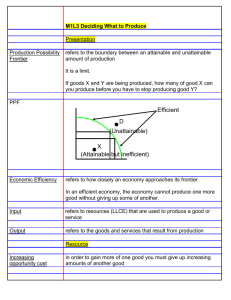
Opportunity Cost
advertisement

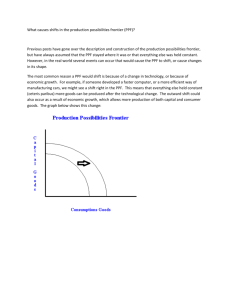
Starter a) The use of production possibility frontiers to depict: opportunity cost (through marginal analysis) economic growth or decline efficient or inefficient allocation of resources possible and unobtainable production b) The distinction between movements along and shifts in production possibility curves, considering the possible causes for such changes c) The distinction between capital and consumer goods d) The use of production possibility frontiers to depict the maximum productive potential of an economy e) Consideration of actual vs. potential growth of an economy A-Level Economics Title: What is a production possibility frontier? • We will be able to explain opportunity cost • We will be able to explain the different factors of production as economic resources. • We will be able to discuss and chart production possibility frontiers. Do you work to live or live to work? • Britons continue to work the longest hours in Europe. • According to the TUC, the UK working week has now crept up to 43.5 hours – three hours longer than the European average. • More than four million full-time employees work more than 48 hours a week (700,000 more than did during the 1990s). • One in six employees regularly clocks up more than 60 hours a week. • It also found 5.26 million Britons work an average of 7.2 hours of unpaid overtime a week. • Stress positively correlates with both depression and coronary heart disease (Tennant, 2001, 2000). What is the Opportunity Cost? Key Term: Why is this relevant? Opportunity Cost The cost of an activity expressed in terms of the next best alternative, which has to be given up when making the choice. Production Possibility Curve This shows the maximum quantities of different combinations of output of two products, given current resources and the state of technology The data below shows the various production possibilities for an economy that produces two goods, cars and television sets. Cars Televisions 1,000 0 800 400 600 800 400 1,200 200 1,600 0 2,000 a. Draw the above combinations of products on a graph. Put cars on the vertical axis and televisions on the horizontal axis. b. How many televisions can be produced when car production is 700? How does this change when 550 cars are produced? c. How does your diagram illustrate: a. Choice b. Scarcity? Production possibility frontiers: What is it all about? Production possibility frontiers: What is it all about? • A production possibility frontier (PPF) shows the maximum possible output combinations of two goods or services an economy can achieve when all resources are fully and efficiently employed What is a Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF)? A graph that shows the maximum combinations of goods that can be produced when resources and technology are used efficiently 12 For simplicity, lets take a world with only 2 products Lets use beer and pizza (a typical college campus?) 13 Beer A typical PPF has the following shape:. The curve has a negative slope. The curve is concave to the origin. Pizza 14 Shape of the PPF? Why Concave? If PPF a straight line, we have constant opportunity costs If PPF concave, we have increasing opportunity costs 15 Consider a straight line PPF Beer Beer given up, the opportunity cost, remains constant Pizza 16 Beer Concave shape, increasing opportunity costs. Beer given up, the opportunity cost, is increasing Pizza 17 What is the Law of Increasing Costs? The opportunity cost of producing a good increases as more of the good is produced 18 Why does the Law of Increasing Opportunity costs hold? Because resources are not perfectly adaptable to all products 19 Beer All points on the curve correspond to full use of resources. A B Pizza 20 Beer Points outside the the PPF are not feasible with existing resources. .A Pizza 21 Beer Periods of unemployment or inefficiency in production correspond to points under the PPF. .A Pizza 22 What is the Law of Increasing Costs? The opportunity cost of producing a good increases as more of the good is produced 23 How do we have more of everything? By increasing our resources 25 Production Possibility Frontier What could increase the PPF? - natural resources found - population (labour) - technology - infrastructure for production Beer Economic growth indicates an increase in the total output of an economy. The PPF shifts to the right ! .A Pizza 27 Can a PPF shift inward (to the left)? YES!! For just the opposite reasons as an outward shift such as a loss of resources 28 Capital goods Economic growth and the Capital Consumer goods tradeoff: A From which point would an economy grow faster, A or B?? Answer is A, with more capital goods B Consumer goods 29