The Cold War - Issaquah Connect
advertisement

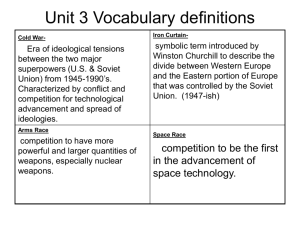
The Cold War Summer School Communism • Single party rule of a country controlling politics and the economy. • The state owns and runs most businesses and decides what goods are to be produced. • Communists regard capitalism and an unjust system the produces great social inequalities and denies the working class a fair share of the societies wealth. Capitalism/Democracy • In a Democratic Government the people get to choose who its leaders are through free elections. • With a Capitalist Economic System, individuals and private businesses make most of the economic decisions. • Business owners decide what to produce and consumers decide what to buy. • Factories, equipment and property are privately owned. Origins • Capitalism and Communism have never gotten along • First Red Scare in the U.S. came after WWI • The Soviets never trusted their Western Allies during WWII. – Stalin believed the U.S. was too slow to invade France, which would have relieved pressure on the Soviet Union. • The U.S. never trusted the Communists to keep their word either. Yalta Conference • February 1945 Stalin, Roosevelt and Churchill all meet to plan post war Europe. • Germany was to be divided into 4 occupation zones each controlled by a different Allied Country. • There would be self government and free elections in Eastern Europe. Tensions Begin to Build • After Germany’s surrender in April the leaders all meet again at Potsdam Conference. – Truman now president after Roosevelt's death. • At Conference Truman hints to Stalin that the U.S. now possessed a new powerful weapon (Atomic bomb). • The U.S. also stopped all aid to the Soviet Union when the War ends and refuses loans for the Soviet Union to rebuild. – Soviet distrust grows • Stalin has not allowed free elections in Eastern Europe. Elections in Poland are rigged for a communist victory • Soviet Occupation force in Eastern Europe grows. – U.S. distrust grows Spread of Communism • In a speech in 1946, Stalin believed that Communism needs to spread all over the world and replace communism. • Fearing the Spread of Communism the U.S. creates policy of Containment. – Keep the Soviets from Expanding Communism anywhere around the world. • Policy was meant for a political strategy not a literal Military one. • U.S. Fear however drive the U.S. to start making military plans. The Bomb and the Iron Curtain • In 1948 the Soviet union finally had the Atomic bomb to become the equal of the U.S. – So the U.S. began developing and even more powerful bomb. • The Arms Race begins • The Iron Curtain was a term coined by Churchill. It was the literal and philosophical divide between Communist Soviet controlled Eastern Europe and Democratically controlled Western Europe. • The city of Berlin while contained completely within Communist East Germany was also split into Western Berlin and East Berlin. – West Berlin was walled off to be separated from East Berlin. Rebuilding plan • Marshall Plan – Best way to stop spread of communism was to rebuild destroyed economies and support freely elected governments. • The U.S. would be able to supply the money and resources to help. • This would Also create strong bonds with the U.S. • Soviets Counter with Molotov Plan – Provide economic aid and rebuilding of Eastern Europe • Truman Doctrine – U.S. policy to support free peoples who are resisting attempted subjugation by armed minorities or outside pressures. • Military and Economic support First Crisis • France, U.S., and British want to unify there 3 German zones into democratic West Germany. • Soviet Union Protests – They plan a blockade of East Berlin that they believed would force U.S. to either give up East Berlin or their unification plans. • Berlin Airlift – Over the next 10 months over 270,000 flights are made into West Berlin bringing food, fuel, and other vital supplies to defeat the Berlin Blockade. – By Sping of 1949, the Soviet Union gives up and West Germany is created. Next Divide • NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) – Military alliance designed for collective security • U.S., Canada, Britain, France, Italy, and other Western European Countries • Warsaw Pact – Communist Security alliance of Soviet Satellite countries in Eastern Europe. – Hungary attempts Revolt • Soviet Army rolls into Budapest and puts down revolt. War in Korea • Korea was also split after the war. – Soviets establish a Communist North – U.S. establishes and Democratic South • June 1950 Communists in the north invade the South. – Truman sends U.S. troops to push the communists out. – U.S. pushes North Koreans all the way up to their Northern border with China. • Newly Communist China fears U.S. invasions and send thousands of troops to push back the U.S. • After 3 years of fighting borders stabilize along original border at the 38th parallel. U.S. Covert Actions • Covert Action is a secret political, economic, or military operation that supports foreign policy. – 1953 Iran - CIA remove Democratically elected Mossadegh after he nationalizes British Oil. – 1954 Guatemala – U.S. overthrows Democratically