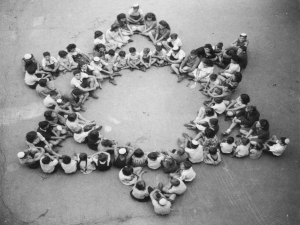End of War powerpoint
advertisement

The Holocaust 1930’s Anti-Semitism grows stronger in Germany. Jews are blamed for the defeat in WWI and economic problems. 1933 Persecution of the Jews becomes public policy. Jews can not hold public office. 1935 Nuremberg Laws- Take away Jews rights, citizenship, jobs, property. Were forced to wear the star of David to be identified. 1938 To revenge his father’s deportation from Germany, a Jewish youth shoots a worker at the German Embassy in Paris. Nazis retaliate, attacking Jewish communities on November 9. They destroyed homes and businesses, and beat up and killed many Jews. This night was called Krystalnacht. Many German Jews were deported to other countries but after taking thousands of refugees many countries began to shut their doors. In an attempt to find another solution, Hitler begins moving Jews to walled up parts of the city to separate them from the rest of the population. They were often starved and beaten within the ghettos. The Final Solution Genocide- systematic killing of a whole people. Also killed gypsies, poles, homosexuals, disabled and mentally ill but mostly the Jews. 1939 As Hitler begins to invade Eastern Europe his SS would round up men, women and children take them to isolated spots and gun them down. Other Jews were taken to slave labor camps in Germany and were made to endure hard labor in bad conditions with very little food. 1942 Extermination camps are completed in Poland. Jews are sent to death in mass in gas chambers disguised as showers, others are beaten and starved to death. Six million Jews are killed. Many people risked their lives to hide the Jews or help them to escape. Impact of the War The Yalta Conference (Feb 1945) FDR, Churchill, Stalin create the United Nations (Atlantic Charter)- 50 nations meet, 11 member security council holds power (major allies and others elected by general assembly) Stalin controls Japanese islands, N½ of Korea, promises free elections in E. Europe Potsdam, Germany- July 45‘- Truman, Churchill, Stalin Disarm Germany Get rid of Nazi party Divide Germany into 4 occupation zonesBritain, France, Germany, Soviets each controlBerlin also divided into 4 zones In Europe 40 million had died Many major cities destroyed by bombs (Berlin, Warsaw, Stalingrad), transportation, crops/ fields millions without homes- Refugees, wander through Europe No electricity, running water, food, supplies Governments- France, Italy, Germany start from scratch, Communist support grows, loses power in France, Italy Nuremburg Trials Nazis on trial for war crimes, International war tribunal, 23 countries 22 defendants, 12 sentenced to death, cremated in ovens at concentration camps Japanese Occupation Controlled by US forces under General MacArthur- 6 months War Crimes trials- tried for crimes against civilians prisoners of war- 1,100 tried, 25 major defendants, 7 sentenced to death, many others serve jail time Cities destroyed by bombs, rebuild, Capitalism takes over- economic recovery- distribute land ownership (wealthy forced to sell), labor unions legal New Constitution (MacArthur constitution) Parliamentary Democracy (elections), 2 house legislature (Diet), basic liberties, Women’s right to vote, Emperor removed from absolute power, still head of state (forced to admit he is not divine) Demilitarization- only allowed a small police force, protection from the US At Home- during Economic boom, money invested Good weather, fertilizer, farm production booms also Women flood workforce, prove competency Population shift, according to war industries, many move west Marriage boom, also divorce boom Discrimination persists African Americans- segregated but prove themselves on the battle field, Tuskegee Airmen, 92nd infantry (Buffaloes) Race riots at home, CORE (congress of Racial Equality) fights for rights, sit-ins 1943- Zoot Suit Riots- Mexican Americans 1944- Korematsu vs. US- Supreme court says Japanese internment was a necessity Post War US US becomes the major world power GI bill of Rights- veterans get money for schools, help to buy homes, start businesses Housing shortage met by track homes (not called that yet)- growth of suburbs, housing communities outside of big cities Major readjustment- Some difficult transition, fathers return from war, women return to the home, Economy- war products not needed, millions out of work/ new industries emerge Price controls removed- inflation, some goods are scarce- some govt. price controls renewed Consumers have $ to spend, economic boom American military defense spending high due to Cold war, 3 million men in military Marshall plan- rebuilding in Europe, good for trade Labor strikes- unions forced to give up, Truman threatens to draft workers Congress refuses to support Civil Rights, Truman orders desegregation of Military, end to discrimination in hiring of federal employees Election of 48’- division in Democrats, Civil Rights platform not popular, congress (Republican) refuses to work w/ Truman- Whistle stop Campaign, traveled the country and gained support. Truman- minimum wage raised, social security extended, flood control/ irrigation, housing for low income families