Bio120--cells lab--post
advertisement

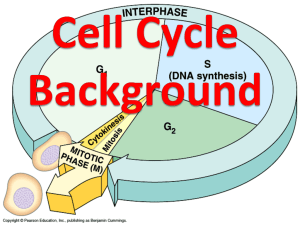
Cells: why they are important • All living things are made of one or more cells. • Cells are the smallest functional unit of living things. • The basic unit of life • The structure and function of cells relates to the structure and function of the entire organism. Types of Cells • Prokayrotic Bacteria • Eukaryotic Everything else – Plants – Animals – Fungi – Algae – protists A Prototypical/Generic Cell 3 3 Major Eukaryotic Cell Parts The major parts of the cell include • Plasma membrane — the outer boundary of the cell, controls/regulates what enters or exits cell • Cytoplasm — within PM, performs most cell activities • Nucleus— contains & protects DNA; “control center” of cell Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm Nucleus You will observe and compare the VISIBLE structure among: • Human Cheek Cell (animal cell) • Elodea Cell (plant cell) • Onion Cell (plant cell) • Have one person at each table set up different slide and then look at eachothers microscopes. Human Cheek Cell—animal cell Elodea Cell: a plant cell (from leaf/above ground part of plant) Onion Cell: plant cell (from below ground plant part) Plant Cell Parts Cell Wall Cell/Plasma membrane Vacuole Chloroplast Nucleus Euks v. Proks Eukaryotic • Large • DNA within nucleus • Many different organelles Prokaryotic • Very small • No nucleus, DNA ‘exposed’ • Very few organelles Typical eukaryotic cell Typical prokaryotic cell Animal Plasma Membrane Cytoplasm Cell wall Nucleus Vacuole chloroplast BIG or small Elodea Onion prokaryote Mitosis and the Cell Theory: • Cells only come from pre-existing cells (part of cell theory) • Existing cells must divide to create new cells – Growth or replacement of damaged/dead cells • New cells need all the DNA/genetic information the original cell had • DNA must be copied, then divided equally, then cell can divide. Mitotic Cell Division – Replication = copying DNA – Mitosis = separation of duplicated chromosomes – Cytokinesis = division of cytoplasm and separation of two cells – Results in two daughter cells, each with a complete set of DNA that is identical to one another and identical to the original cell (genetically identical) 1 copy of each chromosome 1 copy of each chromosome 2 copy of each chromosome 1 copy of each chromosome Replication of DNA during S-phase of interphase • Mitosis divides/separate the two copies of identical chromosomes Parent/mother cell • Cytokinesis divides up the cytoplasm contents daughter cells: each with one copy of each chromosome, genetically identical to the mother cell The Cell Cycle Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase telophase Daughter cells in interphase no nucleus Cell Cycle Stages made simple • • • • • Interphase = nucleus visible, not chromosomes Prophase = chromosomes in a clump Metaphase = chromosomes in a line Anaphase = chromosomes in two clumps Telophase = chromosomes in two clumps; cytokinesis visible Mitosis identification game http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cel l_bio/activities/cell_cycle/01.html