Cells and Cells Processes Review
advertisement

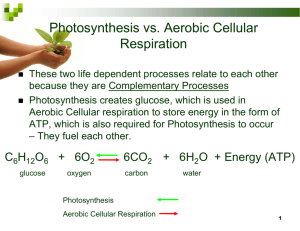
Biology Unit 3 Exam Study Guide Cells and Cell Processes 1. What is the function for each of the following? -Cell Wall: gives the cell structure and support -Plasma (Cell) Membrane: allows certain things in/out of the cell -Vacuoles: stores water and some nutrients -Lysosomes: digests and breaks down things -Ribosomes: makes proteins -Centrioles: organelle used in mitosis -Chloroplasts: makes glucose through the process of photosynthesis -Nucleus: controls the cell -Mitochondria: produces ATP through the process of cellular respiration -Golgi body(apparatus): packages and distributes things -Plasmid: Structures that hold DNA -DNA (genetic material): contains all of the information about the organism -Endoplasmic Reticulum smooth & rough: highway system of the cell -Cytoplasm: fluid part of the cell where the organelles float -Cilia/Flagella: used for movement 2. What are three main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? * Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus, eukaryotic cells have a nucleus *prokaryotic cells are simple, eukaryotic cells are more complex *prokaryotic cells are small, eukaryotic cells are bigger *Prokaryotic cells are unicellular, Eukaryotic cells are multicellular organisms 3. What are the three parts of the Cell Theory? *all living things are composed of one or more cells *cells are the basic unit of structure and function of living things and are the smallest living organism *all cells arise from other cells 4. What three organelles do plant cells contain that animal cells do not? *cell wall *chloroplast * A large central vacuole 5. Define the following terms, describe the movement of water and what happens to the cell: Isotonic Solution Hypotonic Solution Hypertonic Solution Define: equal movement of water in/out of the cell Define: a hypotonic solution refers to a solution that contains less solute (more water) compared to the cytoplasm of the cell Define: A solution that has higher osmotic pressure (or has more solutes) than another solution to which it is compared Water movement: both in and out Water movement: water moves into the cell Water movement: water moves out of the cell What happens to the cell?: stays the same What happens to the cell?: Cell swells and becomes larger What happens to the cell?: Cell shrivels 6. Explain the difference between passive and active transport. Passive transport does not require energy. Active transport requires energy. Also, active transport requires the movement of a substance against a concentration gradient or against the force of nature. 7. Define each of the following types of transport and indicate whether it is passive or active. -simple diffusion: small molecules moving across the cell membrane, passive -facilitated diffusion: large molecules using a protein channel to move across the cell membrane, passive -endocytosis: A process in which cell takes in materials from the outside by engulfing and fusing them with its plasma membrane, active -NA/ Potassium Transport: This protein pump moves substances against a concentration gradient to allow the cell to maintain a negative charge. It requires ATP so it is considered active transport. 8. Give the chemical formula for energy conversions that could occur in a plant or animal cell. How are the processes similar or related? C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H20 + ATP, Cellular Respiration LIGHT + CO2 + H20 C6H12O6 + O2, Photosynthesis. The processes are the same except flipped. ADDITIONAL QUESTIONS THAT WOULD HELP TO STUDY 8. What part of the cell does this picture represent and what is its function? Cell membrane, allows certain things in/out of the cell 9. What types of cells do photosynthesis? Plants, animals or both? Plants 10. What types of cells do cellular respiration? Plants, animals or both? Both 11. What types of cells contain plasmids? Prokaryote, Eukaryote or both? Both 12. How are the equations for photosynthesis and cellular respiration related? The products of photosynthesis are the reactants for cellular respiration. They are opposites. 14. The mitochondria has a folded interior membrane. Why? cell processes can be more efficient, the membranes provide a large surface area, and the membranes form interconnected compartments 15. What process occurs in the mitochondria? Cellular respiration 17. What process occurs in the chloroplast? photosynthesis Other Vocab: Also be familiar with the following words/definitions. ATP, microbes, contractile, diffusion, synthesis, regulation, excretion, osmosis, incapable ATP – energy Microbes – small organisms Contractile – the ability to contract Diffusion – movement of a substance from an area of high to low concentration Synthesis – to make Regulation – to control what happens Excretion – to get rid of Osmosis – movement of water Incapable – not able