Unit 1 - Reading Guide
advertisement

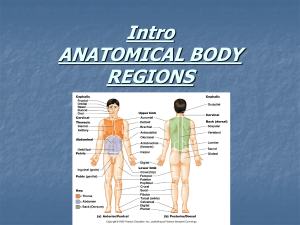
NAME___________________________ Unit 1 Reading Guide This reading guide will be completed on your own with the use of the book. It is a part of your notes however, so be sure to add it to your binder after it has been graded. There is a video that goes along with this reading guide that you will need to watch to supplement this activity. 1. Define anatomy 2. Define Physiology 3. For each of the following statements, indicate if is relates to the study of anatomy or the study of physiology. a. Measuring an organ’s size, shape, and weight ___________________ b. Can be studied in living subjects ___________________ c. Observing a heart in action ___________________ d. Involves dissection ___________________ e. Viewing muscle tissue through a microscope ___________________ f. Drawing blood and determining blood sugar levels ___________________ g. Mainly studied through observation ___________________ h. Mainly studied through experimentation ___________________ i. Studying metabolism ___________________ 4. Using the key choices, identify the organ system to which the following organs or functions belong. Insert the correct letter or term in the answer blanks. Answer choices may be used more than once, or not at all. a. Cardiovascular f. Muscular j. Skeletal b. Digestive g. Nervous k. Urinary c. Endocrine h. Reproductive d. Integumentary i. Respiratory e. Lymphatic _____ 1. Rids the body of nitrogen-containing wastes _____ 2. Is affected by the removal of the thyroid gland _____ 3. Provides support and levers on which the muscular system can act _____ 4. Protects underlying organs from drying out and mechanical damage _____ 5. Produces Vitamin D _____ 6. Breaks down foodstuffs into small particles that can be absorbed _____ 7. Removes carbon dioxide from the body _____ 8. Delivers oxygen and nutrients to body tissues _____ 9. Moves the limbs; allows facial expression _____ 10. Conserves body water or eliminates excesses _____ 11. Provides for conception and child-bearing _____ 12. Controls the body with chemicals called hormones _____ 13. Responsible for the body’s responsiveness _____ 14. Picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels and returns it to blood _____ 15. Includes the blood vessels & heart _____ 16. Includes the pancreas, pituitary, & adrenal glands _____ 17. Includes the kidneys, bladder, & ureters _____ 18. Includes the testes, vas deferens, & urethra _____ 19. Includes the esophagus, large intestine, & rectum _____ 20. Includes the breastbone, vertebral column, & skull _____ 21. Includes the brain, nerves, & sensory receptors Life Functions and Survival Needs 5. What are the 8 life functions? Describe each one briefly 6. What are the 5 survival needs? 7. What is the difference between a life function and a survival need? 8. Match the life function with its corresponding description.. Answer choices may be used more than once, or not at all. a. Keeps the body’s internal environment distinct from the external environment _______Digestion b. Provides new cells for growth and repair _______Excretion c. Occurs when constructive activities occur at a faster rate than destructive activities _______Growth d. e. The tuna sandwich you ate at lunch is broken down into its chemical building blocks Elimination of carbon dioxide by the lungs and elimination of nitrogenous wastes by the kidneys f. Ability to react to stimuli; a major role of the nervous system g. Walking, throwing a ball, riding a bicycle h. All chemical reactions occurring in the body i. At the cellular level, membranes; for the whole organism, the skin _______Maintenance of boundaries _______Metabolism _______Movement _______Responsiveness ______Reproduction . 9. Identify the survival needs that correspond to the following descriptions. Answers may be used more than once, or not at all. a. Appropriate body temperature b. Atmospheric pressure c. Nutrients d. Oxygen e. Water _____ 1. Includes carbohydrates, proteins, fats, and minerals _____ 2. Essential for normal operation of the respiratory system and breathing _____ 3. Single substance accounting for over 60% of body weight _____ 4. Required for the release of energy from foodstuffs _____ 5. Provides the basis for body fluids of all types _____ 6. When too high or too low, physiological activities cease 10. Select the key choices that identify the following body parts or areas. Enter the appropriate letter or corresponding term in the answer blanks. a. b. c. d. e. f. Abdominal Antecubital Axillary Brachial Buccal Cervical g. h. i. j. k. l. Femoral Gluteal Inguinal Lumbar Occipitial Popliteal _____ 1. armpit _____ 2. thigh region _____ 3. buttock area _____ 4. neck region _____ 5. “belly button” area _____ 6. genital area _____ 7. anterior part of elbow _____ 8. posterior of head _____ 9. area where trunk meets thigh _____ 10. lower back _____ 11. cheek _____ 12. anterior part of knee _____ 13. Shoulder blade m. n. o. p. q. Patellar Pubic Scapular Sural Umbilical Regional Terms: Define the following terms using their common/everyday names and write the terms on the body. 1. Abdominal 2. Acromial 3. Antebrachial 4. Antecubital 5. Axillary 6. Brachial 7. Buccal 8. Calcaneal 9. Carpal 10. Cephalic 11. Cervical 12. Coxal 13. Costal 14. Cranial 15. Crural 16. Cubital 17. Digital 18. Dorsum 19. Femoral 20. Frontal 21. Gluteal Do not write just the term’s number as this will not help you study! 26. Mental 27. Nasal 28. Occipital 29. Oral 30. Orbital 31. Otic 32. Palmar 33. Patellar 34. Pedal 35. Pelvic 36. Plantar 37. Pollex 38. Popliteal 39. Pubic 40. Scapular 41. Sternal 42. Sural 43. Tarsal 44. Thoracic 45. Umbilical 46. Vertebral 22. Hallux HINT: Flash cards 23. Inguinal will really help you to 24. Lumbar memorize these body parts! 25. Mammary Page 5 On the following image, you are presented with both the anterior (front-side) and posterior (back-side) views of a human. (Don’t just label with the letter!). You only need to label each term once (meaning you do not have to use the term on both views.) Anterior View Posterior View Page 6