elected Arbenz after United Fruit Company objects to Arbenz’s reforms giving land to peasants. U.S. puts Military in charge. They Jail oposition – 1962 Dominican Republic – Bosch democratically elected removed. He rallies support for a civil War and U.S. sends troops to put down revolt. Weapons get more Powerful • Hydrogen Bomb (H-Bomb) – U.S. creates in 1952 – 500 times more powerful than Atomic Bomb – Soviets have it by 1954 • ICBMs – Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles • Nuclear Missiles can now be fired from one country to another. • Deterrence and MAD – Deterrence policy believed that if we created an arsenal of weapons so large…The Soviet Union would never dare attack us. – MAD – Mutual Assured Destruction • Belief that if there was a war both sides would be able to completely destroy each other. • Keeps both sides from attacking each other • Keeps tensions very high Red Scare at Home • 1947 – Due to fear of communists infiltrating the government, Truman creates loyalty oaths to work for the Federal Government as well as extensive background checks. – Hundreds of Federal workers lost their jobs due potentially being disloyal. • HUAC – House Un-American Activities Committee. – Investigates Communists in Hollywood in 1947 • Results in blacklists in Hollywood due to fear of hiring someone with communist sympathies. • Spies – Hiss – Advisor to Roosevelt at Yalta Conference – Fuchs – physicist who helped Soviets get Atomic Bomb secrets – Rosenberg's – Passing atomic secrets to Soviets – Executed • MaCarthyism – reckless persecution of a person for subversive activities without evidence. Conflicts Intensify • Communist Castro takes over in Cuba – Establishes strong ties to Soviet Union – U.S. plans attack to remove Castro • Bay of Pigs invasion • Fails • Cuban Missile Crisis – Soviet Union Puts Nuclear missiles in Cuba • U.S. creates Blockade of Cuba to prevent weapons from become active. – U.S. and Soviet Union are on verge of War • Finally both sides agree to de-escalation. Soviet union will remove missiles from Cuba if U.S. removes missiles from Turkey. Peaceful resolution. Vietnam • After WWII Vietnam wants freedom from French control and go to war with the French to gain their freedom. • French defeated in Vietnam in 1954 and U.S. fears they will become communist. • Geneva Peace conference splits the country in two. • As French move out the U.S. moves in advisors to help establish a noncommunist state in south Vietnam. • U.S. backed Diem starts building an Army with U.S. advisors to train them. • When the time came for free elections in 1955 as according to the Geneva conference, the U.S. rejected the national vote and only allowed a vote in South Vietnam. • Diem elected president Vietnam Escalates • South Vietnamese rebels called the “Viet Cong” begin fighting Diem in the South. • Diem results to brutal tactic to control South Vietnam and loses more support. – Buddhist monks protest by setting themselves on fire. • U.S. starting to wonder what is really happening in Vietnam. • Gulf of Tonkin Incident – U.S. warship attacked off the coast of North Vietnam – Results in Gulf of Tonkin Resolution • Congress gives president blank check to stop the communists in North Vietnam. • Domino Theory – If Vietnam fell to communism all of the countries around it would as well. Vietnam War • 1965-1973 • The War is no longer about helping South Vietnam. It is an American war now. • Goals were to destroy the Viet Cong. • Cut off support from (NVA) North Vietnamese Army • Ho Chi Minh Trail – Trail through neighboring Laos that NVA used to supply Viet Cong in the South • Guerrilla War – War by which you attack and then hide – Viet Cong would Strike U.S. then hide – U.S. had to go into jungle and find Viet Cong • Very Challenging Opposition at Home • Early war protests were small and achieved little • Media – – – – Vietnam is first media driven war War Correspondents went with troops People saw the War up close every night on news As Americans begin to die at rate of 1200 a month Americans start to question if the war is right. • 1968 – Tet offensive launched by NVA Army on south Vietnamese cities makes many Americans wonder if the war can be won. War Comes to an End • By 1973 the U.S. began removing U.S. forces and let the South Vietnamese Army continue the fighting. • By 1975 the NVA defeat the South and Unite Vietnam. • Aftermath is over 58,000 Americans dead and over 300,000 wounded. • Many Americans believed it was for nothing The Cold War begin to Thaw • Nixon Recognizes China - 1972 • Strategic Arms Limitation Talks (SALT I) – Treaty between the U.S. and Soviet Union in 1973 to Limit the increase of Nuclear weapons. • SALT II – Treaty in 1979 increasing the limits on nuclear weapons. (never ratified by U.S.) • INF treaty - 1987 – Reduces the number of nuclear weapons in Europe Cold War ends • Due to economic issues in the Soviet Union, they could no longer afford to support their large military and continue to exert pressure on satellite countries in Eastern Europe. • Berlin War Falls – November 9th 1989 – Symbolic end to Cold War • Soviet Union Breaks in individual States July 1991.