Cold War: Origins, Conflicts, and End - US History
advertisement

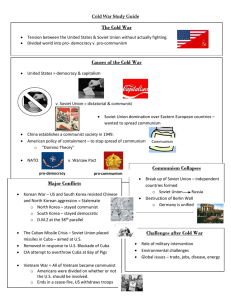
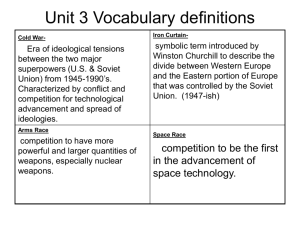
COLD WAR Mr. Fisher US History – 9th Grade Origins of Cold War (Post-WWII Map) • Definition: • Causes of the Cold War • American fear of Communism (Second Red Scare) • Russian dislike of Capitalism • Russian fear of the atomic bomb • Felt left out during the war • Russia’s actions in Soviet occupied Germany • Potsdam Conference: (Dealt with the punishment of Germany) • No free elections, lim’t rights, lim’t food • Iron Curtain (Pic 1, Pic 2) • “Barrier” created by the Soviet Union • Separated Warsaw Pact countries with NATO countries • issue of German unification • Stalin blockades Berlin (Berlin Wall) 2 reasons • Berlin Airlift (sent aid to East Germany by Allied Powers) • Containment Policies (contain Communism) • Depression Dictators WWII Dictators? Communism? • Purposes: • 1.) Influence with American ideas (Capitalism/Democracy, not Comm.) • 2.) Long-term benefits (i.e. trade) • Truman Doctrine ($$ to Greece/Turkey) • Marshall Plan ($$ rebuilding of Europe post-WWII) “Hotter” War – Containment Policies • China: • The Long March • Communists (Mao Zedong) vs. Nationalists (Chiang Kai-shek) • US supports Nationalists ($2 billion in aid), but CONTAINMENT failed • Communist victory (Zedong victor) • Korean War (The Forgotten War – 1950-1953) • Korea ruled by Japan from 1910-WWII (forced to give back possessions) • Peace agreement - Soviet Union obtained north, US allies to obtain South • Soviet Union and China (North Korea) vs. United States (South Korea) • Cease-fire issued by the Soviet Union • Positive – communism contained, no nuclear weapons • Negative – broken Korea nation split in two (North and South Korea) • Vietnam War (1959-1975) • Once part of French Empire – weakened around WWII • Vietnamese want land rid of foreigners led by Ho Chi Minh (Communist) • North Vietnam (China, Russia) vs. South Vietnam (US and allies) • Impact: • One of the largest antiwar movements • US loss – take a lesser role in foreign affairs • North Vietnam victor (capture of Saigon – containment fails) • War Powers Act • President cannot commit troops for more than sixty days • Cuban Missile Crisis (1962) (picture) • Cuban Revolution – Communist (Fidel Castro) • US missiles in Turkey – hit anywhere in Russia • Soviets counters - missile bases in Cuba • US issues a blockade of Cuba • Results: Missiles removed from Turkey and Cuba “Hotter” War – Containment Policies • Soviet-Afghan War (1979-1989) • Afghan – Islam rule but coup changed to communist rule (Comm. Ideas) • Soviets invaded Afghan. to maintain communist ruler • Success with modern technology (helicopter vs. ground troops) • US supporting groups (mujahideen - resistance) • Successful at beating back Soviet expansion • Al-Qaeda headed by Osama bin Laden • Leader of the 9/11 attacks • Effects: • Soviet's = fail • Communism contained Effects and Ending of Cold War • End of the Soviet Union (creation of Russia) • Soviet Union economy in shambles (went bankrupt) • Costly arms race and race to space • Failed Afghan war (“the Soviet Union’s Vietnam”) • New leadership: • Gorbachev to rid of oppressive/communist rule • Change to capitalist econ. • United States as #1 superpower • Fall of the Berlin War • Reunification of Germany