Group Work on Organelles:
advertisement

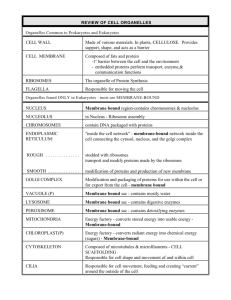
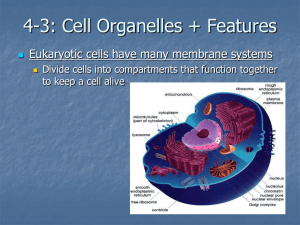
Group Work on Organelles: An example is given. Please complete using the information in your book (pp. 36-42). Organelle Plasma Membrane Nucleus / Nucleolus Ribosome Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Structure Form Follows Function Phospholipid Bilayer creates bilayer with barrier between proteins embedded outside and inside the cell the proteins create channels to allow the selective movement of molecules. Has a nuclear Protects the DNA envelope from the rest of surrounding the cell nucleoplasm. environment-but Envelope has permits proteins pores. Contains to enter and leave chromatin (DNA). the nucleus and mRNA to leave for protein synthesis. Protein and RNA in two subunits. Can be attached to the Rough ER. Function Regulates homeostasis between external environment and the cell. Stores genetic info which determines characteristics of the body. Nucleolus: makes ribosomes. Size allows Protein them to be Synthesis connected (makes to the ER. proteins) Two parts allow it to clamp on to the mRNA so that it can read the genetic code. Membranous Ribosome Modification saccules attachment and editing of and makes the proteins channels proteins studded with directly ribosomes. enter the ER – no energy is wasted on transporting them. - increased S.A. Smooth Endoplasmic Same but Close to Reticulum without golgi for ribosomes. ease of packaging of products for exocytosis. - increased S.A. Golgi Apparatus Stacks of Close to ER membranous (product saccules. makers) so Made of the it can same package material as their goods. the plasma Also close membrane. to plasma membrane for exocytosis. - increased created by the ribosomes. Synthesizes phospholipids, detox drugs, and makes fat based steroids and hormones. Process and package molecules. S.A. Vesicle Small Pieces of membranous golgi – they sacs that are the pinch off of packages. the golgi. Close to membrane for exocytosis. Made of same bilayer so chemically compatable. Lysosome/Peroxisome Membrane Can move bound around to organelles bind with containing vesicles hydrolytic containing enzymes or material to (H2O2). be digested. Contained so that it doesn’t digest other organelles. Mitochondria Double The folds of layered the cristae membrane. increase Inner surface membrane area for the Carry proteins and other products to the membrane or to a lysosome. Digestion of unwanted material (dead cells, bacteria, viruses, etc.) Production of ATP through cellular respiration. Sugar + Cytoskeleton Cilia/Flagella Centriole folded to production Oxygen form cristae. of ATP. The Carbon Within the matrix Dioxide + inner allows the Water + ATP membrane is enzymes an enzyme needed for matrix. the chemical reactions to be activated for respiration. Protein Bones of Structure and fibers within the cell. movement the Highway inside the cell. cytoplasm system for nuclear division (creates spindle fibers) Protein Protein Move cell or filaments stablizes help sweep extentions of the debris over cytoplasm projections. surface of cell. Made of Protein Creates protein stabilizes spindle fibers. filaments. for use during nuclear division