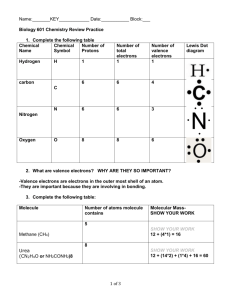
Chapter 11 power point

CHAPTER 11
Chemical Bonding
TYPES OF CHEMICAL
BONDS 11.1
Bond – a force that holds groups of atoms of two or more atoms together and makes them function as a unit
Bond Energy – the amount of energy required to break the bond
Types of Bonds: 4 TYPES
Metallic
Cations packed in “a sea of electrons”Metals
Metals consist of closely packed cations floating in a
“sea of electrons”.
All of the atoms are able to share the electrons.
The electrons are not bound to individual atoms.
Artists rendering of a metallic bond
Type 1: Metallic
Properties of Metals
Good conductors
Ductile
Malleable
Electrons act as a lubricant, allowing cations to move past each other
Metals have a Crystalline Structure
Metals
Packed spheres of the same size and shape:
Body Centered Cubic
Face Centered Cubic
Hexagonal Close
Packed
Example: Body Centered Cubic
(Chromium)
More examples
Face-Centered Cubic (gold) picture
Last example
Hexagonal Close-Packed (zinc) picture
Type 2: IONIC picture IONIC
Bond between closely packed, oppositely charged ions
Bond between a metal and a nonmetal hard solid @ 22 o C high mp temperatures non conductors of electricity in solid phase
good conductors in liquid phase or dissolved in water (aq
)
Covalent Bonding (2 types)
Instead of gaining or losing electrons atoms can get stable by sharing electrons
This is always between two non-metals.
Two fluorine atoms, for example, can form a stable F
2 molecule in which each atom has 8 valence electrons by sharing a pair of electrons.
In covalent bonds they can share more than two electrons
Type 3&4: COVALENT
COVALENT
Electrons are shared
Have low melting, boiling points
Do not conduct electricity when melted or dissolved in water
relatively soft solids as compared to ionic compounds at room temp picture
Covalent bond –subtype #1
Non-polar Covalent
When two of the same elements bond they are called diatomic molecules, some examples of this are
Hydrogen H
2
, Oxygen O
2 and Nitrogen N
2
.
The atoms in these bonds would have the same electronegativities. This means that both atoms attract the shared electrons to that same extent.
picture
Covalent Bonds – subtype #2 picture POLAR COVALENT
Unequal sharing of electrons
Dipole Moment 11.3
A molecule that has a center of positive charge and a center of negative charge
Dipole often represented by an arrow
Points towards negative charge center and its tail indicates the positive charge center
Review: 3 types of bonds thus far
x
LEWIS STRUCTURES
Section 11.6
Lewis Dot Structures
Show valence electrons
Use group number to figure it out
The Octet Rule
The octet rule says that atoms tend to gain, lose or share electrons so they have eight electrons in their outer shell.
There are some exceptions to the octet rule
(imagine that)
BF
3
BCl
3
PF
5
SF
6
Follow the interactive website!
Ionic Bonding: (this should be review) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=T40sM8-SXso
Covalent Bonding: http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/ViewObject.aspx?ID=GCH6404
Drawing Lewis Structures
Arrange the element symbols.
Central atoms are generally those with the highest bonding capacity.
Carbon atoms are always central atoms
Hydrogen atoms are always peripheral atoms
Add up the number of valence electrons from all atoms.
For polyatomic ions, add one electron for each negative charge and subtract one for each positive charge.
Draw a skeleton structure with atoms attached by single bonds.
Complete the octets of peripheral atoms.
Place extra electrons on the central atom.
If the central atom doesn’t have an octet, try forming multiple bonds by moving lone pairs.
