the sites where hearing registers in the brain Frontal lobes – the brain area associated with movement, the sense of smell, and higher mental functions -Motor cortex – the brain area associated with control of muscle movement -Association cortex -all areas of the cerebral cortex that are not primarily sensory or motor in function -Damage to association areas in the left hemi may lead to Aphasia -a speech disturbance resulting from brain damage one type is related to Broca’s area: a language area related to grammar and pronunciation Wernicke’s area is an area related to language comprehension Agnosia is the inability to grasp the meaning of stimuli, such as words, objects, or pictures Facial agnosia is the inability to recognize familiar faces Subcortex all brain structures below the cerebral cortex The Hindbrain Brainstem is the lowest part of the brain, including the cerebellum, medulla, pons, and reticular formation Medulla is the structure that connects the brain with the spinal cord and controls vital life functions: heart rate, breathing, swallowing Pons is an area on the brainstem that acts as a bridge between the medulla and other structures Cerebellum is a brain structure that controls posture and coordination; stores memories related to skills and habits (walking, running, playing music Reticular formation is a network of cells and fibers within the medulla and brainstem; associated with attention, alertness, and some reflexes: breathing, sneezing, coughing, vomiting -as messages flow into the brain, the RF gives priority to some with turning others aside. Reticular Activating System (RAS) is a part of the reticular formation that activates the cerebral cortex, stimulating it to keep it active and alert The forebrain contains two of the most important parts of your body, the thalamus and hypothalamus Thalamus is a brain structure that relays sensory information to the cerebral cortex Hypothalamus is a small area of the brain that regulates emotional behaviors and motives -behaviors are organized or “decided on” before messages leave the brain, causing the body to relax Limbic system is a system in the forebrain that is closely linked with emotional response Amygdala is a part of the limbic system associated with fear responses Hippocampus is a part of the limbic system associated with storing memories Endocrine System Hormone is a glandular secretion that affects bodily functions or behavior Growth hormone is secreted by the pituitary gland that promotes bodily growth -Giantism is excessive bodily growth caused by too much growth hormone -Acromegaly is the enlargement of the arms, hands, feet, and face caused by excess growth hormone production late in the human growth period -Hypopituitary dwarfism is shortness and smallness caused by too little growth hormone Pituitary gland is the “master gland” whose hormones influence other endocrine glands. The hypothalamus directs the pituitary gland Pineal gland helps regulate body rhythms and sleep cycles Melatonin is the hormone released by the pineal gland in response to daily cycles of light and dark; controls body rhythms and sleep cycles Thyroid gland is the endocrine gland that helps regulate the rate of metabolism -Hyperthyroidism is faster metabolism and excitability caused by an overactive thyroid gland -Hypothyroidism is slower metabolism and sluggishness caused by an underactive thyroid gland -Epinephrine is an adrenal hormone that tends to arouse the body; norepinephrine is associated with anger 5Adrenal glands is endocrine glands that arouse the body, regulate salt balance, adjust the body to stress, and affect sexual functioning -Adrenal medulla is the inner core of the adrenal glands; a source of epinephrine and norepinephrine -Adrenal cortex is the outer layer of the adrenal glands; produces hormones that affect salt intake, reactions to stress, and sexual development -Virilism is the development of male sexual characteristic in a female -Premature puberty is the development of sexual maturity in childhood Plasticity the brain’ s capacity to change its structure and functions the more you challenge and engage your brain, especially by learning new skills, the healthier it will be and the better it will function Neurogenesis -the brain loses cells every day; it simultaneously grows new neurons to replace them