4-2: Parts of a Eukaryotic Cell
advertisement

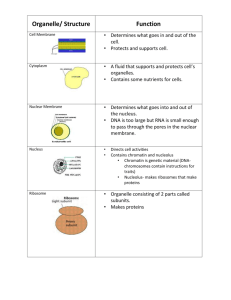
4-3: Cell Organelles + Features Eukaryotic cells have many membrane systems Divide cells into compartments that function together to keep a cell alive Plasma Membrane (Factory Doors) Location: surrounds the cell + its parts Functions: Controls the ease w/ which substances pass into and out of the cell - - known as selectively permeable Separates internal rxns with external environment Allows the cell to excrete wastes and interact with environment Description: made of lipids + proteins Membrane Lipids Major type – phospholipids Hydrophilic (head) – Hydrophobic (tail) Forms a lipid bilayer Heads outward, tails inward Contains sterols between the tails Example: Cholesterol Membrane Proteins Function: transporting molecules through lipid bilayer Two types: Peripheral – located on both interior + exterior surfaces of C.M. Integral – embedded into the bilayer Fluid Mosaic Model States that the lipid bilayer behaves like a fluid, not like a solid Membrane proteins + lipids can move laterally within the bilayer Watch Nucleus (Main Office) Location: in the cytosol Size: most prominent structure Surrounded by a double membrane called nuclear envelope Shape is maintained by skeleton – nuclear matrix Filled with fluid known as nucleoplasm Function: store hereditary information Chromatin – combo. of DNA + proteins - - coils up to chromosomes for cell division Production of RNA – which directs protein synthesis - leaves through nuclear pores Nucleolus – synthesis of ribosomes Mitochondria (Electricity Generator) Location: scattered throughout the cytosol Size: Relatively large Function: site of chemical rxns that transfer nrg from org. compounds to ATP Responsible for producing 95% of nrg for a cell to function Found in high #s in liver + muscles cells Liver cells contain 2500 mitochondria/cell Mitochondria (cont.) Surrounded by 2 membranes Outer membrane serves as a boundary between mitochondria + cytosol Inner membrane has long folds called cristae, which increase surface area for chemical rxns to take place Mitochondria DNA Can reproduce own their own Ancient invasion? ENDOSYMBIOSIS Ribosomes Location: scattered throughout the cytosol or attached to endoplasmic reticulum Made in nucleolus, completed in cytoplasm NOT membrane bound – evolution (prokaryotic cells) Size: relatively small + most numerous; made of protein + RNA Function: Protein synthesis Endoplasmic Reticulum (Assembly Line) Location: within the cytosol, sometimes attached to the nucleus Description: cisternae – membranous tubes + sacs Function: Intracellular highway – a path for molecules to move from one part to another Types of ER Rough ER – covered with ribosomes Produces phospholipids + proteins Prominent in cells that export large amounts of proteins from the cell or use in cell membranes Smooth ER – no ribosomes Synthesis of lipids (cholesterol) Synthesis of steroids in glands Regulate calcium levels in muscles Breakdown toxic substances in liver cells Golgi Apparatus (Packaging Center) Location: within the cytosol Appearance: system of membranes; series of flattened sacs Function: works with ER to modify proteins for transport from cell Vesicles Small, spherical sacs Classified by contents Lysosomes Made by Golgi Contain digestive enzymes breakdown proteins, nucleic acids, carbs, fats Digests old cells (autolysis) or old organelles (autophagy) **FYI - - involved in embryonic development ex. Human hand Vesicles Peroxisomes Abundant in liver + kidney cells Neutralize free radicals (Oxygen ions), detoxify alcohol + other drugs Break down fatty acids for nrg source Glyoxysomes Found in plant seeds Help break down fats to supply embryo with food Protein Synthesis Pathway 1. 2. 3. 4. Proteins assembled by ribosomes on rough ER Vesicles transport proteins to Golgi Golgi modifies proteins + packages them in new vesicles Vesicles release proteins outside cell (vesicles remain in cell to be used again) Cytoskeleton Location: within the cytosol Size: spans the entire length of cell – provides a framework Functions: Provide structure to maintain shape + size Participates in movement of organelles in the cytosol Components of Cytoskeleton Microtubules – hollow tubes Extend from a central point (centrosomes) Form spindle fibers during cell division Microfilaments – thread-like strands Chains made of actin molecules Cell movement + contraction of muscle cells Intermediate filaments – rods Anchor nucleus in place Cilia + Flagella Location: extend from surface of cell Appearance: hair-like organelles Function: assist in movement Cilia – short; present in large numbers Propulsion through water Ex. Nose + inner ear Structure of cilia – cross section Flagella – longer; less numerous Common for only 1 flagellum to be present Whips back and forth to propel cell Ex. E. coli + sperm Centrioles Two short cylinders of microtubules near nuclear envelope Found in animal cells Organize microtubules during animal cell division