Southeast Asia
advertisement

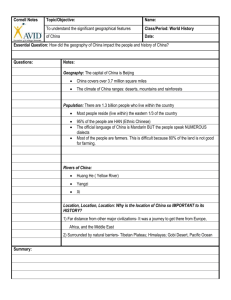
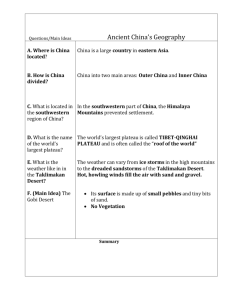
Mallori, Makenzie, Alyssa & Donovan Sea of Okhontisk Java Sea Black Sea Lake Baykal Arafura Sea Bay of Bengal Phillippine Sea Cellebes Sea Savu Sea Banda Sea Flores Sea South China Sea Yellow Sea Sea of Japan (East Sea) Arabian Sea Gulf of Tonkin Coral Sea Aral Sea Caspian Sea Sulu Sea Gulf of Aden Pacific Ocean Himalaya Mountains (highest mountain system on Earth) Altay Mountains Kunlun Mountains Hkakabo Razi is Southeast Asia's highest mountain - 5,881 m (19,295 ft). It’s located in the northern Myanmar state of Kachin. Himalaya Mountains Altay Mountains Kunlun Mountains Thar desert covers approximately 77,000 square miles in India & Pakistan. (Asia’s only subtropical desert.) Takla Makan Desert is China’s largest desert and extends over 123,550 square miles. (One of the worlds largest sandy deserts in the world) Gobi Desert is the largest desert in Asia, covering about 500,000 square miles. Stretching across Northern China into Mongolia. Takla Makan Desert Gobi Desert Thar Desert Angkor an important archaeological site in South-East Asia. Stretching over 401 km2, including forested area. Angkor Archaeological Park contains magnificent remains of the different capitals of the Khmer Empire from the 9th to the 15th century. Ban Chiang is the most important prehistoric settlement so far discovered in South-East Asia. It was the center of remarkable human cultural, social, and technological evolution in the 5th millennium BCE, which occurred independently in this area of South-East Asia and spread widely over the whole region. It’s important stage in human cultural, social and technological evolution. Ben Chiang Pottery Angkor Asia has some of the hottest, coldest, wettest, and driest places on Earth. Asia’s climate can be dived into three zones : North/Central, Southwest and Southeast. The North/Central zone is affected by cold and dry Arctic winds. The Southwest zone is a hot, dry that stretches from the Gobi in Mongolia, through Pakistan, Iran and into the Arabian Peninsula. The Southeast zone is greatly affected by the summer monsoon season. During the monsoon season a low-pressure system south of the Himalayas attracts moist winds from the Indian Ocean. Mainly rice, sugarcane, fishing, cattle, and spices. Buddhism is the most important religion in South-East Asia, & thousands of Buddhist temples cover the area. In Thailand 95 percent of the people are Buddhist, and in nearly every village there is a temple. It’s estimated that the Thai island of Krabi has been inhabited for the past 25,000 to 35,000 years. The largest pagoda in Southeast Asia is the Phra Pathom Chedi located at Nakorn Pathom. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/5 81237/Takla-Makan-Desert http://gobidesert.org/ http://www.worldatlas.com/webimage/countrys /as.htm http://www.eoearth.org/view/article/156497/ http://www.himalayamountains.com/ http://www.chinaculture.org/gb/en_travel/2003 -09/24/content_34924.htm http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/1 7446/Altai-Mountains http://whc.unesco.org/en/list/575 http://www.factmonster.com/dk/encycloped ia/southeast-asia.html http://education.nationalgeographic.com/ed ucation/encyclopedia/asia-resources/?ar_a=1