Diesel Engine Technology: 2007 and Beyond
advertisement

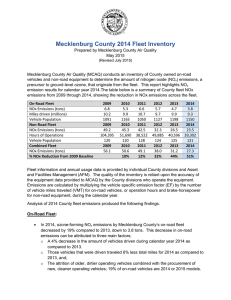
Diesel Engine Technology 2007 and Beyond Patrick Charbonneau Vice President, Chief Technical Officer International Truck and Engine Corporation Agenda The Standards Technology Roadmap – 5 Key Technologies The Technology Enabler Criteria for Success NOx Standards - HDE PM Standards - HDE 0.16 5 PM EURO Adj 0.14 4 NOx EURO Adj 0.12 0.1 3 0.08 2 0.06 NOx FTP PM FTP 0.04 1 Phase-in 0 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 Model Year 2008 2009 0.02 2010 2011 0 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 Model Year 2008 2009 2010 2011 NOx Standards - HLDT NOx Standards - HLDT 1.4 0.2 1.2 NOx EURO Adj PM EURO Adj 0.16 1 0.8 PM g/mile NOx g/mile 0.12 0.6 0.4 NOx FTP 0.08 PM FTP 0.04 0.2 0 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 Model Year 2008 2009 2010 2011 0 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 Model Year 2008 2009 2010 2011 How Diesel Technology Will Reduce Emissions to Meet the Requirements Emissions Reduction •4 Valve Head • Vertical Injector • G2 Injection System – Electronic Pilot – Electronic Trim – Higher Peak Pressure • Advanced Turbo • Cooled EGR • Oxidation Catalyst • Injection System • Boost Technology •Combustion •Advanced Electronics •Advanced Aftertreatment • Advanced NOx Adsorber • Advanced Particulate Trap 2002 2004 2007 2010 Fuel Systems (Fuel Systems of the Future) 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 Rate of Injection 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0.00 1.00 2.00 3.00 4.00 Time 5.00 6.00 7.00 Boost Technologies Combustion Electronics and Electrical Systems Sensors Computing Power Model Based Control Systems 42 Volt Aftertreatment Absorption of Nox, PM & HC emissions during normal operation Periodically add detergent (diesel fuel) and squeeze Soot filter traps all soot particles and hydrocarbon. It needs to burn off the trapped soot particles. A key measure of its performance is the balance point temperature. The balance point temperature varies from engine to engine. Balance point temperature: the engine operating condition and the exhaust temperature where soot burn off rate is greater than or equal to the engine soot output. NOx Adsorber - How Does It Work? It works in three simplified steps: 1. It stores NOx with normal diesel exhaust (Lean). 2. It releases NO2 when it is starved of O2 (Rich). 3. Under the rich condition, CO, HC, and H2 reduce the released NO2 into N2. Fuel Low-Emitting Diesel Engines and Vehicles Become a Clean Air Solution Equivalent or better emissions than gasoline or alternative fuels Still more fuel efficient with lower greenhouse gas emissions Performance and reliability that customers depend on Implications of the Low-Emitting Diesel Technology Road Map Technology can be applied to all engines: – Heavy-duty trucks, buses – Light-duty vehicles 2004 technology is foundation for 2007 Some 2007 technology is available today Use of 2007 technology requires ultra-lowsulfur fuel Widespread supply of ULSF is crucial to this technology, now and in 2007 Technology Roadmaps Gone Wild Conclusions Design and operation of diesel engines will be evolutionized for 2007 for HD and LD Aggressive aftertreatment will be productionfeasible for NOx and PM by 2007 Ultra-low-sulfur diesel fuel is the technology enabler to move to near-zero emissions targeted by EPA/CARB