Animal, Plant & Soil Science Flower Anatomy E2-4
advertisement

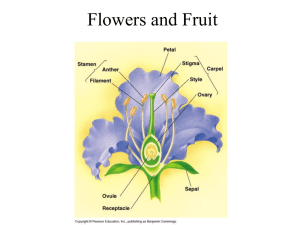
Animal, Plant & Soil Science E2-4 Flower Anatomy Interest Approach l Begin a discussion on sexual reproduction. Ask what students know about sexual reproduction in animals. Although the initial responses may be slow, given time, most students will be able to tell you about animal reproduction. Now, switch to plant sexual reproduction. What do students know? Are there girl and boy plants? (Yes, sometimes.) Do plants have sex ? (Yes.) Do plants have sperm and eggs? (Yes.) Do plants have genitalia? (Yes, although we call them flowers. ) Objectives l 1 Identify the parts of flowers and explain their functions. l 2 Compare and contrast the types of flowers. l 3 Define inflorescence and describe the types of inflorescences. Terms l _ anther l _ bract l _ calyx l _ catkin l _ complete flower l _ corolla l _ corymb l _ cyme l _ determinate l _ dioecious Terms l _ filament l _ head l _ imperfect flower l _ incomplete flower l _ indeterminate l _ inflorescence l _ monoecious l _ ovary l _ panicle Terms l _ pedicel l _ peduncle l _ perfect flower l _ perianth l _ petals l _ pistil l _ pistillate l _ pollen l _ raceme l _ receptacle Terms l _ sepals l _ spadix l _ spike l _ stamen l _ staminate l _ stigma l _ style l _ tepals l _ umbel What are the parts of a flower and their functions? l I. Flowers are the most obvious part of most plants. The purpose of flowers is for plants to be able to reproduce sexually. They are made of many intricate and important parts. Most flowers contain both male and female parts. What are the parts of a flower and their functions? l A. The male part of a flower is called the stamen. l 1. The stamen is made of the stalk-like filament which holds up the sac-like anther. l 2. The anther contains pollen, the grain released by flowers, which contains the sperm. l 3. Flowers that have only male parts are called staminate. What are the parts of a flower and their functions? l B. The female part of a flower is called the pistil. l 1. The pistil is made up of a sticky tissue at its end called the stigma that is receptive to pollen. l 2. Below the stigma is a rod-shaped middle part called the style and a swollen base containing eggs called the ovary. Once the pollen reaches the stigma, it forms a pollen tube down through the style to the ovary where sperm is deposited. l 3. Flowers that have only female parts are called pistillate. What are the parts of a flower and their functions? l C. Flowers often have parts that are neither male nor female. These are the petals, usually colorful leaf-like structures that often attract animals and insects. l 1. When all the petals are fused together, they form a corolla. l 2. Beneath the petals are more leaf-like structures that are often green, called sepals. The sepals support the petals and protect the flower before it opens. l 3. When all the sepals are fused together, they form a calyx. What are the parts of a flower and their functions? l 4. Together, the petals and sepals are called the perianth. l 5. With some plants, a clear distinction between petals and sepals cannot be made. In these cases, the parts of the perianth are called tepals. Tulip flowers and many monocots have tepals. l 6. Some plants have modified leaves at the base of a flower or floral inflorescence called a bract. The bracts may be green but in some cases, such as the poinsettia, are colorful. What are the parts of a flower and their functions? l D. The flower stem is referred to as the pedicel. The portion of the pedicel that holds the flower parts is the receptacle. What are the types of flowers? l II. Flowers come in many shapes, sizes, and colors. Not all of them have all the structures previously mentioned. l A. Plants may produce flowers that are perfect or imperfect. l 1. A flower that has both male and female parts is called a perfect flower. l 2. A flower that is missing either male or female parts is called an imperfect flower. What are the types of flowers? l B. Plants may have flowers that are complete or incomplete. l 1. If a flower has sepals, petals, pistils, and stamens, it is referred to as a complete flower. l 2. If a flower is missing one of these parts, it is referred to as an incomplete flower. l 3. Imperfect flowers are always incomplete. Incomplete flowers may or may not be imperfect. What are the types of flowers? l C. Plants may be classified as monoecious or dioecious. l 1. Monoecious plants bear both male and female flowers on one plant. Corn, cucumbers, and oaks are monecious. l 2. Dioecious plants have male and female flowers on separate