Simple Rules
1. Figure out number of electrons by counting the TOTAL valence electrons in whole compound
2. Place the central element in the middle and surround it with the other elements
3. Place single bonds between elements
4. Place lone pairs around each element until there are a total of eight (Hydrogen only wants 2)
5. Count total electrons surrounding the compound (don’t forget the bonds count as 2 electrons)
If electrons from #1 and #5 don’t match…. Erase electrons and put in double bond and recount
Single, Double and Triple Bonds
With Covalent bonds the elements can share two or more electrons
A Single Bond is when 2 electrons are shared they are represented by a single line in bond diagrams
A Double bond is when 4 electrons are shared they are represented by two lines in bond diagrams
A Triple bond is when 6 electrons are shared they are represented by three lines in bond diagrams
Lewis Dot Structures:
H
2
CO
H
C O
H
H
H
C O
Isomers – multiple correct structures for a single compound
(requires breaking bond to make new compound)
CH
2
Cl
2
H
Cl C Cl
H
Cl
Cl C H
H
ELECTRONEGATIVITY
AND POLARITY
Section 11.2
Electronegativity Values
The electronegativity values can be found in the periodic table
The higher the value the higher the electronegativity
The Pauling scale is used to measure electronegativity. It is a relative scale running from
0.7 to 4.0 (hydrogen = 2.2).
The units for electronegativity are Pauling units.
Electronegativity
The ability of an atom to attract electrons when bonded
1.
Nonmetals have high electronegativity
2.
3.
Metals have low electronegativity
Electronegativity increases across a period and decreases down a group. WHY???
Electronegativity Chart
Why would the metals have low electronegativity numbers?
Why don’t the noble gases have electronegativity numbers?
Nonpolar Covalent Bond
When electrons are shared between 2 atoms, a covalent bond is formed.
If the atoms are identical, e.g. Cl
2
, the electrons are shared equally ( nonpolar )
Cl = 3.0 therefore the ∆EN = 3.0-3.0 = 0
∆EN = electronegativity Difference
0 = nonpolar
Polar Covalent Bond
If the electrons are shared between 2 different atoms, e.g. HBr, the sharing is unequal
The bonding electrons spend more time near the more electronegative atom
H = 2.1 and Br = 2.8 THEREFORE 2.8-2.1 = 0.7
0.7 = a polar covalent bond
H Br
Bond Type by Electronegativity Value
Remember the higher the atom’s electronegativity value, the closer the shared electrons tend to be to that atom when it forms a bond
Therefore, the polarity of a bond depends on the
difference between the electronegativity values of the atoms forming the bond
The greater the difference, the more polar the bond.
Electronegativity
Difference
0.0 to 0.2
0.21 to 1.7
≥ 2.0
Type of Bond
Formed nonpolar covalent polar covalent ionic
Electronegativity Differences
Why is there a gap between 1.7 and 2.0????
If the two atoms are nonmetals =polar covalent bond
If nonmetal & metal = ionic bond
0 to 0.2
Nonpolar covalent
0.21 to 1.7
Polar covalent
Electronegativity Difference
≥ 2.0
Ionic
Sample Problems
Choose the bond that will be more polar
H-P or H-C
O – F or O – I
N – O or S – O
N – H or Si - H
Sample Problems
Choose the bond that will be more polar
H-P or H-C
O – F or O – I
N – O or S – O
N – H or Si - H
Polar Molecules (overall polarity of the molecule)
Note: Not all molecules with polar bonds are polar molecules
The dipoles in symmetrical molecules cancels out
The bond is polar but the molecule is nonpolar
How to determine polar molecules
There are two important factors
1. The polarity of the individual bonds in the molecule;
2. The shape or geometry of the molecule.
Steps to take a)
Determine if a given individual bond is polar, Look at the difference between electronegativity of the atoms in the perioidc table. If the difference is:
0.2 < non polar
0.2 - greater = polar
b) Determine the shape of molecule. For now I will give them to you. Later you will figure out the shape yourself. i) if all bonds are non-polar, then the whole molecule is nonpolar regardless of its shape. ii) If there is symmetry in the molecule so that the polarity of the bonds cancels out, then the molecule is non-polar. (symmetry arround the central atom) iii) If there are polar bonds but there is no symmetry the overall molecule is polar.
Which molecules are polar?
Which molecules are polar?
For these two molecules, even though there are polar bonds the overall molecule is nonpolar because the molecule is symmetrical


![QUIZ 2: Week of 09.03.12 Name: [7pts] 1.) Thoughtful list of 3](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006619037_1-3340fd6e4f1f4575c6d8cf5f79f0ff3e-300x300.png)