Cell Structure Review
advertisement

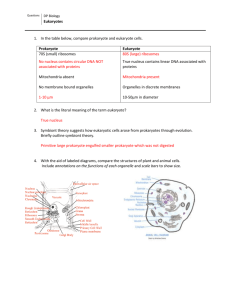
Cell Structure Review • Create a VENN diagram to compare and contrast Prokaryote Cell and Eukaryote Cell: Nucleus Genetic material contained in nucloid region Simple Example: Bacteria Surrounded by a cell membrane Contain genetic information Contain ribosomes Contain organelles Complex Example: plant, animal, fungi, protist • What part of this nested VENN diagram includes prokaryotes: List the levels of organization from smallest to largest. • • • • • • • • • • • Atom Molecule Organelle Cell Tissue Organ Organ System Organism Population Community Ecosystem Draw a diagram and explain endosymbiotic theory? A prokaryote cell engulfs another prokaryote (mitochondrion) cell and creates a simple animal cell. What does permeable mean? Why is a cell membrane semi-permeable? • Permeable means to permit or allow things to pass through. The cell membrane is semi-permeable because it only allows CERTAIN things to pass through. What is the difference between osmosis and diffusion? • Diffusion is simply the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration. • Osmosis deals specifically with water moving from higher concentration to lower concentration. Label the area of high concentration, low concentration and carrier molecule. High Concentration Carrier Molecule Low Concentration Define and give an example: Positive Feedback and Negative Feedback • Positive feedback: the type of feedback when a change in the controlled quantity is further increased by the system. – Example: conversion of enzymes to other enzymes for digestion • Negative feedback: the type of feedback when a change in the controlled quantity is counterbalanced by the system – Example: Guard cell adjusts for changes in temperature and moisture • When doing a microscope lab to observe cheek cells, what lab SAFETY equipment is necessary. Circle all that apply: – Apron – fire extinguisher – Goggles – ear plugs – fire blanket – Gloves – eye washer What would be a research “problem” or question for this experiment? Does molecule size affect permeability of a membrane Explain the procedure for the dialysis tubing lab? Iodine is added to water outside the baggie, starch is added inside the baggie, the iodine molecules move into the baggie turning the starch purple/black What vocabulary term did we demonstrate? Diffusion (iodine into the baggie through the membrane) What did the results demonstrate? The iodine molecules were small enough to travel through the membrane but starch molecules were not List three differences between these cells: 1. Prokaryote has no nucleus only nucleoid region 2. Eukaryote has several membrane-bound organelles; prokaryote has no organelles 3. Prokaryote is small and simple in structure What is the function of these two structures? Movement What is another word for that function? Motility • Cytoplasm: portion of the cell outside of the nucleus • Nucleus: control center of the cell • Contains nearly all the cell’s DNA • Coded instructions for making proteins and other important molecules • Cell membrane: regulates what enters and leaves the cell and provides protection and support •Ribosome: Small particles of RNA found in the cytoplasm that produce proteins by following coded instructions from the nucleus Mitochondria and Choroplasts • Mitochondria: organelles that convert chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are more convenient for the cell to use •Chloroplasts: organelles that capture the energy from sunlight and convert it into chemical energy – photosynthesis