plants. Soybeans, asparagus, kiwi, and hemp are examples of dioecious plants. What are the types of flowers? l D. A good way to tell the difference between a monocot and a dicot is to look closely at the flowers. l 1. Monocots have flowers with flower parts in multiples of three. l 2. Dicots have flowers with flower parts in multiples of four or five. What is an inflorescence and what are the types of inflorescences? l III. Flowers are borne on plant stems in one of two ways. Some plants have solitary flowers, such as the tulip, narcissus, and rose. Other plants have flower clusters, known as an inflorescence. An inflorescence is actually the branching system of the stem. The main stem of an inflorescence is known as the peduncle. Pedicels that branch from the peduncle support individual flowers. What is an inflorescence and what are the types of inflorescences? l A. One way in which types of inflorescence are classified is by the sequence of flowering within the flower cluster. l 1. If the first flower to open is at the apex of the stem and the progression of flowering is downward or outward, the inflorescence is determinate. Some examples of determinate flowers include liatris, kalanchoe, and African violet. l 2. If the last flower to open is terminal on the main axis and the progression of flowering is inward or upward, the inflorescence is indeterminate. Indeterminate types of inflorescences are racemes, corymbs, heads, and umbels. Freesia, cineraria, snapdragon, and stock also have indeterminate inflorescence. What is an inflorescence and what are the types of inflorescences? l B. There a variety of inflorescence types. Some common types are cyme, spike, raceme, panicle, corymb, umbel, spadix, catkin, and head. The spike and the panicle types of inflorescence are the most common among monocot plants. l 1. A cyme takes on several forms, although it is usually a flat-topped inflorescence. u u u a. A dichasium cyme bears a terminal flower on a peduncle with a pair of branches that produce lateral flowers. It may be simple or compound. b. A monochasium cyme has a terminal flower and, below it, one branch that produces a single lateral flower. The terminal flower is the oldest. c. Tomato, potato, and alstroemeria are cymes. Baby s breath is a compound dichasium cyme. What is an inflorescence and what are the types of inflorescences? l 2. A spike is an elongated inflorescence with a central axis along which sessile flowers are attached. Wheat, barley, ryegrass, wheatgrass, gladioli, and liatris are spike inflorescences. l 3. A raceme is an elongated inflorescence with a central axis along which are attached simple pedicels of more or less equal length. Examples of racemes include foxtail millet, snapdragon, delphinium, Scotch broom, and stock. What is an inflorescence and what are the types of inflorescences? l 4. A panicle is an elongated inflorescence with a central axis along which are branches that are themselves branched. Rice, oats, sudangrass, Kentucky bluegrass, tall fescue, timothy, grain sorghum, astilbe, and begonia have a panicle inflorescence. l 5. A corymb is a short and broad, flattopped indeterminate inflorescence having a main vertical axis and pedicels or branches of unequal length. The outer flowers open first. Yarrow is an example of a corymb. What is an inflorescence and what are the types of inflorescences? l 6. An umbel is an inflorescence having several branches arising from a common point. u u u a. A simple umbel consists of flowers with single pedicels. b. Compound umbels have secondary branching in the form of pedicels at the end of a ray. c. Queen Anne s lace and amaryllis have umbels. What is an inflorescence and what are the types of inflorescences? l 7. A spadix is a spike with a thickened, fleshy axis, usually enveloped by a showy bract called a spathe. Floriculture crops with a spadix include calla lily and anthurium. l 8. A catkin is a spike, raceme, or cyme composed of unisexual flowers without petals and falling as a unit. Catkins are found on willows, alders, oaks, and birch. What is an inflorescence and what are the types of inflorescences? l 9. A head is a rounded or flat-topped cluster of sessile flowers. Head inflorescences of the aster family resemble single flowers. These consist of centrally grouped flowers called disc flowers encircled by ray flowers. Some common plants that have a head inflorescence are gerbera daisy, chrysanthemum, sunflower, marigold, dahlia, strawflowers, and cineraria. REVIEW l 1. What are the parts of a flower and their functions? l 2. What are the types of flowers? l 3. What is an inflorescence and what are the types of inflorescences?