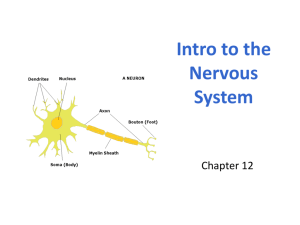
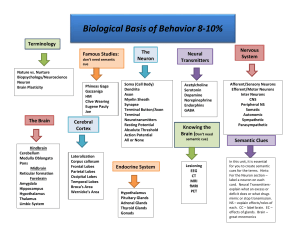
File ap psychology midterm vocabulary 2014 c exam
advertisement
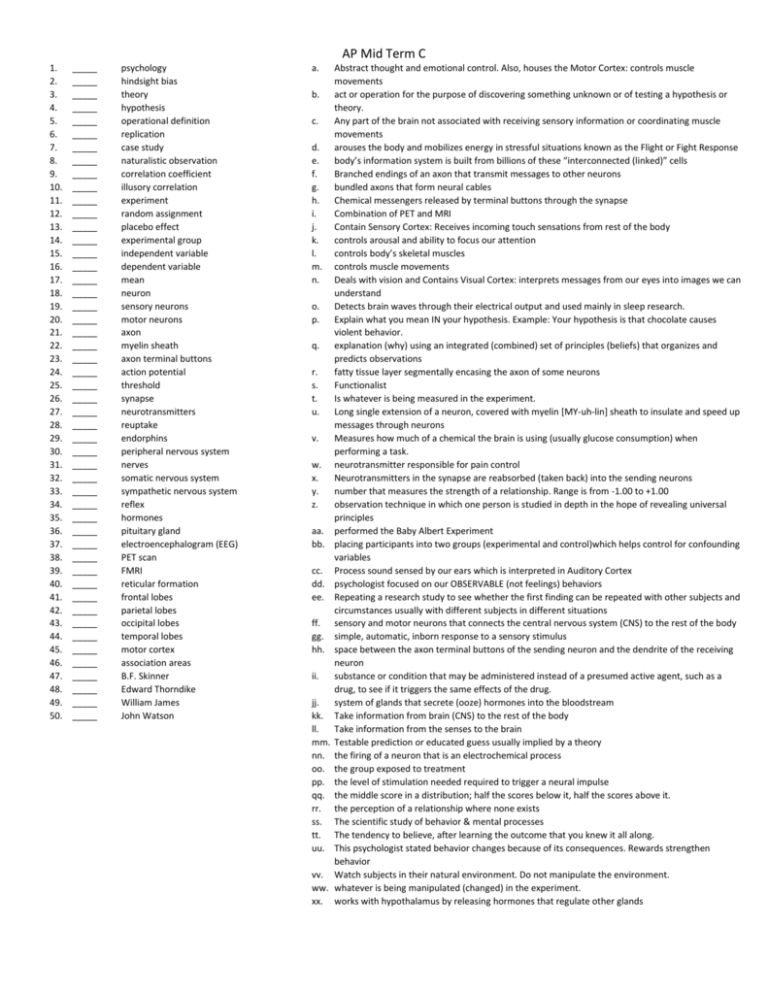
AP Mid Term C 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ psychology hindsight bias theory hypothesis operational definition replication case study naturalistic observation correlation coefficient illusory correlation experiment random assignment placebo effect experimental group independent variable dependent variable mean neuron sensory neurons motor neurons axon myelin sheath axon terminal buttons action potential threshold synapse neurotransmitters reuptake endorphins peripheral nervous system nerves somatic nervous system sympathetic nervous system reflex hormones pituitary gland electroencephalogram (EEG) PET scan FMRI reticular formation frontal lobes parietal lobes occipital lobes temporal lobes motor cortex association areas B.F. Skinner Edward Thorndike William James John Watson a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. m. n. o. p. q. r. s. t. u. v. w. x. y. z. aa. bb. cc. dd. ee. ff. gg. hh. ii. jj. kk. ll. mm. nn. oo. pp. qq. rr. ss. tt. uu. vv. ww. xx. Abstract thought and emotional control. Also, houses the Motor Cortex: controls muscle movements act or operation for the purpose of discovering something unknown or of testing a hypothesis or theory. Any part of the brain not associated with receiving sensory information or coordinating muscle movements arouses the body and mobilizes energy in stressful situations known as the Flight or Fight Response body’s information system is built from billions of these “interconnected (linked)” cells Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to other neurons bundled axons that form neural cables Chemical messengers released by terminal buttons through the synapse Combination of PET and MRI Contain Sensory Cortex: Receives incoming touch sensations from rest of the body controls arousal and ability to focus our attention controls body’s skeletal muscles controls muscle movements Deals with vision and Contains Visual Cortex: interprets messages from our eyes into images we can understand Detects brain waves through their electrical output and used mainly in sleep research. Explain what you mean IN your hypothesis. Example: Your hypothesis is that chocolate causes violent behavior. explanation (why) using an integrated (combined) set of principles (beliefs) that organizes and predicts observations fatty tissue layer segmentally encasing the axon of some neurons Functionalist Is whatever is being measured in the experiment. Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons Measures how much of a chemical the brain is using (usually glucose consumption) when performing a task. neurotransmitter responsible for pain control Neurotransmitters in the synapse are reabsorbed (taken back) into the sending neurons number that measures the strength of a relationship. Range is from -1.00 to +1.00 observation technique in which one person is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles performed the Baby Albert Experiment placing participants into two groups (experimental and control)which helps control for confounding variables Process sound sensed by our ears which is interpreted in Auditory Cortex psychologist focused on our OBSERVABLE (not feelings) behaviors Repeating a research study to see whether the first finding can be repeated with other subjects and circumstances usually with different subjects in different situations sensory and motor neurons that connects the central nervous system (CNS) to the rest of the body simple, automatic, inborn response to a sensory stimulus space between the axon terminal buttons of the sending neuron and the dendrite of the receiving neuron substance or condition that may be administered instead of a presumed active agent, such as a drug, to see if it triggers the same effects of the drug. system of glands that secrete (ooze) hormones into the bloodstream Take information from brain (CNS) to the rest of the body Take information from the senses to the brain Testable prediction or educated guess usually implied by a theory the firing of a neuron that is an electrochemical process the group exposed to treatment the level of stimulation needed required to trigger a neural impulse the middle score in a distribution; half the scores below it, half the scores above it. the perception of a relationship where none exists The scientific study of behavior & mental processes The tendency to believe, after learning the outcome that you knew it all along. This psychologist stated behavior changes because of its consequences. Rewards strengthen behavior Watch subjects in their natural environment. Do not manipulate the environment. whatever is being manipulated (changed) in the experiment. works with hypothalamus by releasing hormones that regulate other glands